| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Newton’s second law of motion is more than a definition; it is a relationship among acceleration, force, and mass. It can help us make predictions. Each of those physical quantities can be defined independently, so the second law tells us something basic and universal about nature. The next section introduces the third and final law of motion.
A rock is thrown straight up. What is the net external force acting on the rock when it is at the top of its trajectory?
(a) Give an example of different net external forces acting on the same system to produce different accelerations. (b) Give an example of the same net external force acting on systems of different masses, producing different accelerations. (c) What law accurately describes both effects? State it in words and as an equation.
The gravitational force on the basketball in [link] is ignored. When gravity is taken into account, what is the direction of the net external force on the basketball—above horizontal, below horizontal, or still horizontal?
A 63.0-kg sprinter starts a race with an acceleration of . What is the net external force on him?
265 N
Since astronauts in orbit are apparently weightless, a clever method of measuring their masses is needed to monitor their mass gains or losses to adjust diets. One way to do this is to exert a known force on an astronaut and measure the acceleration produced. Suppose a net external force of 50.0 N is exerted and the astronaut’s acceleration is measured to be . (a) Calculate her mass. (b) By exerting a force on the astronaut, the vehicle in which they orbit experiences an equal and opposite force. Discuss how this would affect the measurement of the astronaut’s acceleration. Propose a method in which recoil of the vehicle is avoided.
In [link] , the net external force on the 24-kg mower is stated to be 51 N. If the force of friction opposing the motion is 24 N, what force (in newtons) is the person exerting on the mower? Suppose the mower is moving at 1.5 m/s when the force is removed. How far will the mower go before stopping?
Suppose two children push horizontally, but in exactly opposite directions, on a third child in a wagon. The first child exerts a force of 75.0 N, the second a force of 90.0 N, friction is 12.0 N, and the mass of the third child plus wagon is 23.0 kg. (a) What is the system of interest if the acceleration of the child in the wagon is to be calculated? (b) Draw a free-body diagram, including all forces acting on the system. (c) Calculate the acceleration. (d) What would the acceleration be if friction were 15.0 N?
(a) The system is the child in the wagon plus the wagon.
(b
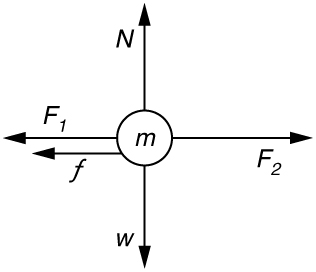
(c) in the direction of the second child’s push.
(d)
The rocket sled shown in [link] accelerates at a rate of . Its passenger has a mass of 75.0 kg. (a) Calculate the horizontal component of the force the seat exerts against his body. Compare this with his weight by using a ratio. (b) Calculate the direction and magnitude of the total force the seat exerts against his body.
(a) . This force is 5.00 times greater than his weight.
(b)
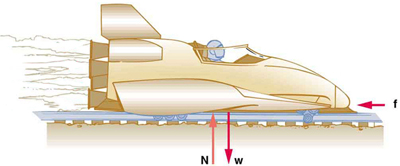
Repeat the previous problem for the situation in which the rocket sled decelerates at a rate of . In this problem, the forces are exerted by the seat and restraining belts.
The weight of an astronaut plus his space suit on the Moon is only 250 N. How much do they weigh on Earth? What is the mass on the Moon? On Earth?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Newton's laws' conversation and receive update notifications?