| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
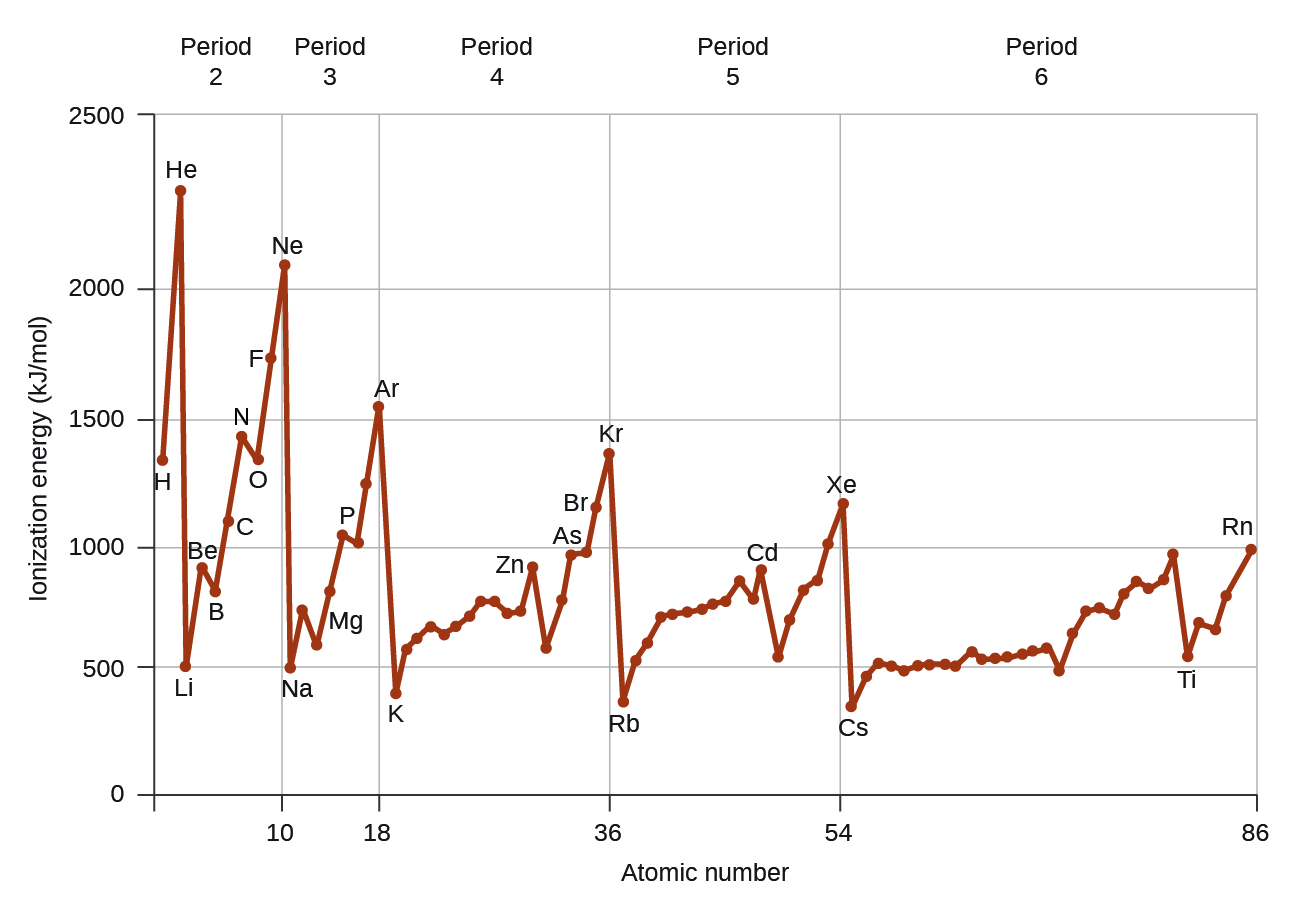
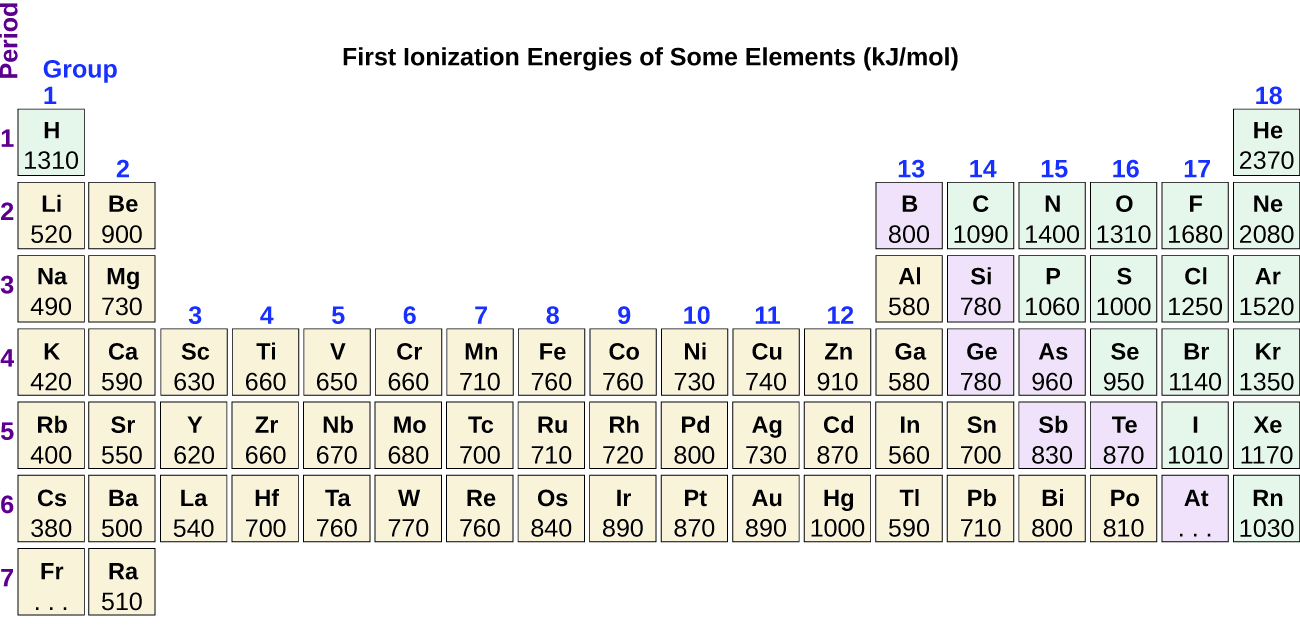
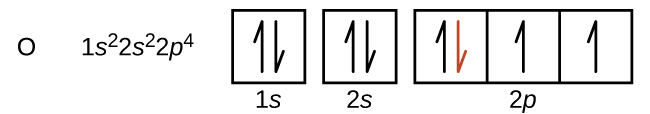
Another deviation occurs as orbitals become more than one-half filled. The first ionization energy for oxygen is slightly less than that for nitrogen, despite the trend in increasing IE 1 values across a period. Looking at the orbital diagram of oxygen, we can see that removing one electron will eliminate the electron–electron repulsion caused by pairing the electrons in the 2 p orbital and will result in a half-filled orbital (which is energetically favorable). Analogous changes occur in succeeding periods (note the dip for sulfur after phosphorus in [link] ).
Removing an electron from a cation is more difficult than removing an electron from a neutral atom because of the greater electrostatic attraction to the cation. Likewise, removing an electron from a cation with a higher positive charge is more difficult than removing an electron from an ion with a lower charge. Thus, successive ionization energies for one element always increase. As seen in [link] , there is a large increase in the ionization energies (color change) for each element. This jump corresponds to removal of the core electrons, which are harder to remove than the valence electrons. For example, Sc and Ga both have three valence electrons, so the rapid increase in ionization energy occurs after the third ionization.
