| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Vermenigvuldig - 2×, 4×, 5× en 10× tot 10de veelvoud; (tafels)
Deel - ÷2, ÷4, ÷5 en ÷10 tot die 10de veelvoud. (tafels)
Integreer die ontwerp van die hoedjie (p. 16) en die geskenkpapier (bl. 24) met Tegnologie. Dit kan ook met die hele klas gelyktydig gedoen word.
Met die talle berekeninge met geld en ander hoeveelhede wat die leerders moet doen, behoort hulle bewus te wees van die feit dat Wiskunde ons daagliks omring.
5 ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 50
50 ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 5
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | |
| tiene | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
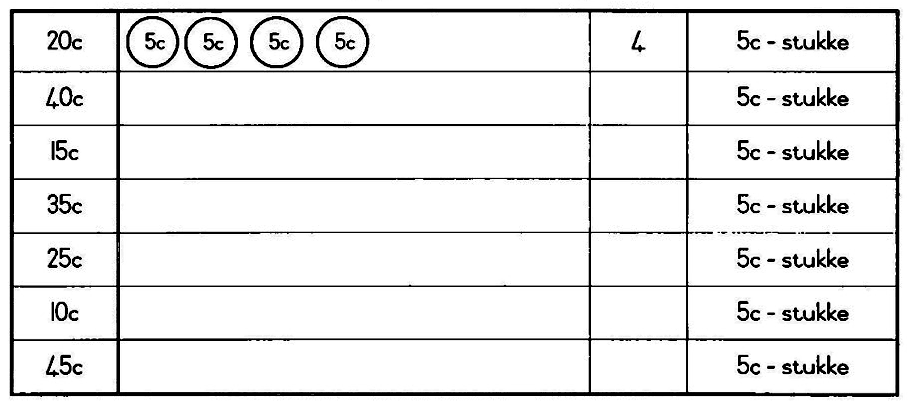
| vywe | 2 | 4 |
Bonnie en Tommie sê:
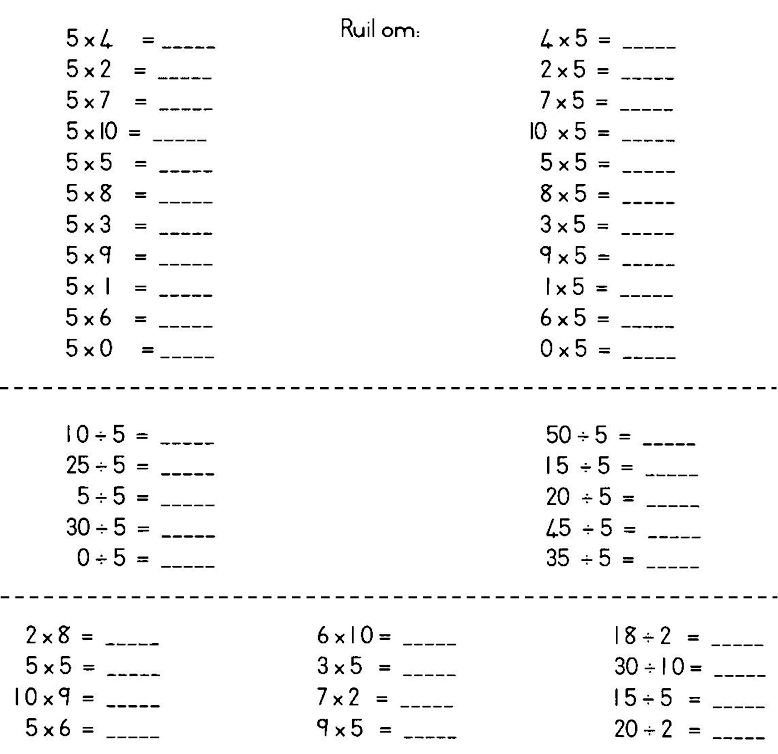
Dit is maklik om met 1c -, 2c -, 5c - en 10c - stukke te werk.
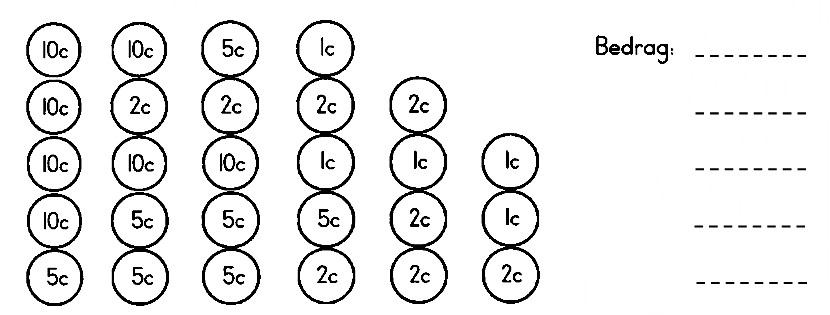
| 16c | __________________________________________________________ |
| 47c | __________________________________________________________ |
| 4c | __________________________________________________________ |
| 63c | __________________________________________________________ |
| 39c | __________________________________________________________ |
| 28c | __________________________________________________________ |
| R1 = 100c | |||||||||||||||||||
| 50c | 50c | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20c | 20c | 20c | 20c | 20c | |||||||||||||||
| 10c | 10c | 10c | 10c | 10c | 10c | 10c | 10c | 10c | 10c | ||||||||||
| 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c | 5c |
| R1 - stukke | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 50c - stukke | 2 | 4 |
| R1 - stukke | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 10c - stukke | 10 | 20 | 30 |
Sy het 'n _____ - stuk gekry.
