| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
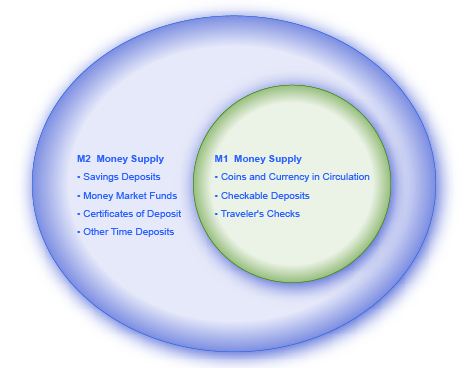
The Federal Reserve System is responsible for tracking the amounts of M1 and M2 and prepares a weekly release of information about the money supply. To provide an idea of what these amounts sound like, according to the Federal Reserve Bank’s measure of the U.S. money stock, at the end of February 2015, M1 in the United States was $3 trillion, while M2 was $11.8 trillion. A breakdown of the portion of each type of money that comprised M1 and M2 in February 2015, as provided by the Federal Reserve Bank, is provided in [link] .
| Components of M1 in the U.S. (February 2015, Seasonally Adjusted) | $ billions |
| Currency | $1,271.8 |
| Traveler’s checks | $2.9 |
| Demand deposits and other checking accounts | $1,713.5 |
| Total M1 | $2,988.2 (or $3 trillion) |
| Components of M2 in the U.S. (February 2015, Seasonally Adjusted) | $ billions |
| M1 money supply | $2,988.2 |
| Savings accounts | $7,712.1 |
| Time deposits | $509.2 |
| Individual money market mutual fund balances | $610.8 |
| Total M2 | $11,820.3 (or $11.8 trillion) |
The lines separating M1 and M2 can become a little blurry. Sometimes elements of M1 are not treated alike; for example, some businesses will not accept personal checks for large amounts, but will accept traveler’s checks or cash. Changes in banking practices and technology have made the savings accounts in M2 more similar to the checking accounts in M1. For example, some savings accounts will allow depositors to write checks, use automatic teller machines, and pay bills over the Internet, which has made it easier to access savings accounts. As with many other economic terms and statistics, the important point is to know the strengths and limitations of the various definitions of money, not to believe that such definitions are as clear-cut to economists as, say, the definition of nitrogen is to chemists.
Where does “plastic money” like debit cards, credit cards, and smart money fit into this picture? A debit card , like a check, is an instruction to the user’s bank to transfer money directly and immediately from your bank account to the seller. It is important to note that in our definition of money, it is checkable deposits that are money, not the paper check or the debit card. Although you can make a purchase with a credit card , it is not considered money but rather a short term loan from the credit card company to you. When you make a purchase with a credit card, the credit card company immediately transfers money from its checking account to the seller, and at the end of the month, the credit card company sends you a bill for what you have charged that month. Until you pay the credit card bill, you have effectively borrowed money from the credit card company. With a smart card , you can store a certain value of money on the card and then use the card to make purchases. Some “smart cards” used for specific purposes, like long-distance phone calls or making purchases at a campus bookstore and cafeteria, are not really all that smart, because they can only be used for certain purchases or in certain places.
In short, credit cards, debit cards, and smart cards are different ways to move money when a purchase is made. But having more credit cards or debit cards does not change the quantity of money in the economy, any more than having more checks printed increases the amount of money in your checking account.
One key message underlying this discussion of M1 and M2 is that money in a modern economy is not just paper bills and coins; instead, money is closely linked to bank accounts. Indeed, the macroeconomic policies concerning money are largely conducted through the banking system . The next section explains how banks function and how a nation’s banking system has the power to create money.
Read a brief article on the current monetary challenges in Sweden.
Money is measured with several definitions: M1 includes currency and money in checking accounts (demand deposits). Traveler’s checks are also a component of M1, but are declining in use. M2 includes all of M1, plus savings deposits, time deposits like certificates of deposit, and money market funds.
If you take $100 out of your piggy bank and deposit it in your checking account, how did M1 change? Did M2 change?
Federal Reserve Statistical Release. November 23, 2013. http://www.federalreserve.gov/RELEASES/h6/current/default.htm#t2tg1link.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?