| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
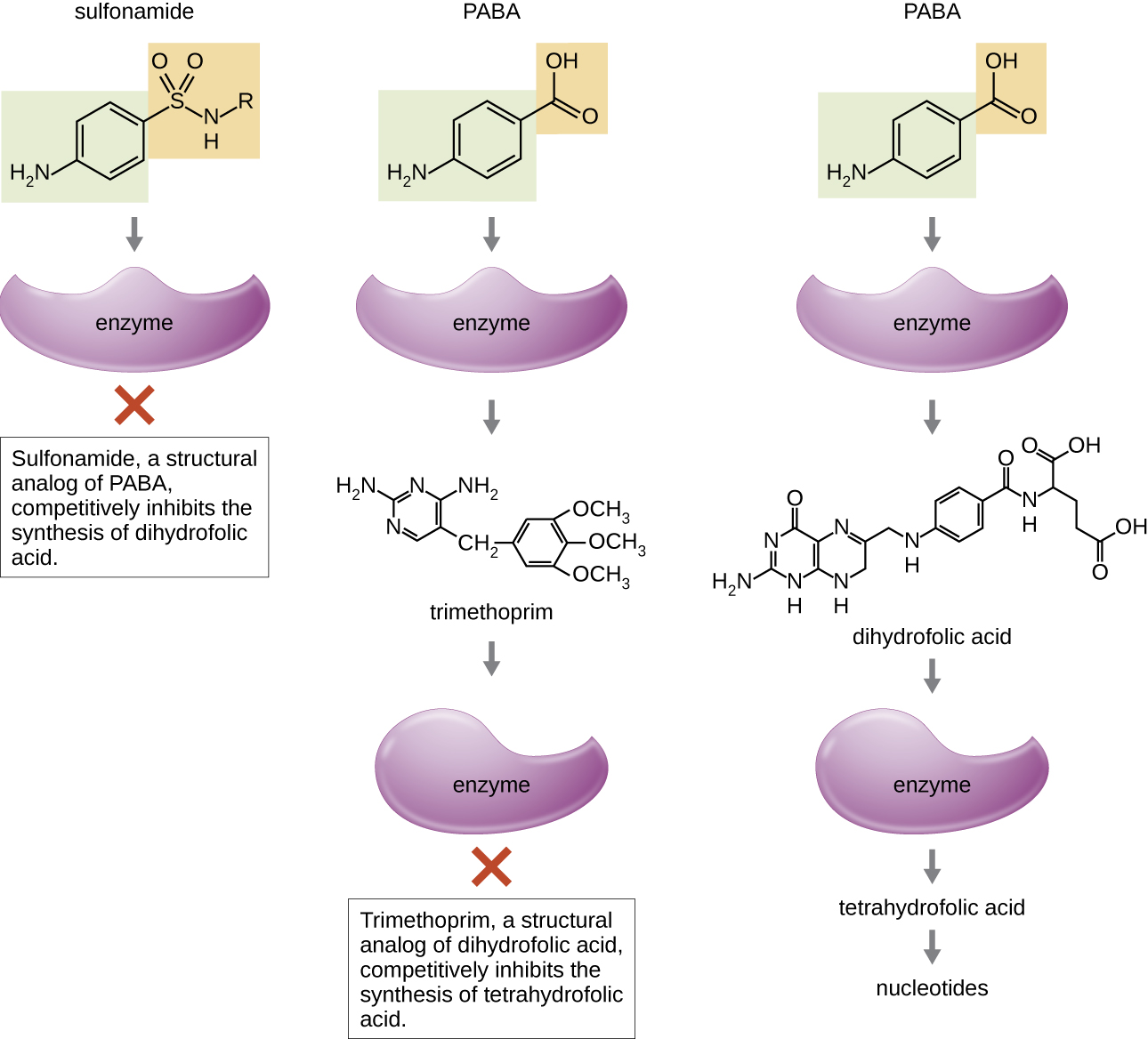
Trimethoprim is a synthetic antimicrobial compound that serves as an antimetabolite within the same folic acid synthesis pathway as sulfonamides. However, trimethoprim is a structural analogue of dihydrofolic acid and inhibits a later step in the metabolic pathway ( [link] ). Trimethoprim is used in combination with the sulfa drug sulfamethoxazole to treat urinary tract infection s, ear infection s, and bronchitis . As discussed, the combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole is an example of antibacterial synergy. When used alone, each antimetabolite only decreases production of folic acid to a level where bacteriostatic inhibition of growth occurs. However, when used in combination, inhibition of both steps in the metabolic pathway decreases folic acid synthesis to a level that is lethal to the bacterial cell. Because of the importance of folic acid during fetal development, sulfa drugs and trimethoprim use should be carefully considered during early pregnancy.
The drug isoniazid is an antimetabolite with specific toxicity for mycobacteria and has long been used in combination with rifampin or streptomycin in the treatment of tuberculosis . It is administered as a prodrug, requiring activation through the action of an intracellular bacterial peroxidase enzyme, forming isoniazid-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and isoniazid-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), ultimately preventing the synthesis of mycolic acid, which is essential for mycobacterial cell walls. Possible side effects of isoniazid use include hepatotoxicity , neurotoxicity , and hematologic toxicity ( anemia ).
| Antimetabolite Drugs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Pathway Target | Mechanism of Action | Drug Class | Specific Drugs | Spectrum of Activity |
| Folic acid synthesis | Inhibits the enzyme involved in production of dihydrofolic acid | Sulfonamides | Sulfamethoxazole | Broad spectrum against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria |
| Sulfones | Dapsone | |||
| Inhibits the enzyme involved in the production of tetrahydrofolic acid | Not applicable | Trimethoprim | Broad spectrum against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria | |
| Mycolic acid synthesis | Interferes with the synthesis of mycolic acid | Not applicable | Isoniazid | Narrow spectrum against Mycobacterium spp., including M. tuberculosis |
Bedaquiline, representing the synthetic antibacterial class of compounds called the diarylquinolones , uses a novel mode of action that specifically inhibits mycobacterial growth. Although the specific mechanism has yet to be elucidated, this compound appears to interfere with the function of ATP synthases, perhaps by interfering with the use of the hydrogen ion gradient for ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation , leading to reduced ATP production. Due to its side effects , including hepatotoxicity and potentially lethal heart arrhythmia, its use is reserved for serious, otherwise untreatable cases of tuberculosis .

To learn more about the general principles of antimicrobial therapy and bacterial modes of action, visit Michigan State University’s Antimicrobial Resistance Learning Site , particularly pages 6 through 9.
Reading thorough Marisa’s health history, the doctor noticed that during her hospitalization in Vietnam, she was catheterized and received the antimicrobial drugs ceftazidime and metronidazole . Upon learning this, the doctor ordered a CT scan of Marisa’s abdomen to rule out appendicitis; the doctor also requested blood work to see if she had an elevated white blood cell count, and ordered a urine analysis test and urine culture to look for the presence of white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria.
Marisa’s urine sample came back positive for the presence of bacteria, indicating a urinary tract infection (UTI). The doctor prescribed ciprofloxacin. In the meantime, her urine was cultured to grow the bacterium for further testing.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
Selective toxicity antimicrobials are easier to develop against bacteria because they are ________ cells, whereas human cells are eukaryotic.
prokaryotic
If human cells and bacterial cells perform transcription, how are the rifamycins specific for bacterial infections?
What bacterial structural target would make an antibacterial drug selective for gram-negative bacteria? Provide one example of an antimicrobial compound that targets this structure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?