| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Many organisms are only able to use one enantiomeric form of certain types of molecules as nutrients and as building blocks to make structures within a cell. Some enantiomeric forms of amino acids have distinctly different tastes and smells when consumed as food. For example, L-aspartame, commonly called aspartame, tastes sweet, whereas D-aspartame is tasteless. Drug enantiomers can have very different pharmacologic affects. For example, the compound methorphan exists as two enantiomers, one of which acts as an antitussive ( dextro methorphan, a cough suppressant), whereas the other acts as an analgesic ( levo methorphan, a drug similar in effect to codeine).
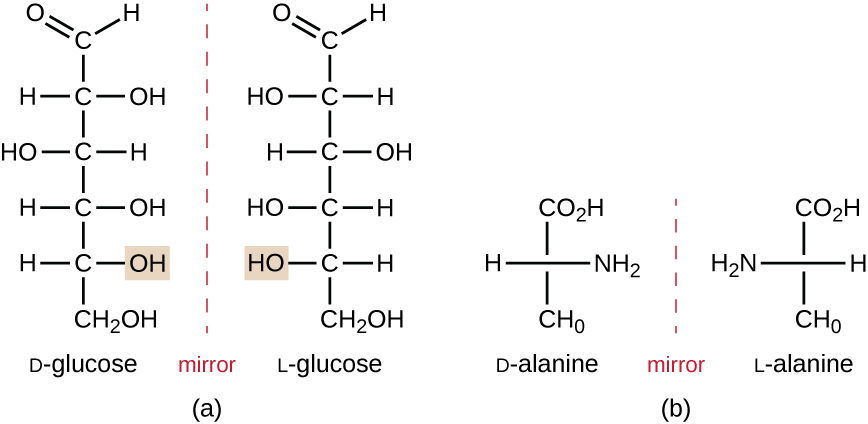
Enantiomers are also called optical isomers because they can rotate the plane of polarized light. Some of the crystals Pasteur observed from wine fermentation rotated light clockwise whereas others rotated the light counterclockwise. Today, we denote enantiomers that rotate polarized light clockwise (+) as d form s, and the mirror image of the same molecule that rotates polarized light counterclockwise (−) as the l form . The d and l labels are derived from the Latin words dexter (on the right) and laevus (on the left), respectively. These two different optical isomers often have very different biological properties and activities. Certain species of molds, yeast, and bacteria, such as Rhizopus , Yarrowia , and Lactobacillus spp., respectively, can only metabolize one type of optical isomer; the opposite isomer is not suitable as a source of nutrients. Another important reason to be aware of optical isomers is the therapeutic use of these types of chemicals for drug treatment, because some microorganisms can only be affected by one specific optical isomer.
In addition to containing carbon atoms, biomolecules also contain functional groups —groups of atoms within molecules that are categorized by their specific chemical composition and the chemical reactions they perform, regardless of the molecule in which the group is found. Some of the most common functional groups are listed in [link] . In the formulas, the symbol R stands for “residue” and represents the remainder of the molecule. R might symbolize just a single hydrogen atom or it may represent a group of many atoms. Notice that some functional groups are relatively simple, consisting of just one or two atoms, while some comprise two of these simpler functional groups. For example, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is present in several classes of organic compounds as part of larger functional groups such as ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, and amides. In ketones, the carbonyl is present as an internal group, whereas in aldehydes it is a terminal group.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?