| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
For thousands of years, humans have used various physical methods of microbial control for food preservation . Common control methods include the application of high temperatures, radiation, filtration, and desiccation (drying), among others. Many of these methods nonspecifically kill cells by disrupting membranes, changing membrane permeability, or damaging proteins and nucleic acids by denaturation, degradation, or chemical modification. Various physical methods used for microbial control are described in this section.
Heating is one of the most common—and oldest—forms of microbial control. It is used in simple techniques like cooking and canning . Heat can kill microbes by altering their membranes and denaturing proteins. The thermal death point (TDP) of a microorganism is the lowest temperature at which all microbes are killed in a 10-minute exposure. Different microorganisms will respond differently to high temperatures, with some (e.g., endospore-formers such as C. botulinum ) being more heat tolerant. A similar parameter, the thermal death time (TDT) , is the length of time needed to kill all microorganisms in a sample at a given temperature. These parameters are often used to describe sterilization procedures that use high heat, such as autoclaving . Boiling is one of the oldest methods of moist-heat control of microbes, and it is typically quite effective at killing vegetative cells and some viruses. However, boiling is less effective at killing endospores; some endospores are able to survive up to 20 hours of boiling. Additionally, boiling may be less effective at higher altitudes, where the boiling point of water is lower and the boiling time needed to kill microbes is therefore longer. For these reasons, boiling is not considered a useful sterilization technique in the laboratory or clinical setting.
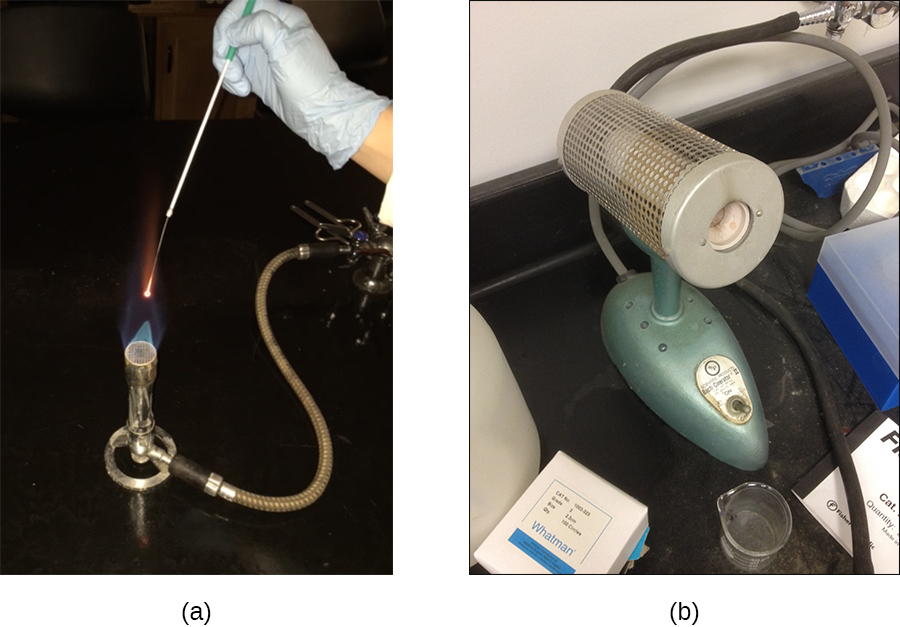
Many different heating protocols can be used for sterilization in the laboratory or clinic, and these protocols can be broken down into two main categories: dry-heat sterilization and moist-heat sterilization . Aseptic technique in the laboratory typically involves some dry-heat sterilization protocols using direct application of high heat, such as sterilizing inoculating loops ( [link] ). Incineration at very high temperatures destroys all microorganisms. Dry heat can also be applied for relatively long periods of time (at least 2 hours) at temperatures up to 170 °C by using a dry-heat sterilizer, such as an oven. However, moist-heat sterilization is typically the more effective protocol because it penetrates cells better than dry heat does.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?