| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Despite the presence of saliva and the mechanical forces of chewing and eating, some microbes thrive in the mouth. These microbes can cause damage to the teeth and can cause infections that have the potential to spread beyond the mouth and sometimes throughout the body.
Cavities of the teeth, known clinically as dental caries , are microbial lesions that cause damage to the teeth. Over time, the lesion can grow through the outer enamel layer to infect the underlying dentin or even the innermost pulp . If dental caries are not treated, the infection can become an abscess that spreads to the deeper tissues of the teeth , near the roots, or to the bloodstream.
Tooth decay results from the metabolic activity of microbes that live on the teeth. A layer of proteins and carbohydrates forms when clean teeth come into contact with saliva. Microbes are attracted to this food source and form a biofilm called plaque . The most important cariogenic species in these biofilms is Streptococcus mutans . When sucrose , a disaccharide sugar from food, is broken down by bacteria in the mouth, glucose and fructose are produced. The glucose is used to make dextran , which is part of the extracellular matrix of the biofilm. Fructose is fermented, producing organic acids such as lactic acid . These acids dissolve the minerals of the tooth, including enamel , even though it is the hardest material in the body. The acids work even more quickly on exposed dentin ( [link] ). Over time, the plaque biofilm can become thick and eventually calcify. When a heavy plaque deposit becomes hardened in this way, it is called tartar or dental calculus ( [link] ). These substantial plaque biofilms can include a variety of bacterial species, including Streptococcus and Actinomyces species.
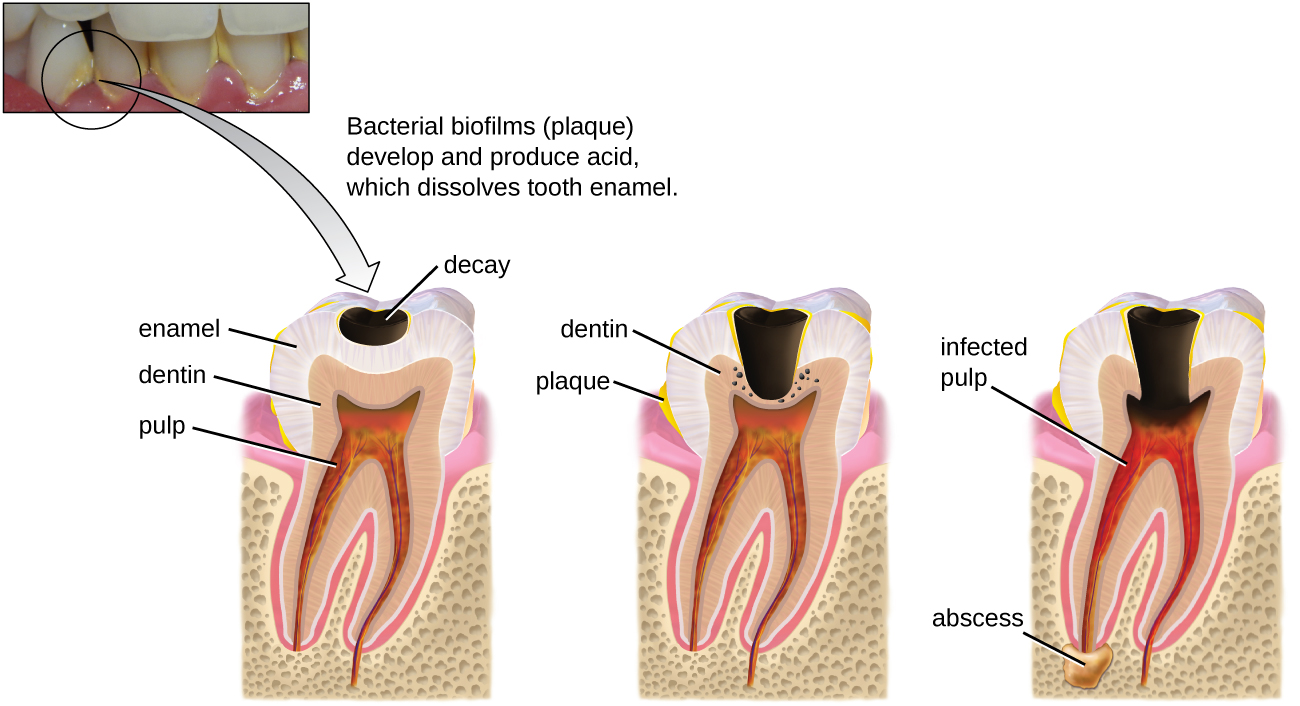
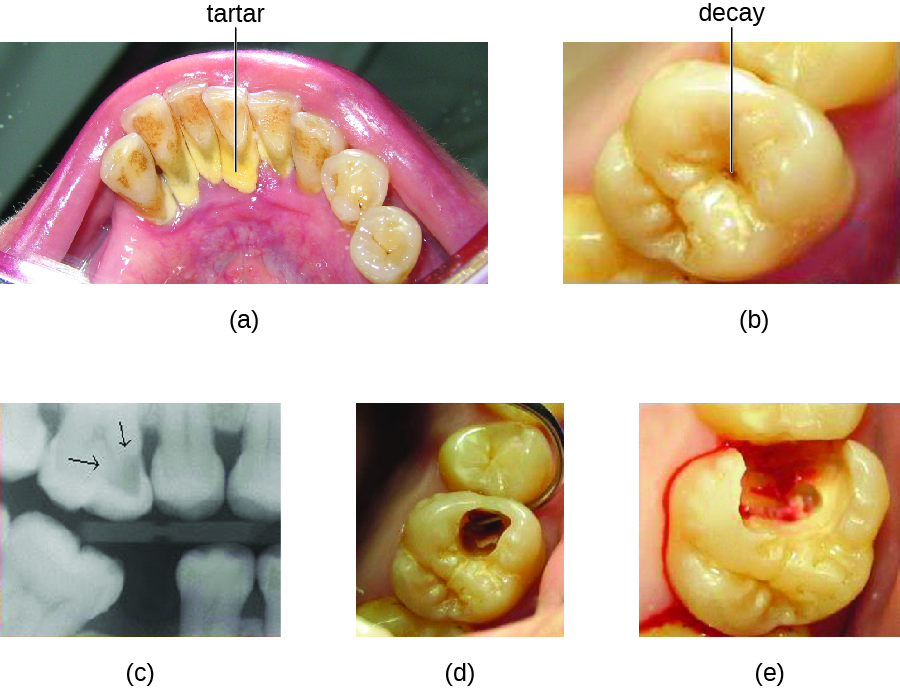
Some tooth decay is visible from the outside, but it is not always possible to see all decay or the extent of the decay. X-ray imaging is used to produce radiographs that can be studied to look for deeper decay and damage to the root or bone ( [link] ). If not detected, the decay can reach the pulp or even spread to the bloodstream. Painful abscesses can develop.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?