| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Material : Cassette and CD player with music. ( The Carnival of the Animals by the composer Saint-Saëns is a good choice.)
When the music starts to play the learners imitate the movements of certain animals.
As soon as the music stops the learners must “freeze” until the music resumes.
Each time that the music starts up again, the learner has to imitate a different animal.
Examples of animals and their movements:
The bear: crawling on all fours.
Trotting horses: the knees are lifted high.
Frog jumping: hop from haunches to arms.
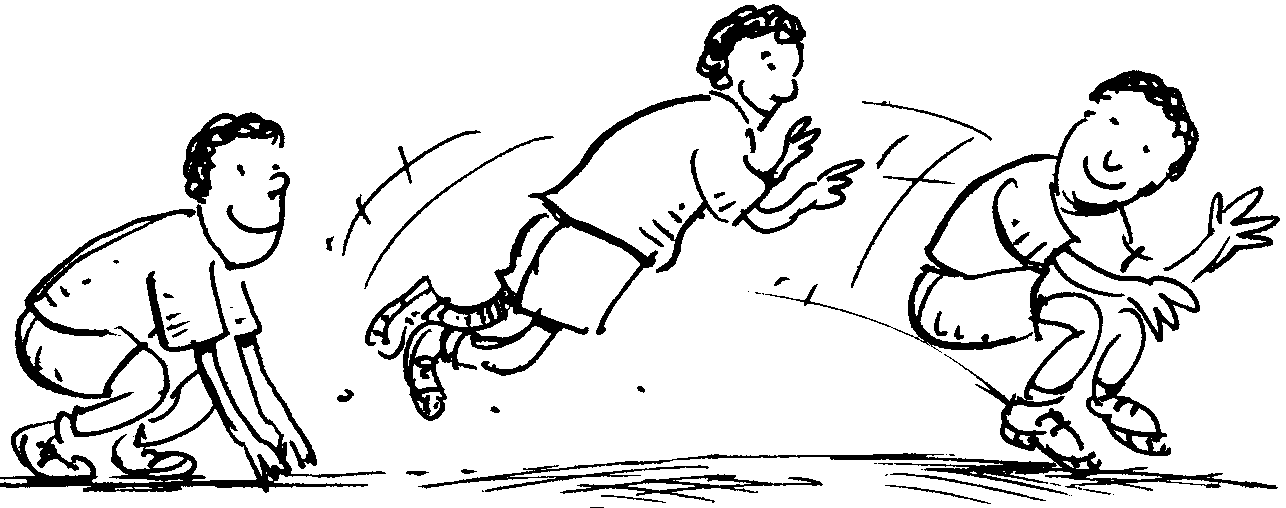
Flying birds: run about flapping the arms.
Rabbit hop: hop about on haunches without touching the ground with the hands.
Learners can be encouraged to create their own animals and movements.
At the end of the exercise the learners or the educator can select the learner who made the most interesting animal movements.
Material : Cassette and CD player with music. Any cheerful rhythmical music is suitable. Examples of slow and fast music can be alternated.

Encourage creative movements but stop uncontrolled wild movements that can cause injuries immediately.
The double crab position : Learner A stands on all fours in an inverted position (i.e. with the abdomen facing the sky) and learner B stands in the same position but with his/her feet on learner A’s knees and his/her hands on B’s shoulders.
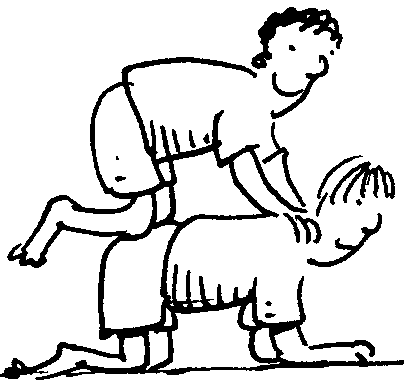
The double-decker bus position : Learner A stands on the ground on all fours and learner B on all fours with his/her knees on A’s back and his/her hands on learner A’s shoulders.
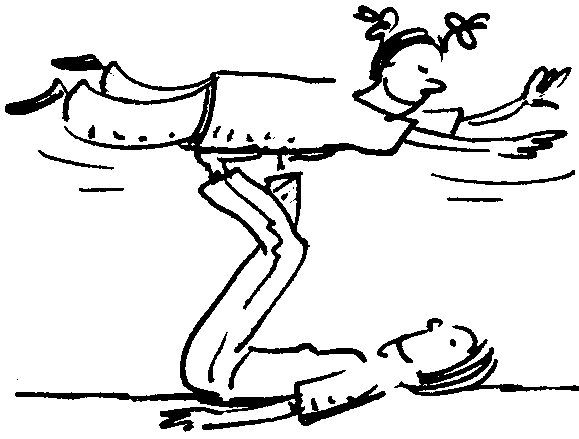
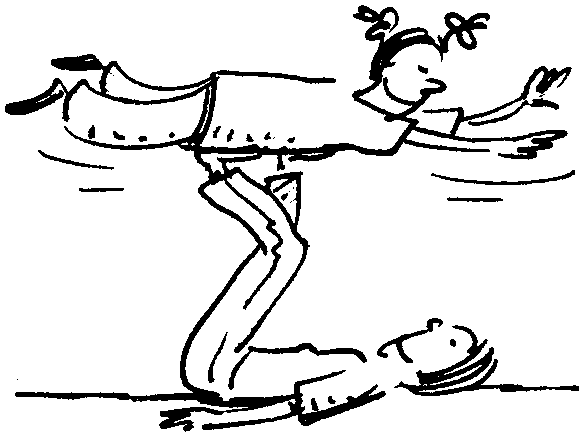
The helicopter position : Learner A lies on his back with his/her legs in the air. Learner B lies with his/her abdomen on learner A’s feet while stretching the body and with arms pointing forwards.

LEARNING OUTCOME 4: PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT AND MOVEMENT
The learner will be able to demonstrate an understanding of, and participate in, activities that promote movement and physical development.
Assessment Standard
We know this when the learner
4.2 demonstrates different ways to locomote, rotate, elevate and balance, using various parts of the body, with control.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Life orientation grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?