| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Discrimination involves acting on the belief that members of a certain group are inferior solely because of a factor such as race, gender, or religion. There are many types of discrimination but the focus here will be on discrimination in labor markets, which arises if workers with the same skill levels—as measured by education, experience, and expertise—receive different pay receive different pay or have different job opportunities because of their race or gender.
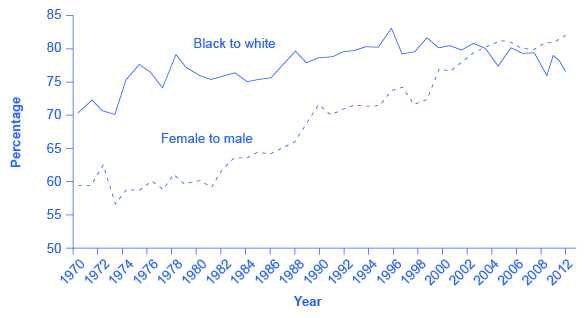
A possible signal of labor market discrimination is when one group is paid less than another. [link] shows the average wage of black workers as a ratio of the average wage of white workers and the average wage of female workers as a ratio of the average wage of male workers. Research by the economists Francine Blau and Laurence Kahn shows that the gap between the earnings of women and men did not move much in the 1970s, but has declined since the 1980s. According to the U.S. Census, the gap between the earnings of blacks and whites diminished in the 1970s, but has not changed in 50 years. In both gender and race, an earnings gap remains.
An earnings gap between average wages, in and of itself, does not prove that discrimination is occurring in the labor market. We need to apply the same productivity characteristics to all parties (employees) involved. Gender discrimination in the labor market occurs when women are paid less than men despite having comparable levels of education, experience, and expertise. (Read the Clear It Up about the sex-discrimination suit brought against Wal-Mart.) Similarly, racial discrimination in the labor market exists when racially diverse employees are paid less than their coworkers of the majority race despite having comparable levels of education, experience, and expertise. To bring a successful gender discrimination lawsuit, a female employee must prove that she is paid less than a male employee who holds a similar job, with similar educational attainment, and with similar expertise. Likewise, someone who wants to sue on the grounds of racial discrimination must prove that he or she is paid less than an employee of another race who holds a similar job, with similar educational attainment, and with similar expertise.
In one of the largest class-action sex-discrimination cases in U.S. history, 1.2 million female employees of Wal-Mart claimed that the company engaged in wage and promotion discrimination. In 2011, the Supreme Court threw out the case on the grounds that the group was too large and too diverse for the case to be considered a class action suit. Lawyers for the women regrouped and are now suing in smaller groups. Part of the difficulty for the female employees is that the court said that pay and promotion decisions were made by local managers and were not necessarily policies of the company as a whole. Consequently, female Wal-Mart employees in Texas are arguing that their new suit will challenge the management of a “discrete group of regional district and store managers.” They claim these managers made biased pay and promotion decisions. However, in 2013, a smaller California class action suit against the company was again rejected by a federal district court.
On other issues, Wal-Mart made the news again in 2013 when the National Labor Relations Board found Wal-Mart guilty of illegally penalizing and firing workers who took part in labor protests and strikes. Wal-Mart has already paid $11.7 million in back wages and compensation damages to women in Kentucky who were denied jobs due to their sex.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?