| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
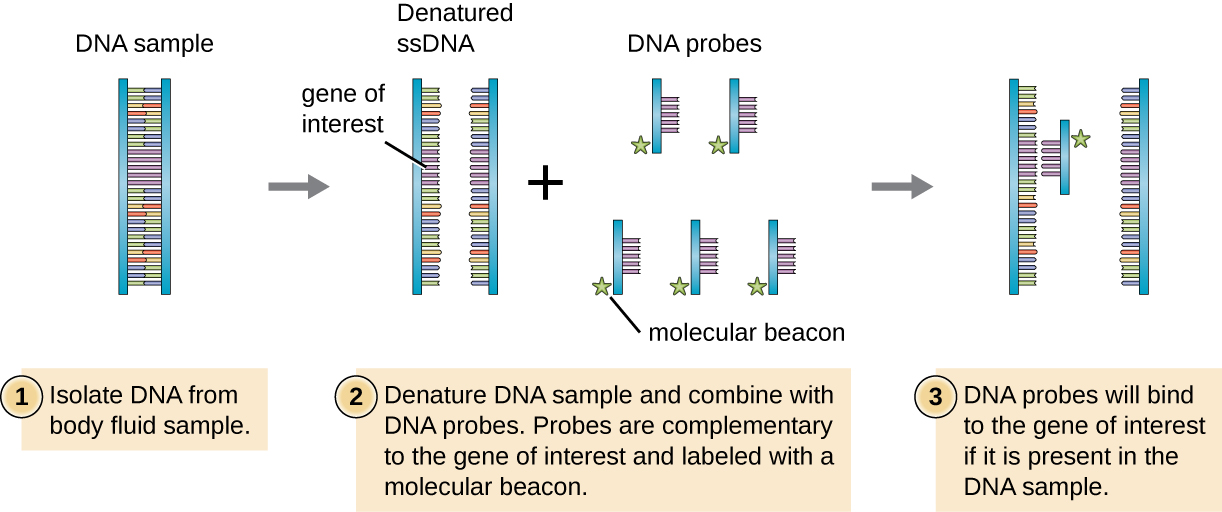
To screen a genomic library for a particular gene or sequence of interest, researchers must know something about that gene. If researchers have a portion of the sequence of DNA for the gene of interest, they can design a DNA probe , a single-stranded DNA fragment that is complementary to part of the gene of interest and different from other DNA sequences in the sample. The DNA probe may be synthesized chemically by commercial laboratories, or it may be created by cloning, isolating, and denaturing a DNA fragment from a living organism. In either case, the DNA probe must be labeled with a molecular tag or beacon, such as a radioactive phosphorus atom (as is used for autoradiography ) or a fluorescent dye (as is used in fluorescent in situ hybridization, or FISH), so that the probe and the DNA it binds to can be seen ( [link] ). The DNA sample being probed must also be denatured to make it single-stranded so that the single-stranded DNA probe can anneal to the single-stranded DNA sample at locations where their sequences are complementary. While these techniques are valuable for diagnosis, their direct use on sputum and other bodily samples may be problematic due to the complex nature of these samples. DNA often must first be isolated from bodily samples through chemical extraction methods before a DNA probe can be used to identify pathogens.
The mild, flu-like symptoms that Kayla is experiencing could be caused by any number of infectious agents. In addition, several non-infectious autoimmune conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also have symptoms that are consistent with Kayla’s early symptoms. However, over the course of several weeks, Kayla’s symptoms worsened. She began to experience joint pain in her knees, heart palpitations, and a strange limpness in her facial muscles. In addition, she suffered from a stiff neck and painful headaches. Reluctantly, she decided it was time to seek medical attention.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
There are a number of situations in which a researcher might want to physically separate a collection of DNA fragments of different sizes. A researcher may also digest a DNA sample with a restriction enzyme to form fragments. The resulting size and fragment distribution pattern can often yield useful information about the sequence of DNA bases that can be used, much like a bar-code scan, to identify the individual or species to which the DNA belongs.
Gel electrophoresis is a technique commonly used to separate biological molecules based on size and biochemical characteristics, such as charge and polarity. Agarose gel electrophoresis is widely used to separate DNA (or RNA) of varying sizes that may be generated by restriction enzyme digestion or by other means, such as the PCR ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?