| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
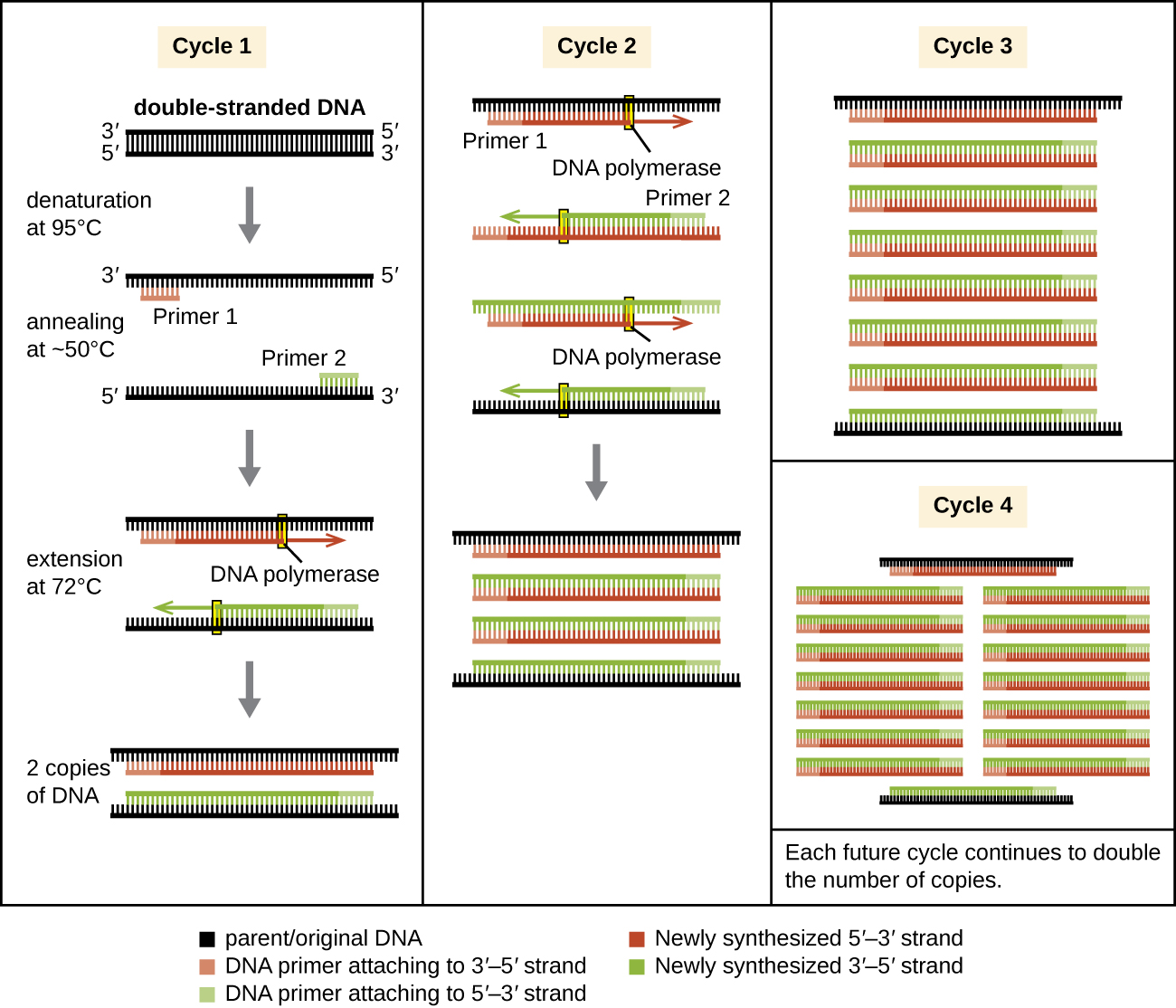
Natural DNA replication is designed to copy the entire genome, and initiates at one or more origin sites. Primers are constructed during replication, not before, and do not consist of a few specific sequences. PCR targets specific regions of a DNA sample using sequence-specific primers. In recent years, a variety of isothermal PCR amplification methods that circumvent the need for thermal cycling have been developed, taking advantage of accessory proteins that aid in the DNA replication process. As the development of these methods continues and their use becomes more widespread in research, forensic, and clinical labs, thermal cyclers may become obsolete.

Deepen your understanding of the polymerase chain reaction by viewing this animation and working through an interactive exercise.
Several later modifications to PCR further increase the utility of this technique. Reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) is used for obtaining DNA copies of a specific mRNA molecule. RT-PCR begins with the use of the reverse transcriptase enzyme to convert mRNA molecules into cDNA . That cDNA is then used as a template for traditional PCR amplification. RT-PCR can detect whether a specific gene has been expressed in a sample. Another recent application of PCR is real-time PCR , also known as quantitative PCR (qPCR) . Standard PCR and RT-PCR protocols are not quantitative because any one of the reagents may become limiting before all of the cycles within the protocol are complete, and samples are only analyzed at the end. Because it is not possible to determine when in the PCR or RT-PCR protocol a given reagent has become limiting, it is not possible to know how many cycles were completed prior to this point, and thus it is not possible to determine how many original template molecules were present in the sample at the start of PCR. In qPCR, however, the use of fluorescence allows one to monitor the increase in a double-stranded template during a PCR reaction as it occurs. These kinetics data can then be used to quantify the amount of the original target sequence. The use of qPCR in recent years has further expanded the capabilities of PCR, allowing researchers to determine the number of DNA copies, and sometimes organisms, present in a sample. In clinical settings, qRT-PCR is used to determine viral load in HIV-positive patients to evaluate the effectiveness of their therapy.
A basic sequencing technique is the chain termination method , also known as the dideoxy method or the Sanger DNA sequencing method , developed by Frederick Sanger in 1972. The chain termination method involves DNA replication of a single-stranded template with the use of a DNA primer to initiate synthesis of a complementary strand, DNA polymerase, a mix of the four regular deoxynucleotide (dNTP) monomers, and a small proportion of dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs), each labeled with a molecular beacon . The ddNTPs are monomers missing a hydroxyl group (–OH) at the site at which another nucleotide usually attaches to form a chain ( [link] ). Every time a ddNTP is randomly incorporated into the growing complementary strand, it terminates the process of DNA replication for that particular strand. This results in multiple short strands of replicated DNA that are each terminated at a different point during replication. When the reaction mixture is subjected to gel electrophoresis, the multiple newly replicated DNA strands form a ladder of differing sizes. Because the ddNTPs are labeled, each band on the gel reflects the size of the DNA strand when the ddNTP terminated the reaction.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?