| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Photoautotrophs, such as plants, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria, are the energy source for a majority of the world’s ecosystems. Photoautotrophs harness the Sun’s solar energy by converting it to chemical energy in the form of ATP (and NADP). The energy stored in ATP is used to synthesize complex organic molecules, such as glucose. The rate at which photosynthetic producers incorporate energy from the Sun is called gross primary productivity . However, not all of the energy incorporated by producers is available to the other organisms in the food web because producers must also grow and reproduce, which consumes energy. Net primary productivity is the energy that remains in the producers after accounting for these organisms’ respiration and heat loss. The net productivity is then available to the primary consumers at the next trophic level.
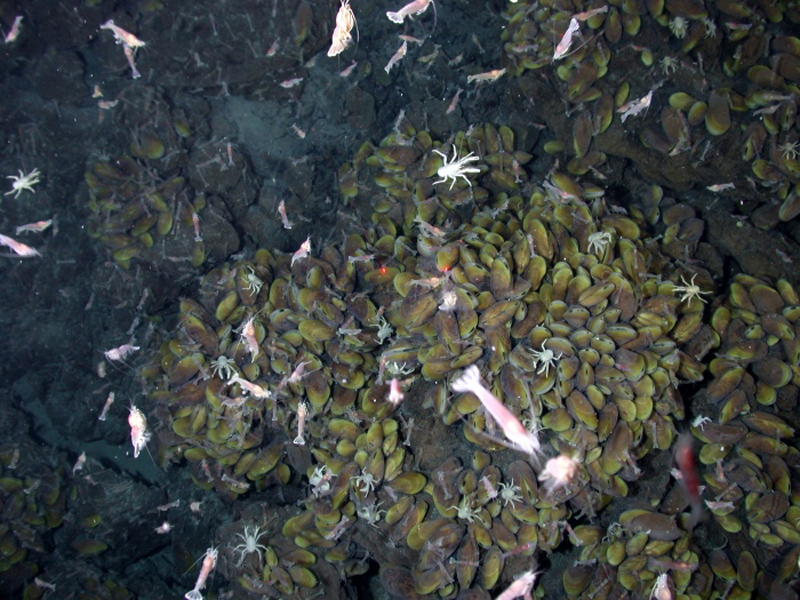
Chemoautotrophs are primarily bacteria and archaea that are found in rare ecosystems where sunlight is not available, such as those associated with dark caves or hydrothermal vents at the bottom of the ocean ( [link] ). Many chemoautotrophs in hydrothermal vents use hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S), which is released from the vents as a source of chemical energy; this allows them to synthesize complex organic molecules, such as glucose, for their own energy and, in turn, supplies energy to the rest of the ecosystem.

One of the most important consequences of ecosystem dynamics in terms of human impact is biomagnification. Biomagnification is the increasing concentration of persistent, toxic substances in organisms at each successive trophic level. These are substances that are fat soluble, not water soluble, and are stored in the fat reserves of each organism. Many substances have been shown to biomagnify, including classical studies with the pesticide dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), which were described in the 1960s bestseller, Silent Spring by Rachel Carson. DDT was a commonly used pesticide before its dangers to apex consumers, such as the bald eagle, became known. In aquatic ecosystems, organisms from each trophic level consumed many organisms in the lower level, which caused DDT to increase in birds (apex consumers) that ate fish. Thus, the birds accumulated sufficient amounts of DDT to cause fragility in their eggshells. This effect increased egg breakage during nesting and was shown to have devastating effects on these bird populations. The use of DDT was banned in the United States in the 1970s.
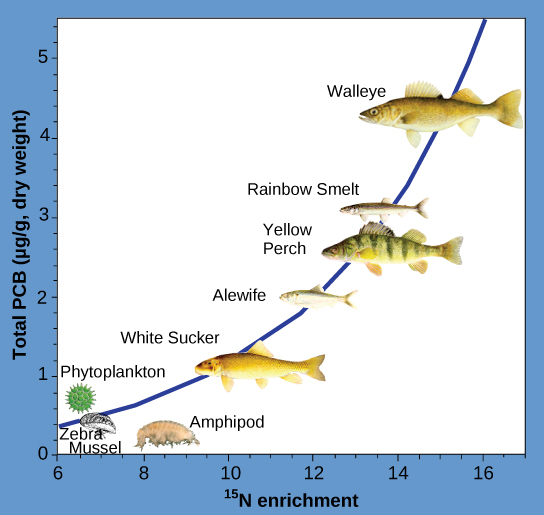
Other substances that biomagnify are polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), which were used as coolant liquids in the United States until their use was banned in 1979, and heavy metals, such as mercury, lead, and cadmium. These substances are best studied in aquatic ecosystems, where predatory fish species accumulate very high concentrations of toxic substances that are at quite low concentrations in the environment and in producers. As illustrated in a study performed by the NOAA in the Saginaw Bay of Lake Huron of the North American Great Lakes ( [link] ), PCB concentrations increased from the producers of the ecosystem (phytoplankton) through the different trophic levels of fish species. The apex consumer, the walleye, has more than four times the amount of PCBs compared to phytoplankton. Also, based on results from other studies, birds that eat these fish may have PCB levels at least one order of magnitude higher than those found in the lake fish.
Other concerns have been raised by the biomagnification of heavy metals, such as mercury and cadmium, in certain types of seafood. The United States Environmental Protection Agency recommends that pregnant women and young children should not consume any swordfish, shark, king mackerel, or tilefish because of their high mercury content. These individuals are advised to eat fish low in mercury: salmon, shrimp, pollock, and catfish. Biomagnification is a good example of how ecosystem dynamics can affect our everyday lives, even influencing the food we eat.
Ecosystems exist underground, on land, at sea, and in the air. Organisms in an ecosystem acquire energy in a variety of ways, which is transferred between trophic levels as the energy flows from the base to the top of the food web, with energy being lost at each transfer. There is energy lost at each trophic level, so the lengths of food chains are limited because there is a point where not enough energy remains to support a population of consumers. Fat soluble compounds biomagnify up a food chain causing damage to top consumers. even when environmental concentrations of a toxin are low.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Environmental biology' conversation and receive update notifications?