| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
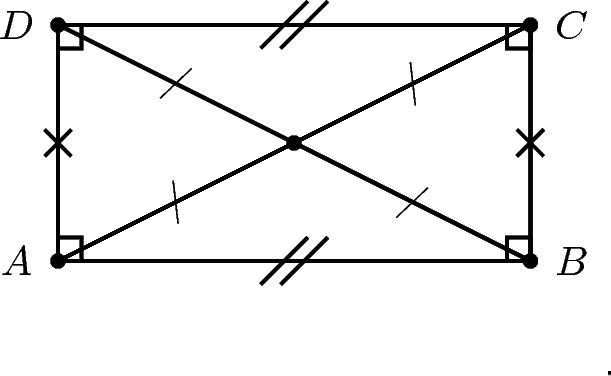
A rhombus is a parallelogram that has all four sides of equal length. A summary of the properties of a rhombus is:
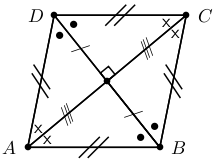
A square is a rhombus that has all four angles equal to 90 .
A summary of the properties of a square is:
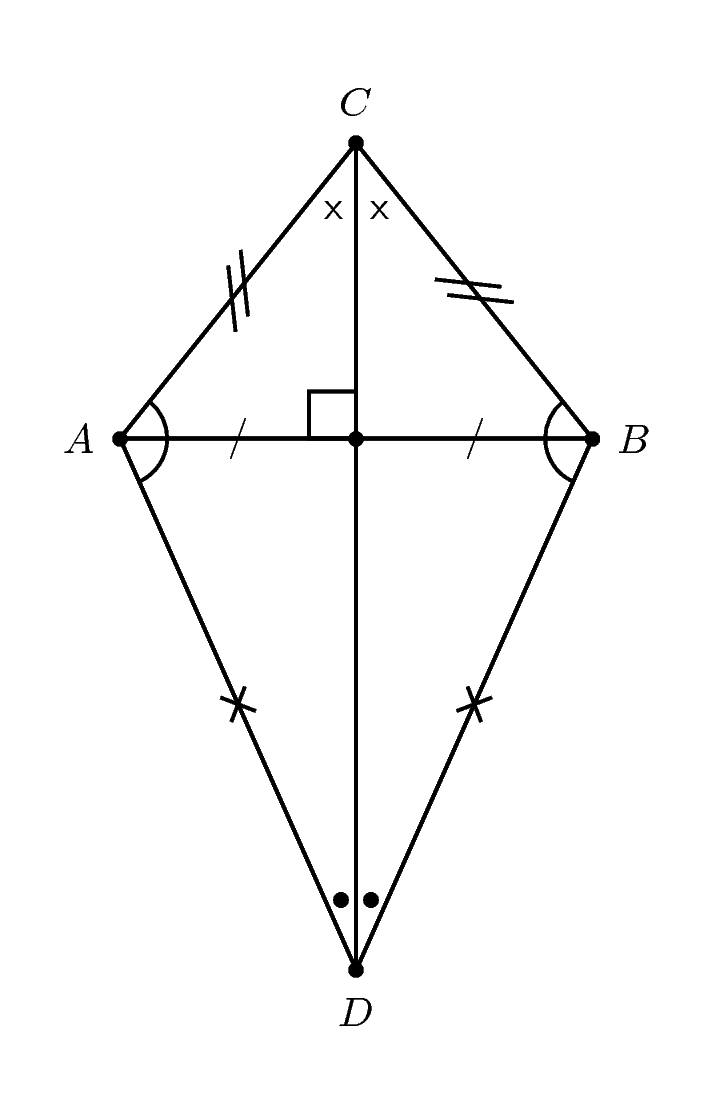
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides equal.
A summary of the properties of a kite is:
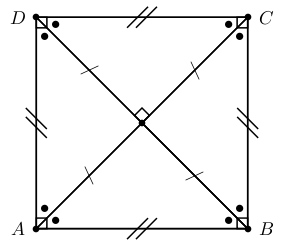
Rectangles are a special case (or a subset) of parallelograms. Rectangles are parallelograms that have all angles equal to 90. Squares are a special case (or subset) of rectangles. Squares are rectangles that have all sides equal in length. So all squares are parallelograms and rectangles. So if you are asked to prove that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, it is enough to show that both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. But if you are asked to prove that a quadrilateral is a square, then you must also show that the angles are all right angles and the sides are equal in length.
Polygons are all around us. A stop sign is in the shape of an octagon, an eight-sided polygon. The honeycomb of a beehive consists of hexagonal cells. The top of a desk is a rectangle. Note that although in the first two of these cases the sides of the polygon are all the same, but this need not be the case. Polygons with all sides and angles the same are called 'regular', while those with some sides or angles that are different are called 'irregular'. Although we often work with irregular triangles and quadrilaterals, once one gets up to polygons with greater than four sides, the more interesting ones are often the regular ones.
In this section, you will learn about similar polygons.
Fill in the table using the diagram and then answer the questions that follow.
| = | =... | ... |
| = | =... | =... |
| = | ... | =... |
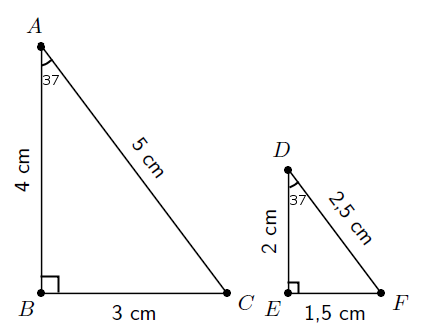
If two polygons are similar , one is an enlargement of the other. This means that the two polygons will have the same angles and their sides will be in the same proportion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 maths [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?