| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. How much do you still remember of what you learnt about fractions in Gr. 4? Let us start with a competition – girls against boys! Take turns and see if you can answer the following questions. Your educator will tell you who must answer first and will also award points (2 points for every correct answer and 5 points if the boys can answer a question that the girls can’t, and vice versa).
1.1 What is a fraction?
1.2 If I write what do I call the 2?
1.3 What operation sign can replace the — in ?
1.4 What is the function of the denominator?
1.5 If I cut up a whole into more and more sections, each section becomes ______
1.6 What do I call the 7 in ?
1.7 Fractions of the same size are called _____ fractions.
1.8 The fewer the number of sections the whole is divided into, the _____they are.
1.9 What is the function of the numerator?
1.10 How do we simplify our fractions?
LET US REVISE
A fraction is an equal part of a whole.
Four-fifths
4: Counts how many equal parts I am working with and is called the numerator.
5: The denominator says how many equal parts the whole has been divided into.
2. Let us test your knowledge by means of a few practical activities. Look at the following and answer the questions:
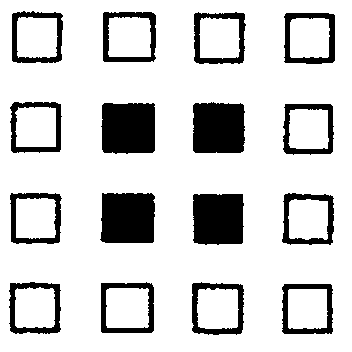
2.1 Colour in the figures that show halves:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
2.2 Colour in only the figures that show quarters:
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e)
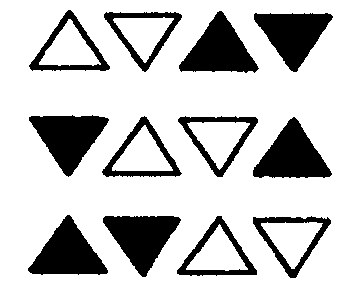
2.3 Neatly colour in the figures that show sixths:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
2.4 Why didn’t you colour in the other figure c ?
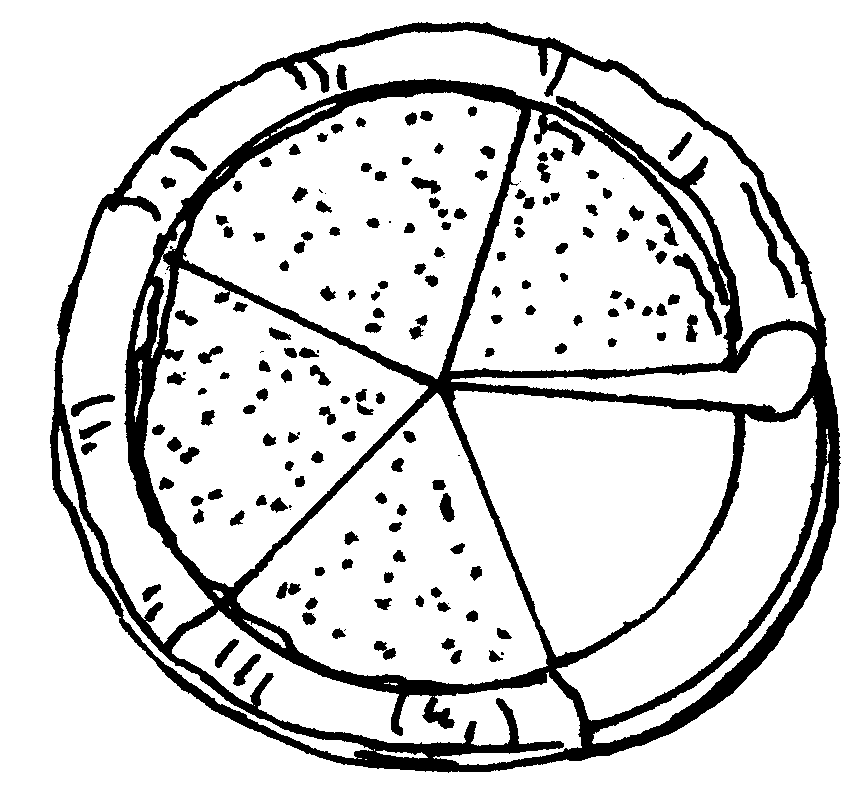
2.5 What fraction is cut out in each of the following figures?
i) ii) iii) iv) v) vi)
vii) viii) ix) x) xi)
A.
