| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Another case involving the Cherokee also found its way to the highest court in the land. This legal struggle— Worcester v. Georgia —asserted the rights of non-natives to live on Indian lands. Samuel Worcester was a Christian missionary and federal postmaster of New Echota, the capital of the Cherokee nation. A Congregationalist, he had gone to live among the Cherokee in Georgia to further the spread of Christianity, and he strongly opposed Indian removal.
By living among the Cherokee, Worcester had violated a Georgia law forbidding whites, unless they were agents of the federal government, to live in Indian territory. Worcester was arrested, but because his federal job as postmaster gave him the right to live there, he was released. Jackson supporters then succeeded in taking away Worcester’s job, and he was re-arrested. This time, a court sentenced him and nine others for violating the Georgia state law banning whites from living on Indian land. Worcester was sentenced to four years of hard labor. When the case of Worcester v. Georgia came before the Supreme Court in 1832, Chief Justice John Marshall ruled in favor of Worcester, finding that the Cherokee constituted “distinct political communities” with sovereign rights to their own territory.
In 1832, Chief Justice of the Supreme Court John Marshall ruled in favor of Samuel Worcester in Worcester v. Georgia . In doing so, he established the principle of tribal sovereignty. Although this judgment contradicted Cherokee Nation v. Georgia , it failed to halt the Indian Removal Act. In his opinion, Marshall wrote the following:
From the commencement of our government Congress has passed acts to regulate trade and intercourse with the Indians; which treat them as nations, respect their rights, and manifest a firm purpose to afford that protection which treaties stipulate. All these acts, and especially that of 1802, which is still in force, manifestly consider the several Indian nations as distinct political communities, having territorial boundaries, within which their authority is exclusive, and having a right to all the lands within those boundaries, which is not only acknowledged, but guaranteed by the United States. . . .
The Cherokee Nation, then, is a distinct community, occupying its own territory, with boundaries accurately described, in which the laws of Georgia can have no force, and which the citizens of Georgia have no right to enter but with the assent of the Cherokees themselves or in conformity with treaties and with the acts of Congress. The whole intercourse between the United States and this nation is, by our Constitution and laws, vested in the government of the United States.
The act of the State of Georgia under which the plaintiff in error was prosecuted is consequently void, and the judgment a nullity. . . . The Acts of Georgia are repugnant to the Constitution, laws, and treaties of the United States.
How does this opinion differ from the outcome of Cherokee Nation v. Georgia just one year earlier? Why do you think the two outcomes were different?
The Supreme Court did not have the power to enforce its ruling in Worcester v. Georgia , however, and it became clear that the Cherokee would be compelled to move. Those who understood that the only option was removal traveled west, but the majority stayed on their land. In order to remove them, the president relied on the U.S. military. In a series of forced marches, some fifteen thousand Cherokee were finally relocated to Oklahoma. This forced migration, known as the Trail of Tears , caused the deaths of as many as four thousand Cherokee ( [link] ). The Creek, Choctaw, Chickasaw, and Seminole peoples were also compelled to go. The removal of the Five Civilized Tribes provides an example of the power of majority opinion in a democracy.
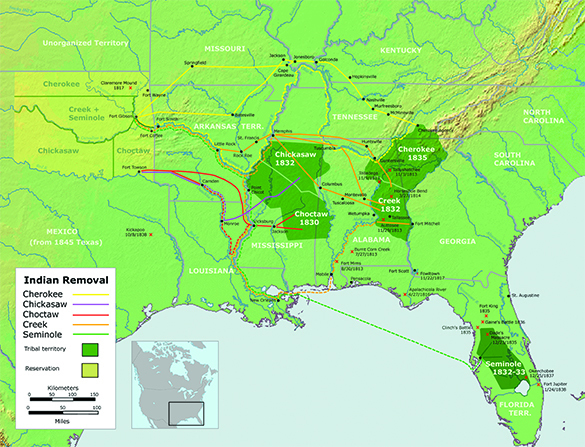
Explore the interactive Trail of Tears map at PBS.org to see the routes the Five Civilized Tribes traveled when they were expelled from their lands. Then listen to a collection of Cherokee oral histories including verses of a Cherokee-language song about the Trail of Tears. What do you think is the importance of oral history in documenting the Cherokee experience?
The policy of removal led some Indians to actively resist. In 1832, the Fox and the Sauk, led by Sauk chief Black Hawk (Makataimeshekiakiah), moved back across the Mississippi River to reclaim their ancestral home in northern Illinois. A brief war in 1832, Black Hawk’s War, ensued. White settlers panicked at the return of the native peoples, and militias and federal troops quickly mobilized. At the Battle of Bad Axe (also known as the Bad Axe Massacre), they killed over two hundred men, women, and children. Some seventy white settlers and soldiers also lost their lives in the conflict ( [link] ). The war, which lasted only a matter of weeks, illustrates how much whites on the frontier hated and feared Indians during the Age of Jackson.

Popular culture in the Age of Jackson emphasized the savagery of the native peoples and shaped domestic policy. Popular animosity found expression in the Indian Removal Act. Even the U.S. Supreme Court’s ruling in favor of the Cherokee in Georgia offered no protection against the forced removal of the Five Civilized Tribes from the Southeast, mandated by the 1830 Indian Removal Act and carried out by the U.S. military.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?