Hy het _____ 50c - stukke gekry.
Sy het 2 ____ - stukke gekry.
Wie weet?
R1 = _____c R2 = _____c R3 = _____c
R4 = _____c R5 = _____c R10 = _____c
| R45 + R23 = __________ | R60 + R28 = __________ |
| R28 + R52 = __________ | R39 + R16 + R20 = __________ |
| 48c - 15c = __________ | 96c - 50c = __________ |
| 80c - 27c = __________ | 94c - 30c - 16c = __________ |
50c + 50c + 50c + 50c + 50c + 50c + 50c = __________
1. Bonnie het 3 sjokolades gekoop. Elkeen het 31c gekos. Hoeveel het sy daarvoor betaal?
Sy het_________________________________.
Hoeveel kleingeld het sy gekry as sy met 'n R1-stuk betaal het?
Sy het__________________________________.
2. Tommie het 5 sakkies albasters gekoop. Elke sakkie het R2,10 gekos. Hoeveel het hy vir alles saam betaal?
Hy het__________________________________.
Hy het R12 gegee. Hoeveel kleingeld het hy gekry?
Hy het__________________________________.
3. Bonnie wil graag vir haar 'n pen koop. Die pen kos R13 en sy het net R10,80 in haar beursie. Hoeveel het sy te min?
Sy het__________________________________.
4. Tommie koop elke dag vir hom 'n roomys wat R2 kos. Hy het nog R14 in sy beursie. Vir hoeveel dae kan hy nog elke dag 'n roomys koop?
Hy kan_________________________________.
5. Mamma het vir Tommie en Bonnie R65 gegee wat hulle gelykop tussen hulle moes verdeel. Hoeveel het elkeen gekry?
Elkeen het________________________________.
6. Hoeveel c in:
R1,67 = ______c R2,99 = ______c R3,06 = ______c
R1,20 + R1,15 = ______c R0,55 + R4,10 = ______c
7. Maak elke bedrag R1,50 meer:
R20,20_______________ R29, 49__________________
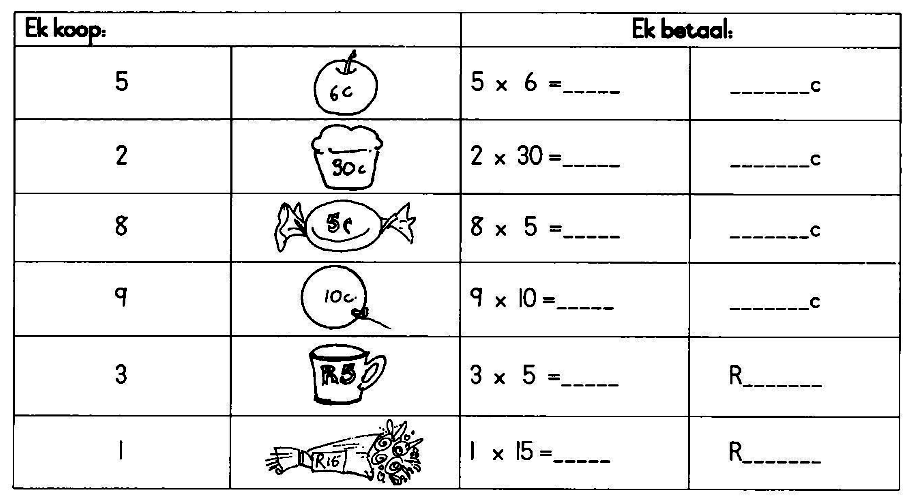
| Koop vir: | Betaal met: | Kleingeld: |
| 35c | 50c | ____________________ |
| 79c | 90c | ____________________ |
| R75 | R100 | ____________________ |
partytjie kan nooi.
1. Hoeveel kinders sal hulle dan altesaam wees?
Hulle sal ______ kinders wees. (Maak seker dat jou antwoord reg is.)
2. Bereken hoeveel van alles gekoop moet word en wat dit sal kos.

Leeruitkomste 1: Die leerder is in staat om getalle en die verwantskappe daarvan te herken, te beskryf en voor te stel, en om tydens probleemoplossing bevoeg en met selfvertroue te tel, te skat, te bereken en te kontroleer.
Assesseringstandaard 1.1: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder aan en terug tel in:
1.1.1 die intervalle aangedui vir graad 2 met toenemende getalomvang;
Assesseringstandaard 1.6: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder geldprobleme oplos wat totale en kleingeld in rand en sent behels, insluitend herleiding tussen rand en sent;
Assesseringstandaard 1.8: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder die gepaste simbole in berekeninge kan gebruik om probleme wat die volgende behels;
Assesseringstandaard 1.9: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder hoofberekeninge uitvoer
Leeruitkomste 2: Die leerder is in staat om patrone en verwantskappe te herken, te beskryf en voor te stel en probleme op te los deur algebraïese taal en vaardighede te gebruik.
Assesseringstandaard 2.2: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder eenvoudige getalreekse tot minstens 1 000 kopieer en uitbrei.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wiskunde graad 3' conversation and receive update notifications?