| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
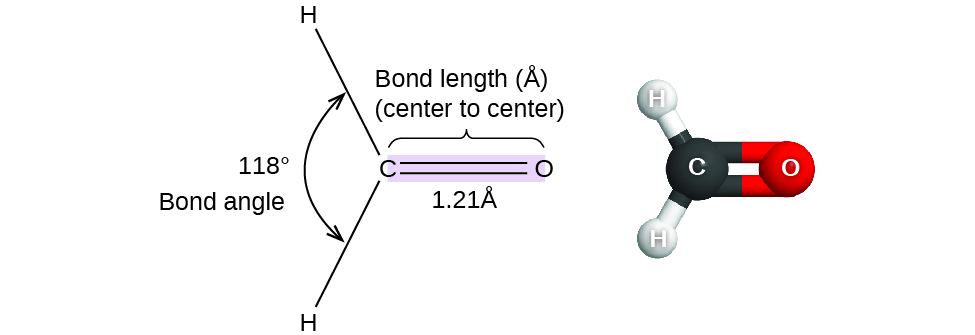
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space ( [link] ). A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees. A bond distance (or bond length) is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms along the straight line joining the nuclei. Bond distances are measured in Ångstroms (1 Å = 10 –10 m) or picometers (1 pm = 10 –12 m, 100 pm = 1 Å).
Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure. The VSEPR model assumes that electron pairs in the valence shell of a central atom will adopt an arrangement that minimizes repulsions between these electron pairs by maximizing the distance between them. The electrons in the valence shell of a central atom form either bonding pairs of electrons, located primarily between bonded atoms, or lone pairs. The electrostatic repulsion of these electrons is reduced when the various regions of high electron density assume positions as far from each other as possible.
VSEPR theory predicts the arrangement of electron pairs around each central atom and, usually, the correct arrangement of atoms in a molecule. We should understand, however, that the theory only considers electron-pair repulsions. Other interactions, such as nuclear-nuclear repulsions and nuclear-electron attractions, are also involved in the final arrangement that atoms adopt in a particular molecular structure.
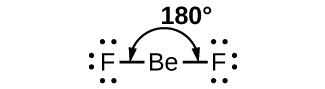
As a simple example of VSEPR theory, let us predict the structure of a gaseous BeF 2 molecule. The Lewis structure of BeF 2 ( [link] ) shows only two electron pairs around the central beryllium atom. With two bonds and no lone pairs of electrons on the central atom, the bonds are as far apart as possible, and the electrostatic repulsion between these regions of high electron density is reduced to a minimum when they are on opposite sides of the central atom. The bond angle is 180° ( [link] ).
[link] illustrates this and other electron-pair geometries that minimize the repulsions among regions of high electron density (bonds and/or lone pairs). Two regions of electron density around a central atom in a molecule form a linear geometry; three regions form a trigonal planar geometry; four regions form a tetrahedral geometry; five regions form a trigonal bipyramidal geometry; and six regions form an octahedral geometry.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?