| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The first step is to convert our information into binary. We used the sentence “hello, this is our test message,” repeated four times, as our text message. To get it into binary, we used standard ASCII text mapping.
hello = 01101000 01100101 01101100 01101100 01101111
The next step is converting this vector of zeros and ones into a matrix. The vector is simply broken up into blocks of length L, and each block is used to form column of the matrix.
Now the fun begins. The primary method of modulation in DMT is by inverse Fourier Transform. Although it may seem counterintuitive to do so, by taking the inverse Fourier Transform of a vector or a matrix of vectors, it effectively treats each value as the Fourier coefficient of a sinusoid. Then, one could transmit this sum of sinusoids to a receiver that would in turn take the Fourier Transform (the inverse transform of the inverse transform, of course) and retrieve the original vectors.
But instead of taking the transform of our vectors of zeros and ones, we first convert bit streams of length B to specific complex numbers. We draw these complex numbers from a constellation map (a table of values spread out along the complex plane). See the figure below for an example of a 4 bit mapping.
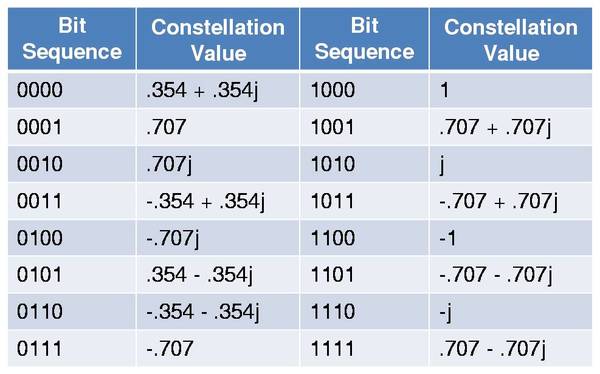
Why would we do that, you might ask. Doesn’t converting binary numbers to complex ones just make things more complicated? Well, DMT utilizes the inverse Fourier Transform in order to attain its modulation. So taking the IFFT of a vector of complex numbers will result in a sum of sinusoids, which are great signals to be sending over any channel (they are the eigenfunctions of linear, time-invariant systems).
But before taking the inverse transform, the vectors/columns of the matrix must be mirrored and complex conjugated. The Inverse Fourier Transform of a conjugate symmetric signal results in a real signal. And since we can only transmit real signals in the real world, this is what we want.
If we were transmitting over an ideal wire system, we would be done at this point. We could simply send it over the line and start demodulating. But with most channels, especially our acoustic one, this is not the case. The channel’s impulse response has non-zero duration, and will therefore cause inter-symbol interference in our output.
Intersymbol interference occurs during the convolution of the input and impulse response. Since the impulse response has more than a single value length, it will thus cause one block’s information to bleed into the next one.
To prevent this, we added what is called a cyclic prefix to each block. As long as the length of the cyclic prefix is at least as long as the impulse response, it should prevent ISI. However, it has a secondary effect as well. We created the prefix by adding the last N values of each block (where N is the length of the response) to the beginning, preserving the order. Doing this effectively converts the linear convolution of the impulse response with the block sequence to circular convolution with each block separately, since there will now be the “wrap-around” effect. This will be handy later when we start characterizing the channel, since circular convolution in time is equivalent to multiplication of DFT’s in frequency.
00010110011010001 =>01000100010110011010001
The first six bits in the second bit stream, 010001, is the cylcic prefix. Note that although these values are binary, they could essentially range from -1 to 1 since they sample the sinusoid sum that was formed after inverse Fourier Transforming.
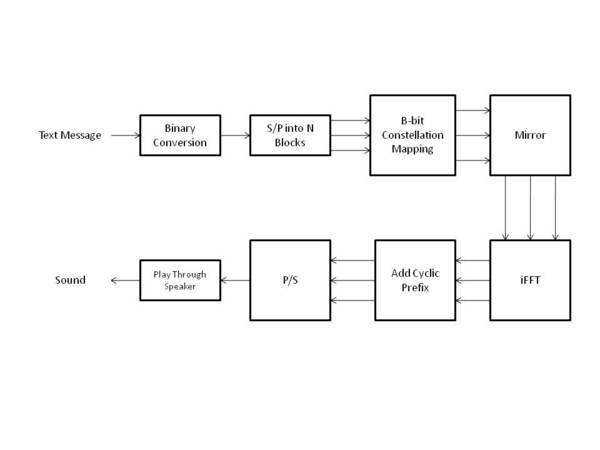
Please see the block diagram below. It summarizes the entire transmission process covered above.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Discrete multi-tone communication over acoustic channel' conversation and receive update notifications?