| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An important quality for an antimicrobial drug is selective toxicity , meaning that it selectively kills or inhibits the growth of microbial targets while causing minimal or no harm to the host. Most antimicrobial drugs currently in clinical use are antibacterial because the prokaryotic cell provides a greater variety of unique targets for selective toxicity, in comparison to fungi, parasites, and viruses. Each class of antibacterial drugs has a unique mode of action (the way in which a drug affects microbes at the cellular level), and these are summarized in [link] and [link] .
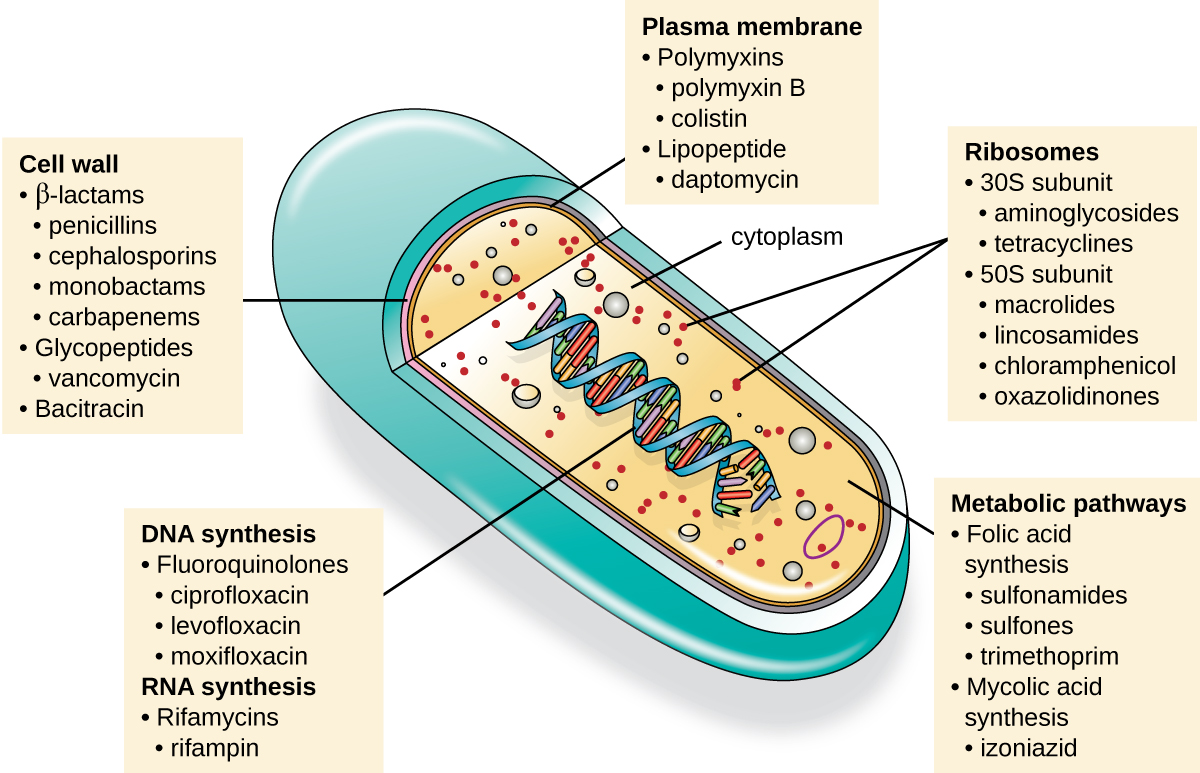
| Common Antibacterial Drugs by Mode of Action | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mode of Action | Target | Drug Class |
| Inhibit cell wall biosynthesis | Penicillin-binding proteins | β-lactams: penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems |
| Peptidoglycan subunits | Glycopeptides | |
| Peptidoglycan subunit transport | Bacitracin | |
| Inhibit biosynthesis of proteins | 30S ribosomal subunit | Aminoglycosides, tetracyclines |
| 50S ribosomal subunit | Macrolides, lincosamides, chloramphenicol, oxazolidinones | |
| Disrupt membranes | Lipopolysaccharide, inner and outer membranes | Polymyxin B, colistin, daptomycin |
| Inhibit nucleic acid synthesis | RNA | Rifamycin |
| DNA | Fluoroquinolones | |
| Antimetabolites | Folic acid synthesis enzyme | Sulfonamides, trimethoprim |
| Mycolic acid synthesis enzyme | Isonicotinic acid hydrazide | |
| Mycobacterial adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase inhibitor | Mycobacterial ATP synthase | Diarylquinoline |
Several different classes of antibacterials block steps in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan , making cells more susceptible to osmotic lysis ( [link] ). Therefore, antibacterials that target cell wall biosynthesis are bactericidal in their action. Because human cells do not make peptidoglycan, this mode of action is an excellent example of selective toxicity.
Penicillin, the first antibiotic discovered, is one of several antibacterials within a class called β-lactams . This group of compounds includes the penicillins , cephalosporins , monobactams , and carbapenems , and is characterized by the presence of a β-lactam ring found within the central structure of the drug molecule ( [link] ). The β-lactam antibacterials block the crosslinking of peptide chains during the biosynthesis of new peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall. They are able to block this process because the β-lactam structure is similar to the structure of the peptidoglycan subunit component that is recognized by the crosslinking transpeptidase enzyme, also known as a penicillin-binding protein (PBP) . Although the β-lactam ring must remain unchanged for these drugs to retain their antibacterial activity, strategic chemical changes to the R groups have allowed for development of a wide variety of semisynthetic β-lactam drugs with increased potency , expanded spectrum of activity , and longer half-lives for better dosing, among other characteristics.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?