| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inflation can cause redistributions of purchasing power that hurt some and help others. People who are hurt by inflation include those who are holding a lot of cash, whether it is in a safe deposit box or in a cardboard box under the bed. When inflation happens, the buying power of cash is diminished. But cash is only an example of a more general problem: anyone who has financial assets invested in a way that the nominal return does not keep up with inflation will tend to suffer from inflation. For example, if a person has money in a bank account that pays 4% interest, but inflation rises to 5%, then the real rate of return for the money invested in that bank account is negative 1%.
The problem of a good-looking nominal interest rate being transformed into an ugly-looking real interest rate can be worsened by taxes. The U.S. income tax is charged on the nominal interest received in dollar terms, without an adjustment for inflation. So, a person who invests $10,000 and receives a 5% nominal rate of interest is taxed on the $500 received—no matter whether the inflation rate is 0%, 5%, or 10%. If inflation is 0%, then the real interest rate is 5% and all $500 is a gain in buying power. But if inflation is 5%, then the real interest rate is zero and the person had no real gain—but owes income tax on the nominal gain anyway. If inflation is 10%, then the real interest rate is negative 5% and the person is actually falling behind in buying power, but would still owe taxes on the $500 in nominal gains.
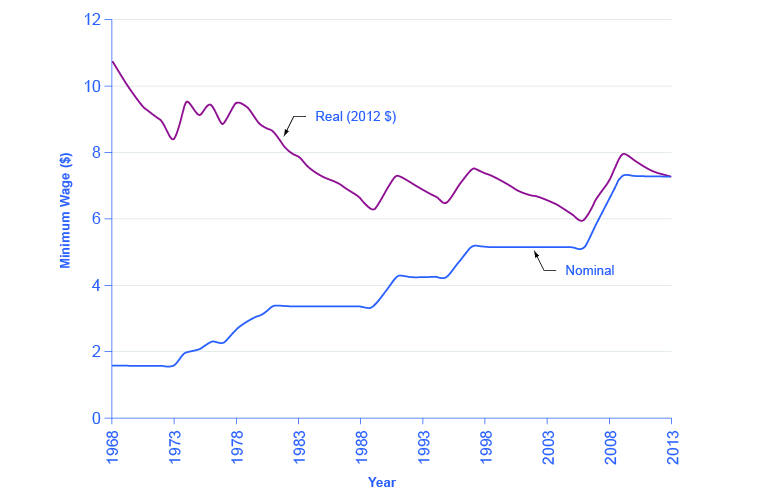
Inflation can cause unintended redistributions for wage earners, too. Wages do typically creep up with inflation over time eventually. The last row of [link] at the start of this chapter showed that average hourly wage in the U.S. economy increased from $3.23 in 1970 to $19.55 in 2014, which is an increase by a factor of almost six. Over that time period, the Consumer Price Index increased by an almost identical amount. However, increases in wages may lag behind inflation for a year or two, since wage adjustments are often somewhat sticky and occur only once or twice a year. Moreover, the extent to which wages keep up with inflation creates insecurity for workers and may involve painful, prolonged conflicts between employers and employees. If the minimum wage is adjusted for inflation only infrequently, minimum wage workers are losing purchasing power from their nominal wages, as shown in [link] .
One sizable group of people has often received a large share of their income in a form that does not increase over time: retirees who receive a private company pension. Most pensions have traditionally been set as a fixed nominal dollar amount per year at retirement. For this reason, pensions are called “defined benefits” plans. Even if inflation is low, the combination of inflation and a fixed income can create a substantial problem over time. A person who retires on a fixed income at age 65 will find that losing just 1% to 2% of buying power per year to inflation compounds to a considerable loss of buying power after a decade or two.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of macroeconomics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?