| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
REINFORCING, by using concrete and lintels over doors and window openings.
Stability
Structures are stabilized to prevent them from collapsing when forces or loads are put on them. To prevent a structure from falling down or collapsing we must try to make the internal forces bigger than the external forces under all conditions. How can you prevent a chair from collapsing when you sit on it? There are rails acting as ties at the bottom holding the legs together and preventing the legs from being pushed outwards.
A flagpole doesn’t need any supports under normal conditions. When the wind blows it can be supported by using guy ropes or ties that are flexible, but stop the poles from bending too far.
Different forces can act on different parts of a structure. Forces that structures have to stand up to are:
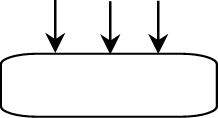

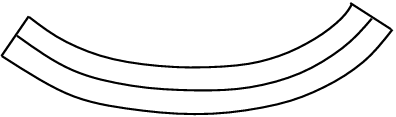

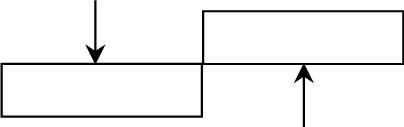
When one force is balanced by another they are said to be in EQUILIBRIUM.
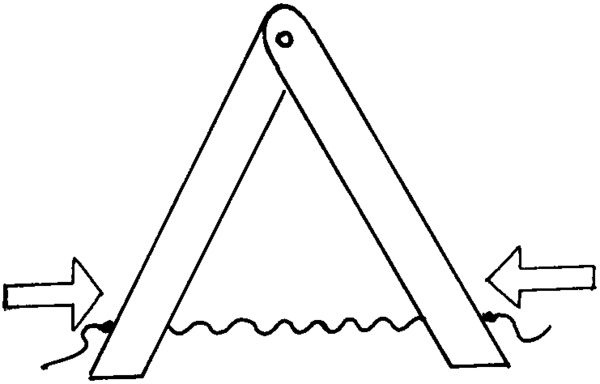
When you build a structure, you do not always have to use solid material like wood or metal. Flexible material, such as wire, can be used for parts of the structure which will only be stretched or in tension. Wire can be used in tension (being stretched), but not in compression (be squashed).
Load from the top of the structure keeps the wire in tension and the structure remains rigid.
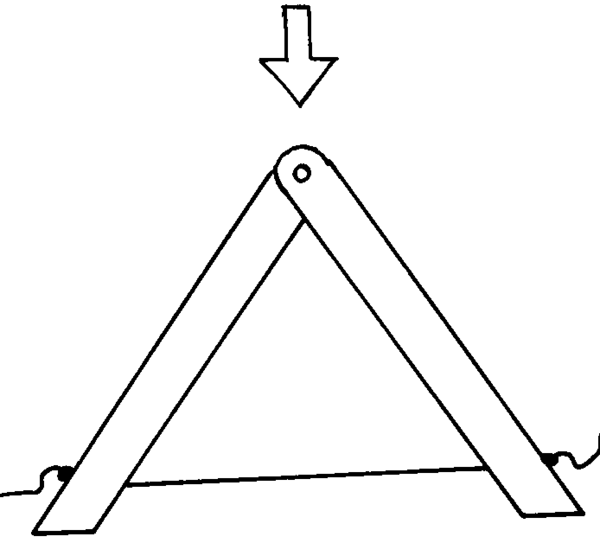
When the structure is loaded from the sides the wire is compressed (squashed) and it collapses. It is unstable.
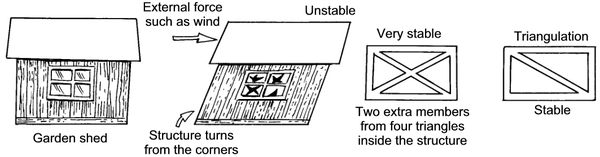
Triangles are very useful when building structures. They can help to make a very strong and rigid structure. To make a rectangle more stable is to put in two more members from corner to corner. Four triangles are formed. This way of making structures more stable is called TRIANGULATION. It is often used when building bridges or cranes. It is not always necessary to put in two members, one would be enough. The second extra member is called the redundant member. When designing structures it is easy to use more members that are really needed. They will only add more weight to the finished structure and make it more expensive.
By making the base size of a structure heavier or wider, you can also make it more stable.
Choice 1:
Design and make a horizontal structure using 25 paper straws and a glue gun. Your structure must support a marble as far out from the table as possible. Your structure must not come in contact with the floor or any of the other furniture in the room. It must support the marble for at least 30 seconds.
Choice 2:
Design and make a tower using 25 paper straws and a glue gun. Your tower must support a marble for at least 30 seconds as high as possible.
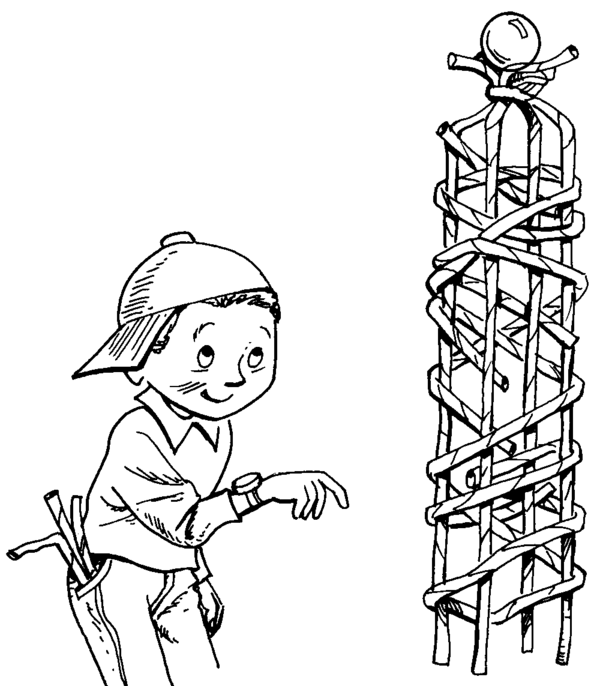

