| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Several ancient civilizations appear to have had some understanding that disease could be transmitted by things they could not see. This is especially evident in historical attempts to contain the spread of disease. For example, the Bible refers to the practice of quarantining people with leprosy and other diseases, suggesting that people understood that diseases could be communicable. Ironically, while leprosy is communicable, it is also a disease that progresses slowly. This means that people were likely quarantined after they had already spread the disease to others.
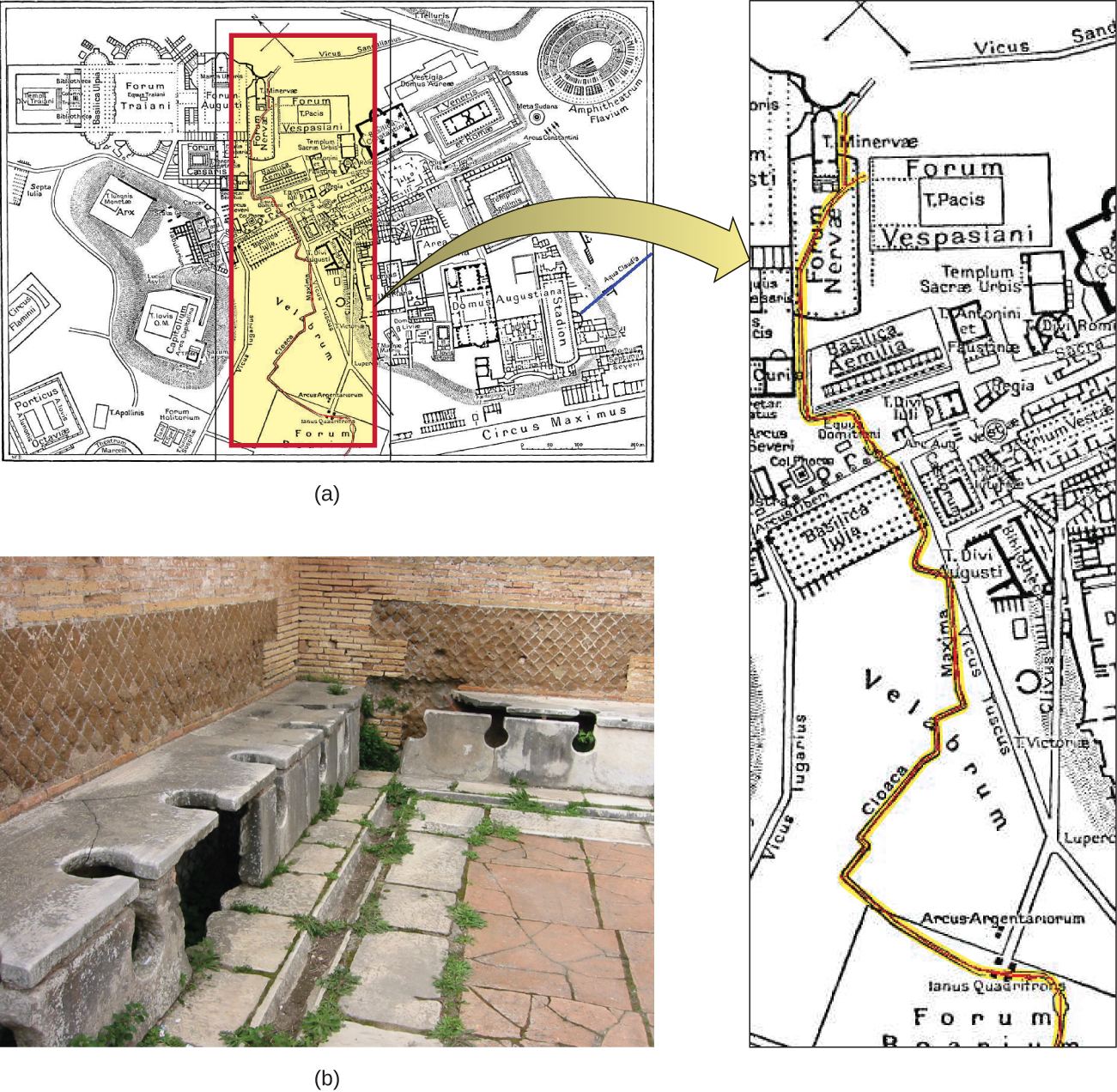
The ancient Greeks attributed disease to bad air, mal’aria , which they called “miasmatic odors.” They developed hygiene practices that built on this idea. The Romans also believed in the miasma hypothesis and created a complex sanitation infrastructure to deal with sewage. In Rome, they built aqueducts, which brought fresh water into the city, and a giant sewer, the Cloaca Maxima , which carried waste away and into the river Tiber ( [link] ). Some researchers believe that this infrastructure helped protect the Romans from epidemics of waterborne illnesses.
Even before the invention of the microscope, some doctors, philosophers, and scientists made great strides in understanding the invisible forces—what we now know as microbes—that can cause infection, disease, and death.
The Greek physician Hippocrates (460–370 BC) is considered the “father of Western medicine” ( [link] ). Unlike many of his ancestors and contemporaries, he dismissed the idea that disease was caused by supernatural forces. Instead, he posited that diseases had natural causes from within patients or their environments. Hippocrates and his heirs are believed to have written the Hippocratic Corpus , a collection of texts that make up some of the oldest surviving medical books. G. Pappas et al. “Insights Into Infectious Disease in the Era of Hippocrates.” International Journal of Infectious Diseases 12 (2008) 4:347–350. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2007.11.003. Hippocrates is also often credited as the author of the Hippocratic Oath, taken by new physicians to pledge their dedication to diagnosing and treating patients without causing harm.
While Hippocrates is considered the father of Western medicine, the Greek philosopher and historian Thucydides (460–395 BC) is considered the father of scientific history because he advocated for evidence-based analysis of cause-and-effect reasoning ( [link] ). Among his most important contributions are his observations regarding the Athenian plague that killed one-third of the population of Athens between 430 and 410 BC. Having survived the epidemic himself, Thucydides made the important observation that survivors did not get re-infected with the disease, even when taking care of actively sick people. Thucydides. The History of the Peloponnesian War. The Second Book . 431 BC. Translated by Richard Crawley. http://classics.mit.edu/Thucydides/pelopwar.2.second.html. This observation shows an early understanding of the concept of immunity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?