| Successive Ionization Energies for Selected Elements (kJ/mol) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | IE 1 | IE 2 | IE 3 | IE 4 | IE 5 | IE 6 | IE 7 |
| K | 418.8 | 3051.8 | 4419.6 | 5876.9 | 7975.5 | 9590.6 | 11343 |
| Ca | 589.8 | 1145.4 | 4912.4 | 6490.6 | 8153.0 | 10495.7 | 12272.9 |
| Sc | 633.1 | 1235.0 | 2388.7 | 7090.6 | 8842.9 | 10679.0 | 13315.0 |
| Ga | 578.8 | 1979.4 | 2964.6 | 6180 | 8298.7 | 10873.9 | 13594.8 |
| Ge | 762.2 | 1537.5 | 3302.1 | 4410.6 | 9021.4 | Not available | Not available |
| As | 944.5 | 1793.6 | 2735.5 | 4836.8 | 6042.9 | 12311.5 | Not available |
Ba
The electron affinity [EA] is the energy change for the process of adding an electron to a gaseous atom to form an anion (negative ion).
This process can be either endothermic or exothermic, depending on the element. The EA of some of the elements is given in [link] . You can see that many of these elements have negative values of EA, which means that energy is released when the gaseous atom accepts an electron. However, for some elements, energy is required for the atom to become negatively charged and the value of their EA is positive. Just as with ionization energy, subsequent EA values are associated with forming ions with more charge. The second EA is the energy associated with adding an electron to an anion to form a –2 ion, and so on.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?