| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Mistakes in the process of DNA replication can cause spontaneous mutation s to occur. The error rate of DNA polymerase is one incorrect base per billion base pairs replicated. Exposure to mutagen s can cause induced mutation s , which are various types of chemical agents or radiation ( [link] ). Exposure to a mutagen can increase the rate of mutation more than 1000-fold. Mutagens are often also carcinogen s , agents that cause cancer. However, whereas nearly all carcinogens are mutagenic, not all mutagens are necessarily carcinogens.
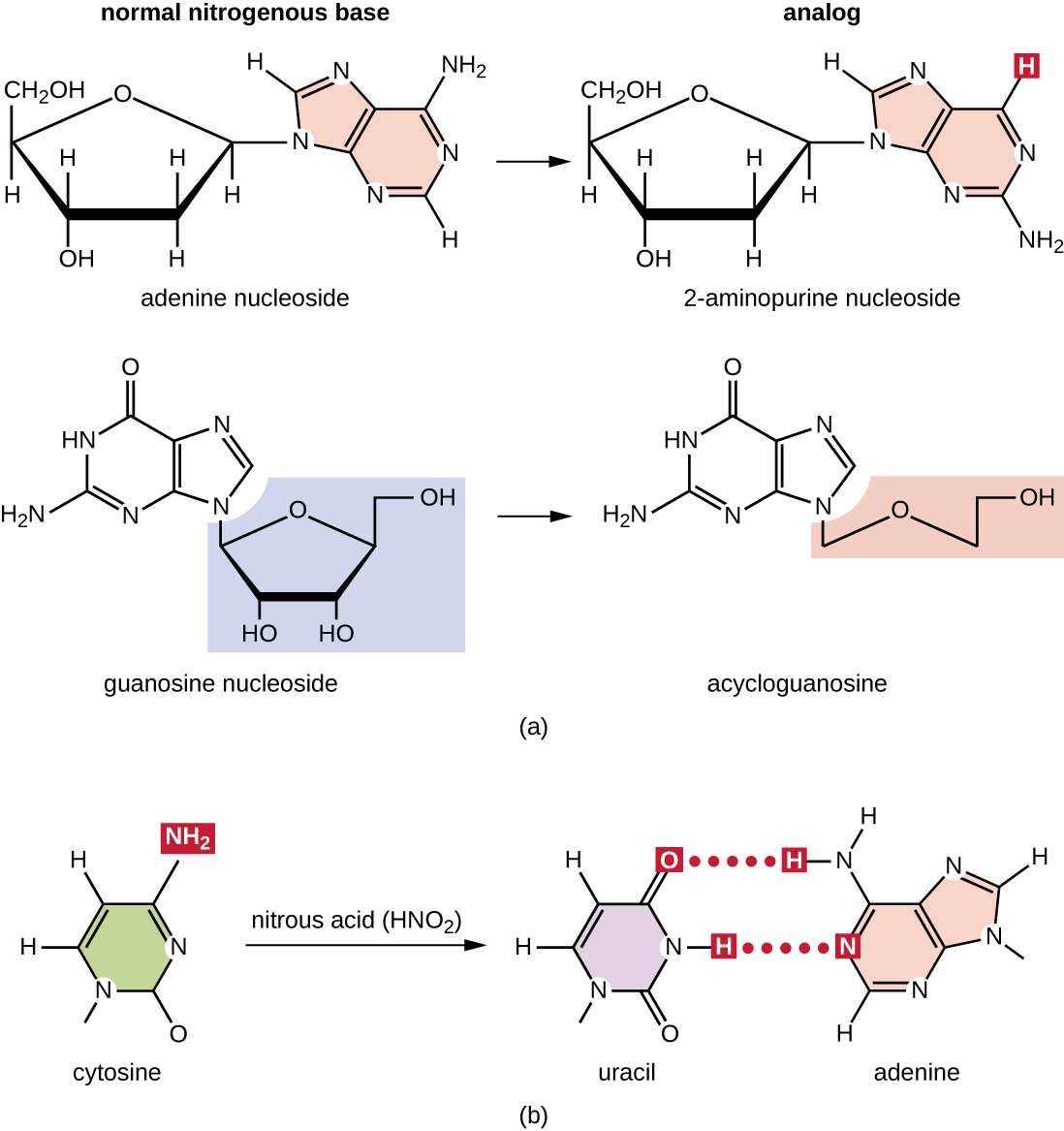
Various types of chemical mutagens interact directly with DNA either by acting as nucleoside analogs or by modifying nucleotide bases. Chemicals called nucleoside analog s are structurally similar to normal nucleotide bases and can be incorporated into DNA during replication ( [link] ). These base analogs induce mutations because they often have different base-pairing rules than the bases they replace. Other chemical mutagens can modify normal DNA bases, resulting in different base-pairing rules. For example, nitrous acid deaminates cytosine, converting it to uracil. Uracil then pairs with adenine in a subsequent round of replication, resulting in the conversion of a GC base pair to an AT base pair. Nitrous acid also deaminates adenine to hypoxanthine, which base pairs with cytosine instead of thymine, resulting in the conversion of a TA base pair to a CG base pair.
