| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A wave is an oscillation or periodic movement that can transport energy from one point in space to another. Common examples of waves are all around us. Shaking the end of a rope transfers energy from your hand to the other end of the rope, dropping a pebble into a pond causes waves to ripple outward along the water's surface, and the expansion of air that accompanies a lightning strike generates sound waves (thunder) that can travel outward for several miles. In each of these cases, kinetic energy is transferred through matter (the rope, water, or air) while the matter remains essentially in place. An insightful example of a wave occurs in sports stadiums when fans in a narrow region of seats rise simultaneously and stand with their arms raised up for a few seconds before sitting down again while the fans in neighboring sections likewise stand up and sit down in sequence. While this wave can quickly encircle a large stadium in a few seconds, none of the fans actually travel with the wave-they all stay in or above their seats.
Waves need not be restricted to travel through matter. As Maxwell showed, electromagnetic waves consist of an electric field oscillating in step with a perpendicular magnetic field, both of which are perpendicular to the direction of travel. These waves can travel through a vacuum at a constant speed of 2.998 10 8 m/s, the speed of light (denoted by c ).
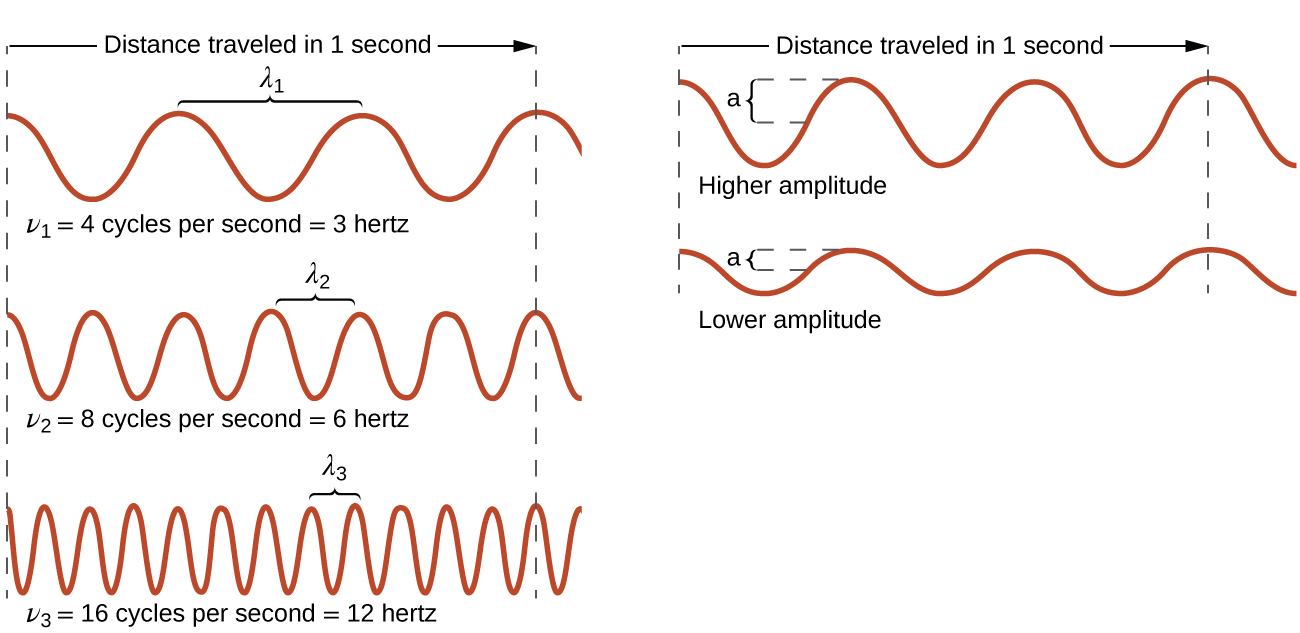
All waves, including forms of electromagnetic radiation, are characterized by, a wavelength (denoted by λ , the lowercase Greek letter lambda), a frequency (denoted by ν , the lowercase Greek letter nu), and an amplitude . As can be seen in [link] , the wavelength is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs in a wave (measured in meters in the SI system). Electromagnetic waves have wavelengths that fall within an enormous range-wavelengths of kilometers (10 3 m) to picometers (10 −12 m) have been observed. The frequency is the number of wave cycles that pass a specified point in space in a specified amount of time (in the SI system, this is measured in seconds). A cycle corresponds to one complete wavelength. The unit for frequency, expressed as cycles per second [s −1 ], is the hertz (Hz) . Common multiples of this unit are megahertz, (1 MHz = 1 10 6 Hz) and gigahertz (1 GHz = 1 10 9 Hz). The amplitude corresponds to the magnitude of the wave's displacement and so, in [link] , this corresponds to one-half the height between the peaks and troughs. The amplitude is related to the intensity of the wave, which for light is the brightness, and for sound is the loudness.
The product of a wave's wavelength ( λ ) and its frequency ( ν ), λν , is the speed of the wave. Thus, for electromagnetic radiation in a vacuum:
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional: As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases. The inverse proportionality is illustrated in [link] . This figure also shows the electromagnetic spectrum , the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation. Each of the various colors of visible light has specific frequencies and wavelengths associated with them, and you can see that visible light makes up only a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Because the technologies developed to work in various parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are different, for reasons of convenience and historical legacies, different units are typically used for different parts of the spectrum. For example, radio waves are usually specified as frequencies (typically in units of MHz), while the visible region is usually specified in wavelengths (typically in units of nm or angstroms).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?