| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix. The two DNA strands are antiparallel , such that the 3ʹ end of one strand faces the 5ʹ end of the other ( [link] ). The 3ʹ end of each strand has a free hydroxyl group, while the 5ʹ end of each strand has a free phosphate group. The sugar and phosphate of the polymerized nucleotides form the backbone of the structure, whereas the nitrogenous bases are stacked inside. These nitrogenous bases on the interior of the molecule interact with each other, base pairing.
Analysis of the diffraction patterns of DNA has determined that there are approximately 10 bases per turn in DNA. The asymmetrical spacing of the sugar-phosphate backbones generates major grooves (where the backbone is far apart) and minor grooves (where the backbone is close together) ( [link] ). These grooves are locations where proteins can bind to DNA. The binding of these proteins can alter the structure of DNA, regulate replication , or regulate transcription of DNA into RNA.
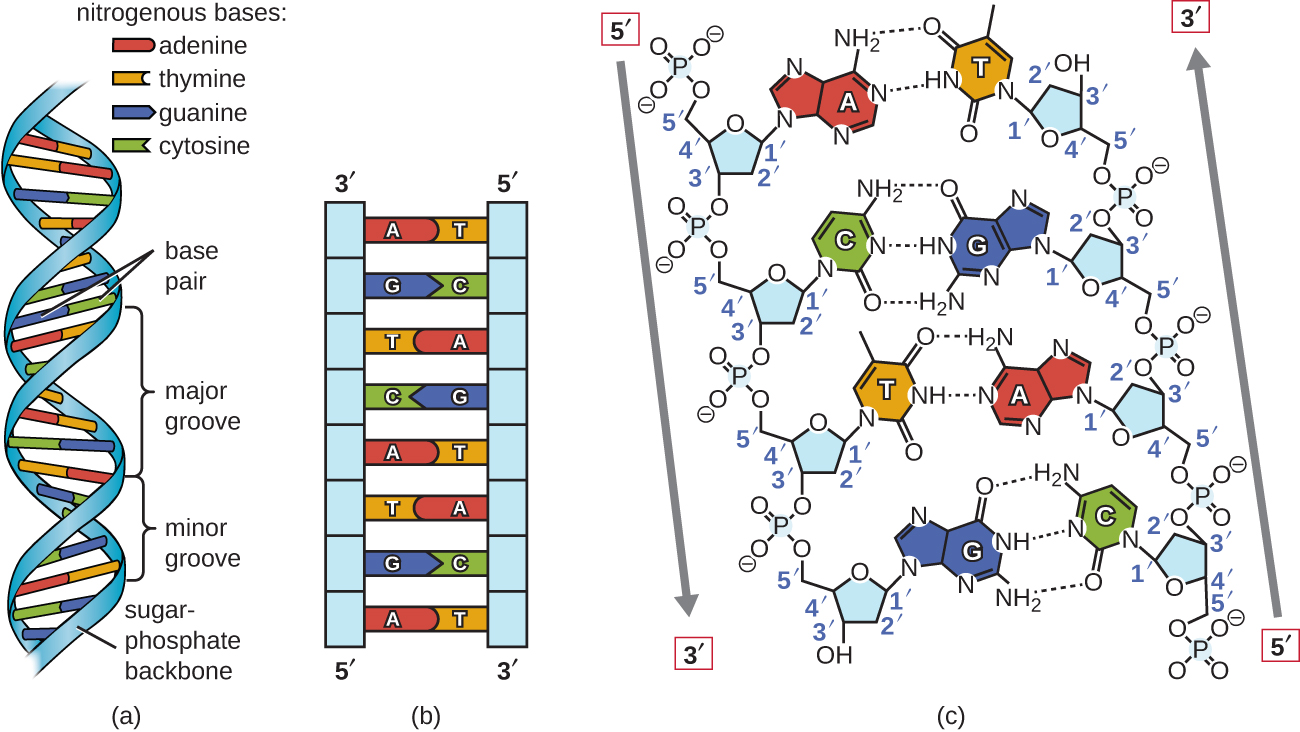
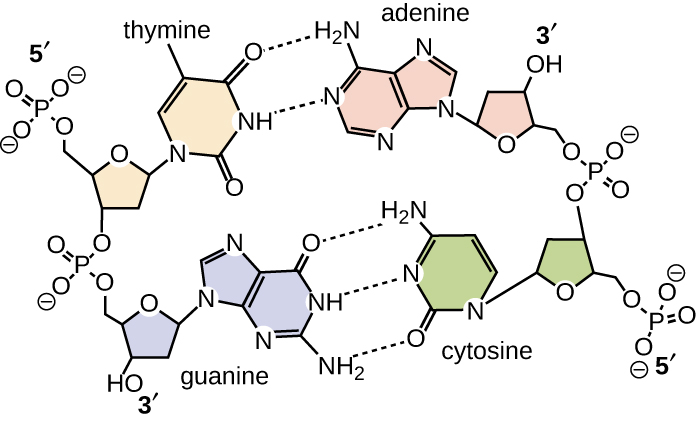
Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine. In DNA, adenine (A) and thymine (T) are complementary base pairs , and cytosine (C) and guanine (G) are also complementary base pairs, explaining Chargaff’s rules ( [link] ). The base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds between them, whereas cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between them.
In the laboratory, exposing the two DNA strands of the double helix to high temperatures or to certain chemicals can break the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases, thus separating the strands into two separate single strands of DNA (single-stranded DNA [ ssDNA ]). This process is called DNA denaturation and is analogous to protein denaturation, as described in Proteins . The ssDNA strands can also be put back together as double-stranded DNA ( dsDNA ), through reannealing or renaturing by cooling or removing the chemical denaturants, allowing these hydrogen bonds to reform. The ability to artificially manipulate DNA in this way is the basis for several important techniques in biotechnology ( [link] ). Because of the additional hydrogen bonding between the C = G base pair, DNA with a high GC content is more difficult to denature than DNA with a lower GC content.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?