| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
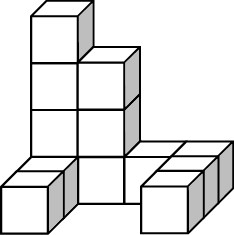
Front
4.2 from the left side:
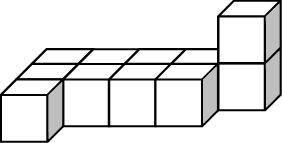
Front
4.3 from the right corner:
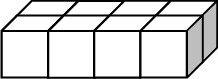
Front
Activity 4:
To investigate and approximate volume of three-dimensional objects [LO 4.8]
1. Pack sugar cubes into the matchbox and fill it with the cubes. How many do you need?
2. Now do the same with the other boxes and complete the table below:
| Object (box) | Number of sugar cubes needed to fill the box |
| Matchbox | |
3. Measure the cube of sugar and record your findings:
4. The matchbox can contain …………. cubes; we say its volume is about ……..… cubic centimetres.
5. When we measure what can go into the space in a container, we are measuring VOLUME and we need three measurements: length, width and height.
6. Instead of counting each little cube of sugar, what would be a quicker way of calculating the volume of a box? Discuss this with a friend and then write down your answer on the dotted line.
7. How many sugar cubes will you need to fill a box that is 20cm long, 15cm wide and 7cm high (a 2 litre ice-cream container)? Write down your calculations and then compare them with those of a friend.
| Learning outcomes(LOs) |
| LO 2 |
| Patterns, Functions and AlgebraThe learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills. |
| Assessment standards(ASs) |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 2.1 investigates and extends numeric and geometric patterns looking for a relationship or rules, including patterns: |
|
| 2.1.2 not limited to sequences involving constant difference or ratio. |
| 2.2 describes observed relationships or rules in own words. |
| LO 3 |
| Space and Shape (Geometry ) The learner will be able to describe and represent characteristics and relationships between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions. |
| We know this when the learner: |
3.2 describes, sorts and compares two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects from the environment according to geometrical properties including:
|
| 3.3 investigates and compares (alone and/or as a member of a group or team) two-dimensional shapes and three dimensional objects studied in this grade according to the properties already studied, by: |
| 3.3.1 making three-dimensional models using cut-out polygons (supplied); |
|
| 3.4 recognises and describes lines of symmetry in two-dimensional shapes, including those in nature and its cultural art forms; |
| 3.5 makes two-dimensional shapes, three-dimensional objects and patterns from geometric objects and shapes (e.g. tangrams) with a focus on tiling (tessellation) and line symmetry; |
| 3.6 recognises and describes natural and cultural two-dimensional shapes, three-dimensional objects and patterns in terms of geometric properties; |
| 3.7 describes changes in the view of an object held in different positions. |
| LO 4 |
| measurementThe learner will be able to use appropriate measuring units, instruments and formulae in a variety of contexts. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 4.8 investigates and approximates (alone and /or as a member of a group or team): |
4.8.2 area of polygons (using square grids and tiling) in order to develop an understanding of square units;
|
ACTIVITY 1: 3D Objects
1. Investigation – practical
2. Using a net – practical
3. Practical – Tetrahedron (tetra – Greek = 4)
| Object | Surfaces | Flat or curved | Corners | Edges |
| Rectangular prism | 6 | Flat | 8 | 12 |
| Cube | 6 | Flat | 8 | 12 |
| Tetrahedron | 4 | flat | 5 | 7 |
ACTIVITY 2: Symmetry
1. PROJECT – own – practical
2. Shapes


2.1 and 2.2 and 2.3 Cutting and folding and ruling lines of symmetry,
e.g.
( Note: in a rectangle diagonals cannot be used for just folding.)
ACTIVITY 3: objects seen from different angles
1.1 to 1.4 Practical – studying a building from various angles
2. and 3. Practical – working with cubes
4.1 to 4.3 Drawing – difficult!
ACTIVITY 4: volume
1. own
2. own investigation
3. 1 cm; 1 cm; 1 cm
4. own
5. -
6. Discussion (length x breadth x height)
7. 2 100 sugar cubes

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?