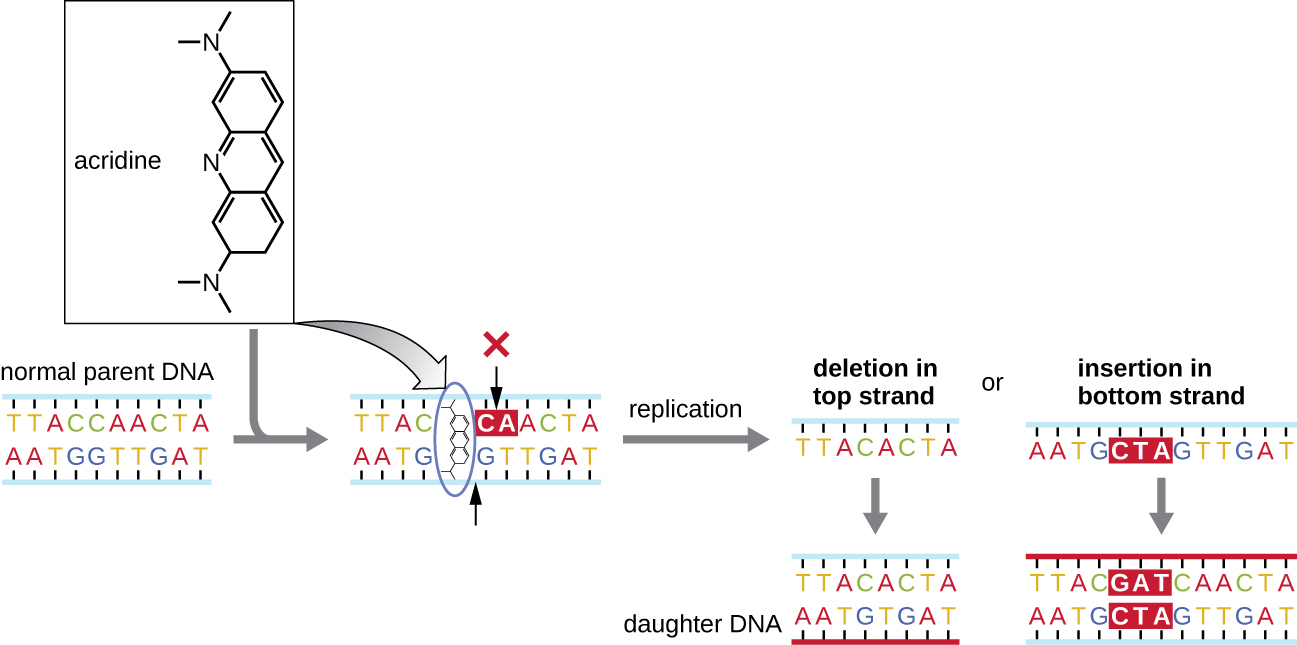
Chemical mutagens known as intercalating agent s work differently. These molecules slide between the stacked nitrogenous bases of the DNA double helix, distorting the molecule and creating atypical spacing between nucleotide base pairs ( [link] ). As a result, during DNA replication, DNA polymerase may either skip replicating several nucleotides (creating a deletion ) or insert extra nucleotides (creating an insertion ). Either outcome may lead to a frameshift mutation . Combustion products like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are particularly dangerous intercalating agents that can lead to mutation-caused cancers. The intercalating agents ethidium bromide and acridine orange are commonly used in the laboratory to stain DNA for visualization and are potential mutagens.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?