| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
means since the parentheses indicate that the exponent 3 is directly connected to the factor . Remember that the grouping symbols indicate that the quantities inside are to be considered as one single number.
means since the exponent 2 applies only to the factor .
Write each of the following without exponents.
Select a number to show that is not always equal to .
Suppose we choose to be 5. Consider both and .
Notice that only when .
Select a number to show that is not always equal to .
Select . Then , but . .
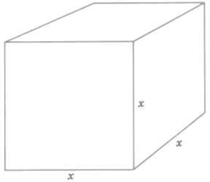
In ,
Cube with
length
width
depth
Volume
In Section [link] we were introduced to the order of operations. It was noted that we would insert another operation before multiplication and division. We can do that now.
Use the order of operations to simplify each of the following.
Use the order of operations to simplify the following.
For the following problems, write each of the quantities using exponential notation.
3 squared times to the fifth
cubed plus to the seventh
For the following problems, expand the quantities so that no exponents appear.
For the following problems, select a number (or numbers) to show that
is not generally equal to .
is not generally equal to .
For what real numbers, and , is equal to ?
Use the order of operations to simplify the quantities for the following problems.
( [link] ) Use algebraic notation to write the statement "a number divided by eight, plus five, is equal to ten."
( [link] ) Draw a number line that extends from to 5 and place points at all real numbers that are strictly greater than but less than or equal to 2.
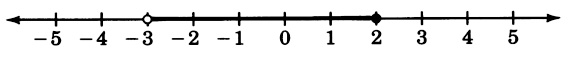
( [link] ) Is every integer a whole number?
( [link] ) Use the commutative property of multiplication to write a number equal to the number .
( [link] ) Use the distributive property to expand .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?