It is also important to get a structure’s centre of gravity so that it is able to balance. All objects have a point where they are held in balance by the force of gravity. This balancing point is called the centre of gravity, because it is the place where the whole weight of the object seems to centre. The balancing point of a rectangular shape, such as a square or a circle, is in the centre.
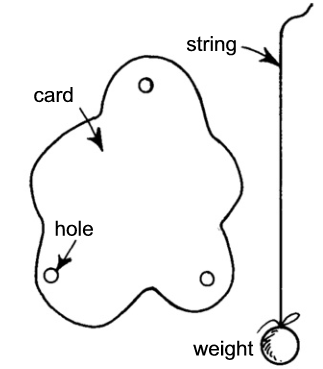
How can you find the balancing point of an irregular shape?
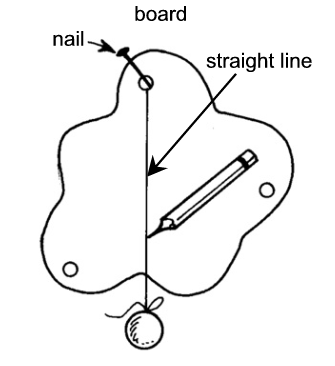
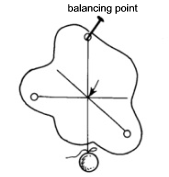
Where do you think is the best place for the heavy cargo to be stowed on a ship?
Gravity is the pull that objects have on other objects around them. Because the Earth itself is the largest object in our world, the pull of its gravity is the strongest we can feel. Gravity keeps everything resting on the ground. An object centre of gravity is found when it just balances on the edge of a table before it falls off.
Any object will balance on a pivot when its centre of gravity is low.
How can you change an object’s centre of gravity?