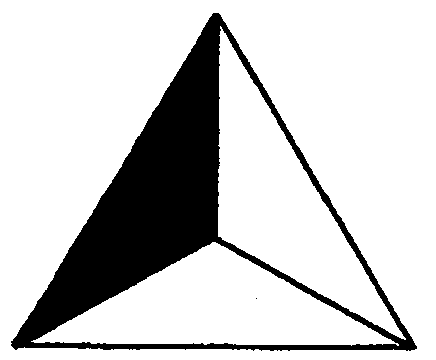
B.
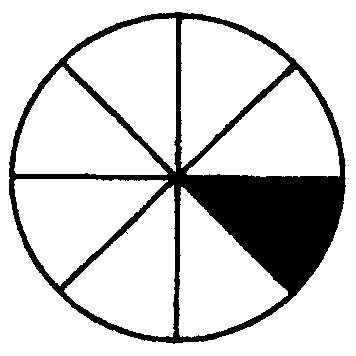
C.
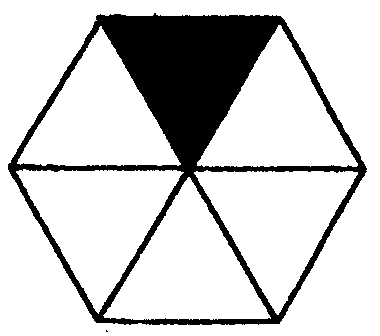
D.
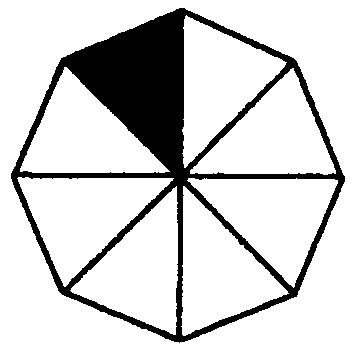
E.

F.
G.
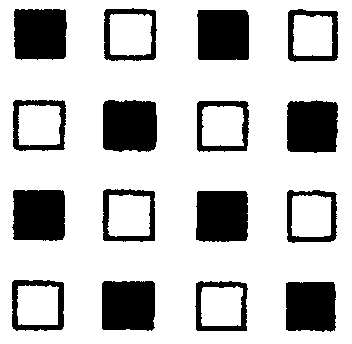
H.
I.
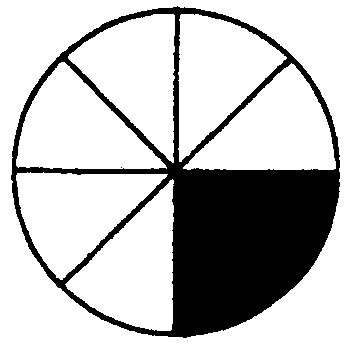
J.
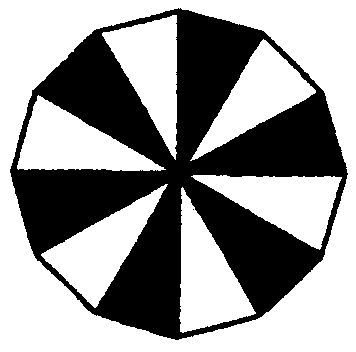
K.
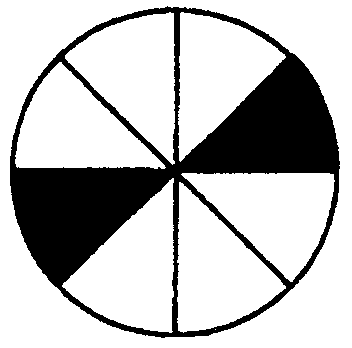
| Diagram | Number of equal parts | Number of parts coloured in | Fraction coloured in | Number of parts not coloured in | Fraction not coloured in | |
| E.g. | A | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||
| B | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| C | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| D | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| E | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| F | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| G | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| H | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| I | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| J | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | |
| K | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... | ..................... |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?