| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Laboratory tests to detect antibodies and antigens outside of the body (e.g., in a test tube) are called in vitro assays. When both antibodies and their corresponding antigens are present in a solution, we can often observe a precipitation reaction in which large complexes (lattices) form and settle out of solution. In the next several sections, we will discuss several common in vitro assays.
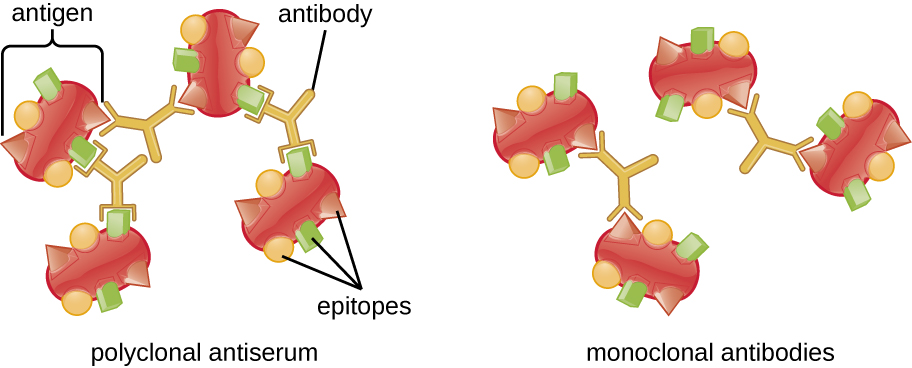
A visible antigen-antibody complex is called a precipitin , and in vitro assays that produce a precipitin are called precipitin reactions . A precipitin reaction typically involves adding soluble antigens to a test tube containing a solution of antibodies. Each antibody has two arms, each of which can bind to an epitope. When an antibody binds to two antigens, the two antigens become bound together by the antibody. A lattice can form as antibodies bind more and more antigens together, resulting in a precipitin ( [link] ). Most precipitin tests use a polyclonal antiserum rather than monoclonal antibodies because polyclonal antibodies can bind to multiple epitopes, making lattice formation more likely. Although mAbs may bind some antigens, the binding will occur less often, making it much less likely that a visible precipitin will form.
The amount of precipitation also depends on several other factors. For example, precipitation is enhanced when the antibodies have a high affinity for the antigen. While most antibodies bind antigen with high affinity, even high-affinity binding uses relatively weak noncovalent bonds, so that individual interactions will often break and new interactions will occur.
In addition, for precipitin formation to be visible, there must be an optimal ratio of antibody to antigen. The optimal ratio is not likely to be a 1:1 antigen-to-antibody ratio; it can vary dramatically, depending on the number of epitopes on the antigen and the class of antibody. Some antigens may have only one or two epitopes recognized by the antiserum, whereas other antigens may have many different epitopes and/or multiple instances of the same epitope on a single antigen molecule.
[link] illustrates how the ratio of antigen and antibody affects the amount of precipitation. To achieve the optimal ratio, antigen is slowly added to a solution containing antibodies, and the amount of precipitin is determined qualitatively. Initially, there is not enough antigen to produce visible lattice formation; this is called the zone of antibody excess. As more antigen is added, the reaction enters the equivalence zone (or zone of equivalence), where both the optimal antigen-antibody interaction and maximal precipitation occur. If even more antigen were added, the amount of antigen would become excessive and actually cause the amount of precipitation to decline.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?