| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inleiding
Wat is ’n meganisme?
Aktiwiteit 1
| LU 1.2 | ||||
Meganismes en beweging
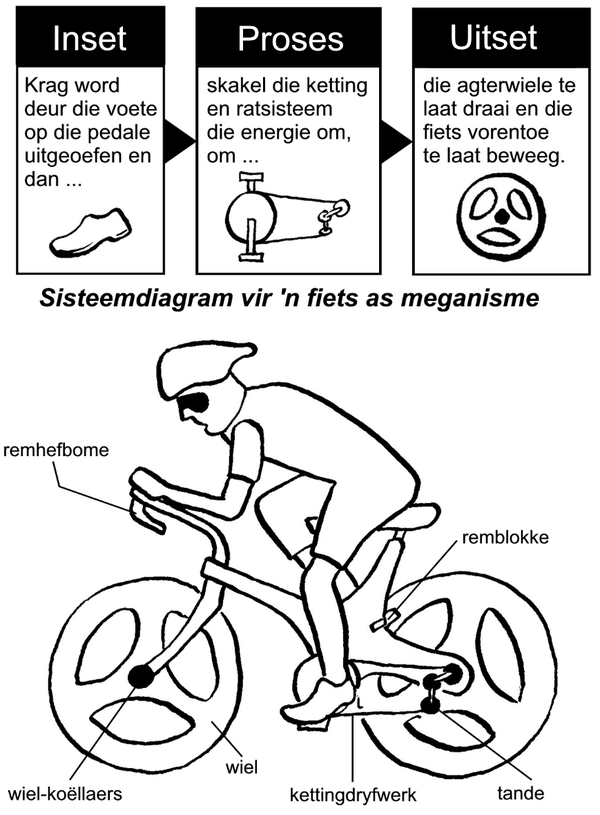
Aktiwiteit 2
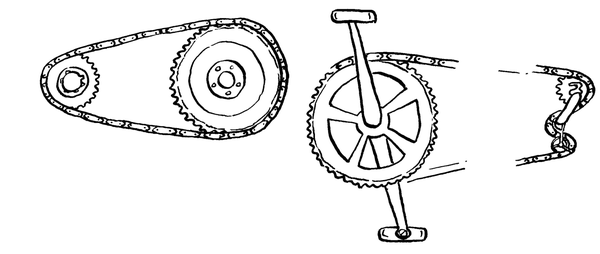
| LU 2.3 | ||||
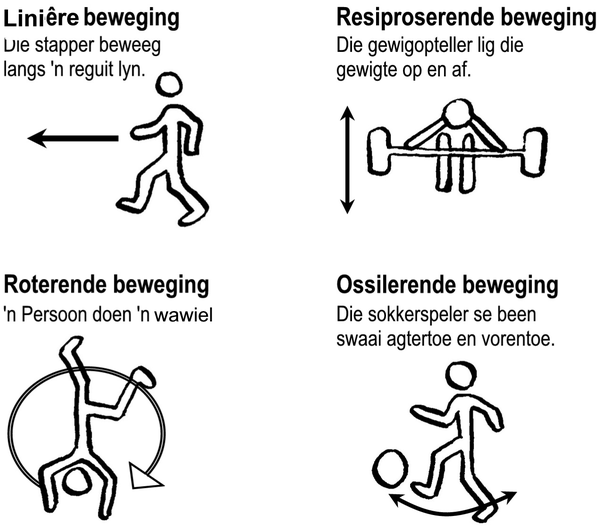
Aktiwiteit 3
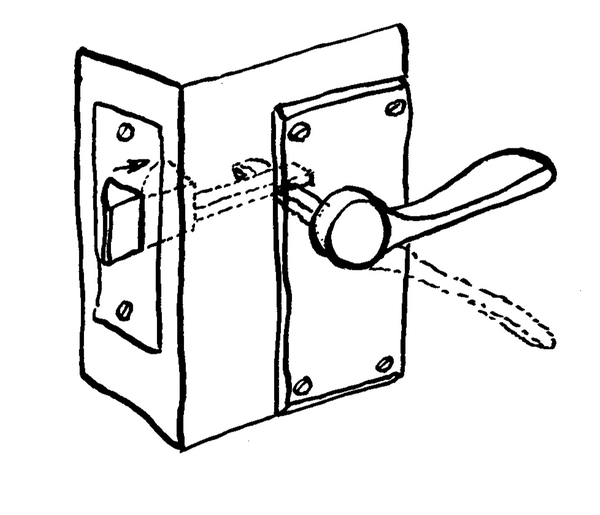
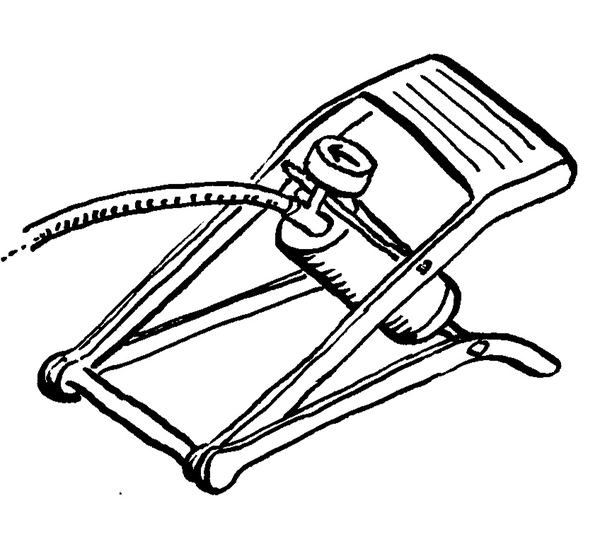
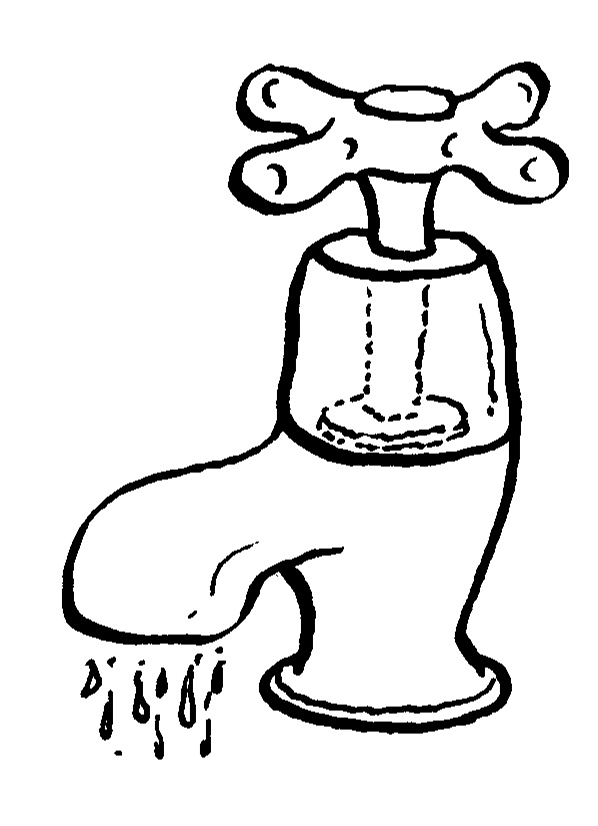
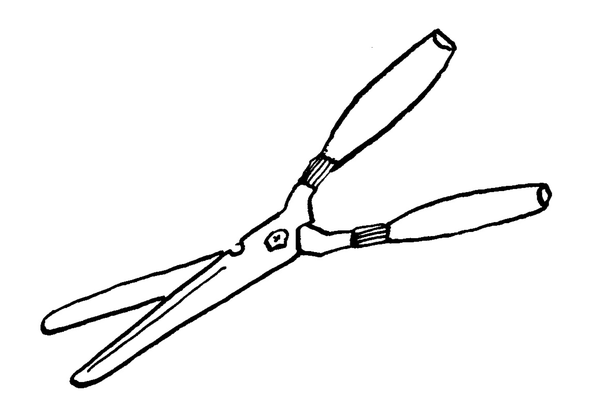
| LU 2.3 | ||||
Tipes meganismes
Meganismes word almal in masjinerie gebruik. Daar is vyf tipes meganismes:
Aktiwiteit 4
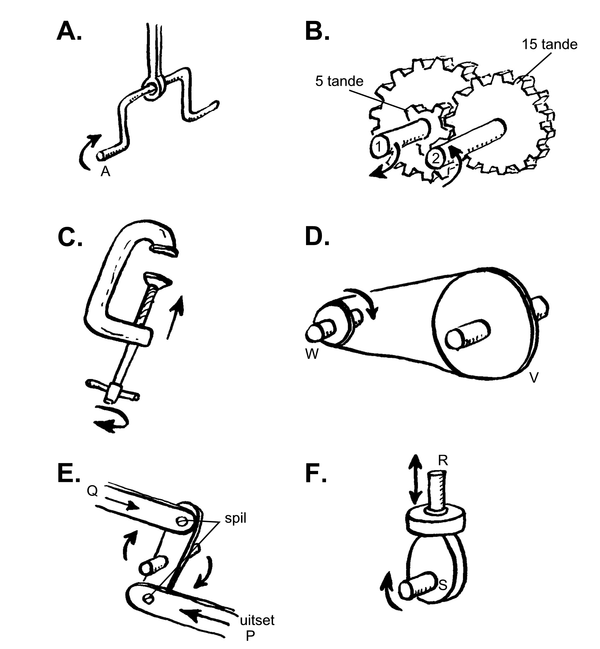
| LU 2.3 | ||||
| Leeruitkomstes(LUs) |
| LU 1 |
| TEGNOLOGIESE PROSESSE EN VAARDIGHEDE Die leerder is in staat om tegnologies prosesse en vaardighede eties en verantwoordelikheid toe te pas deur gepaste inligtings- en kommunikasietegnologie te gebruik. |
| Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder: |
ondersoek:
|
| LU 2 |
| TEGNOLOGIESE KENNIS EN BEGRIP Die leerder is in staat om relevante tegnologiese kennis te verstaan en dit eties en verantwoordelik toe te pas. |
| Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder: |
strukture:2.1 kennis en begrip toon van strukture:
|
stelsels en beheer:2.3 deur praktiese analise, kennis en begrip van interaktiewe meganiese sisteme en subsisteme demonstreer en sulke sisteme en subsisteme met diagrammatiese sisteemdiagramme voorstel:
|
AKTIWITEIT 1
AKTIWITEIT 2
AKTIWITEIT 3

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Tegnologie graad 9' conversation and receive update notifications?