Requirements :
Method:

1. Colour in the man to make him more human in the front and back using felt tip pens. Carefully glue a drawing pin to the bottom of the card.
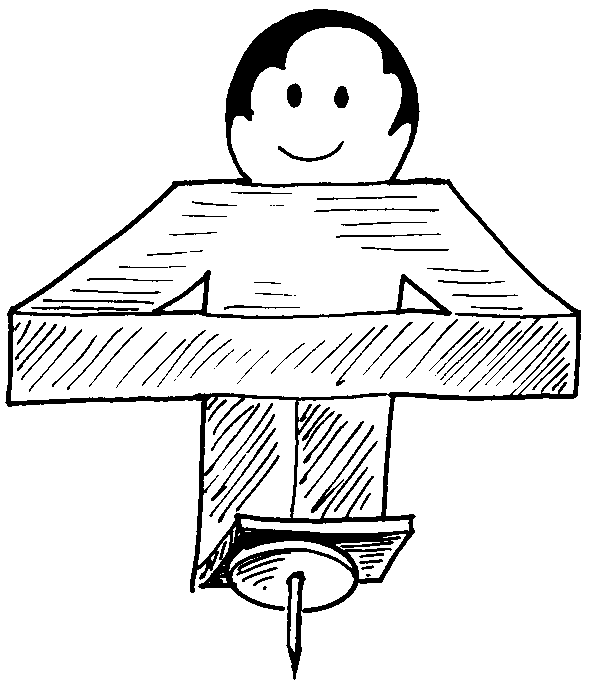
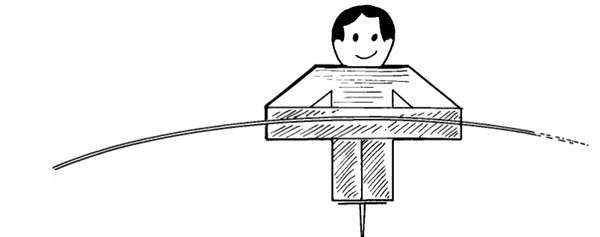
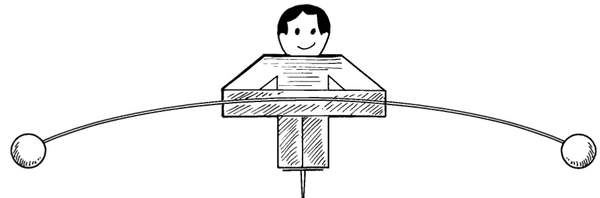
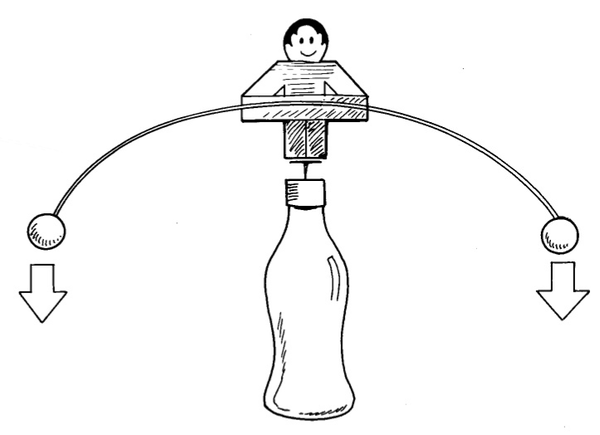
4. Carefully stand the balancing man on top of a bottle. He wobbles slightly, but should keep his balance.
JOINING TECHNIQUES
| Paper/card | Glue, paper clips, a stapler, paper fasteners, washers, string or yarn, tape, pins |
| Textile | Textile glue glues material onto material, PVA glue glues material to paper, card or wood, string , yarn, fasteners (buttons, velcro, zips, hooks and eyes, snap-fasteners, press-studs, strings, laces, ribbon) |
| Wood | Nails, pins, screws, woodglue, joints |
| Metal | Screws, bolts and nuts, soldering, glue, rivets |
| Plastic | Screws, glue |
| Assessment standards (ASs) |
| We know this when the learner: |
| structures: |
| 2.1 demonstrates knowledge and understanding of structures. |
| processing :2.2 demonstrates knowledge and understanding of how materials can be processed to change or improve properties (e.g. strength, fire resistance, waterproofing, taste, volume, texture). |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?