| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
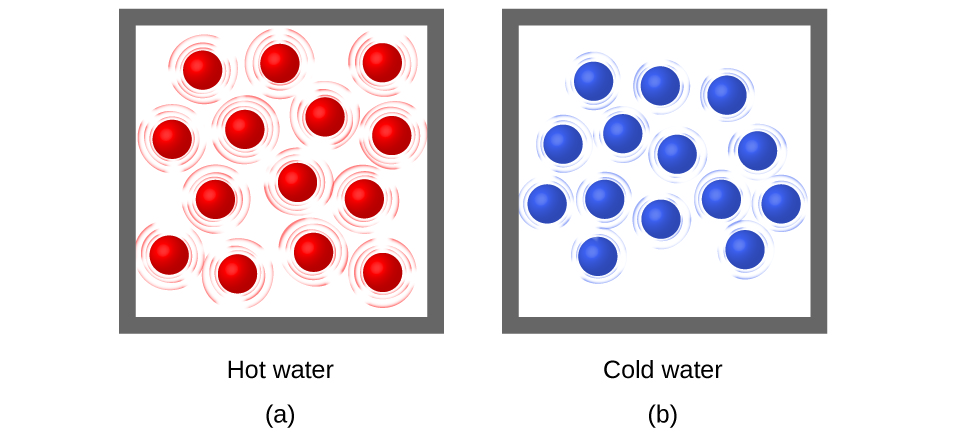
Thermal energy is kinetic energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules. Temperature is a quantitative measure of “hot” or “cold.” When the atoms and molecules in an object are moving or vibrating quickly, they have a higher average kinetic energy (KE), and we say that the object is “hot.” When the atoms and molecules are moving slowly, they have lower KE, and we say that the object is “cold” ( [link] ). Assuming that no chemical reaction or phase change (such as melting or vaporizing) occurs, increasing the amount of thermal energy in a sample of matter will cause its temperature to increase. And, assuming that no chemical reaction or phase change (such as condensation or freezing) occurs, decreasing the amount of thermal energy in a sample of matter will cause its temperature to decrease.

Click on this interactive simulation to view the effects of temperature on molecular motion.
Most substances expand as their temperature increases and contract as their temperature decreases. This property can be used to measure temperature changes, as shown in [link] . The operation of many thermometers depends on the expansion and contraction of substances in response to temperature changes.
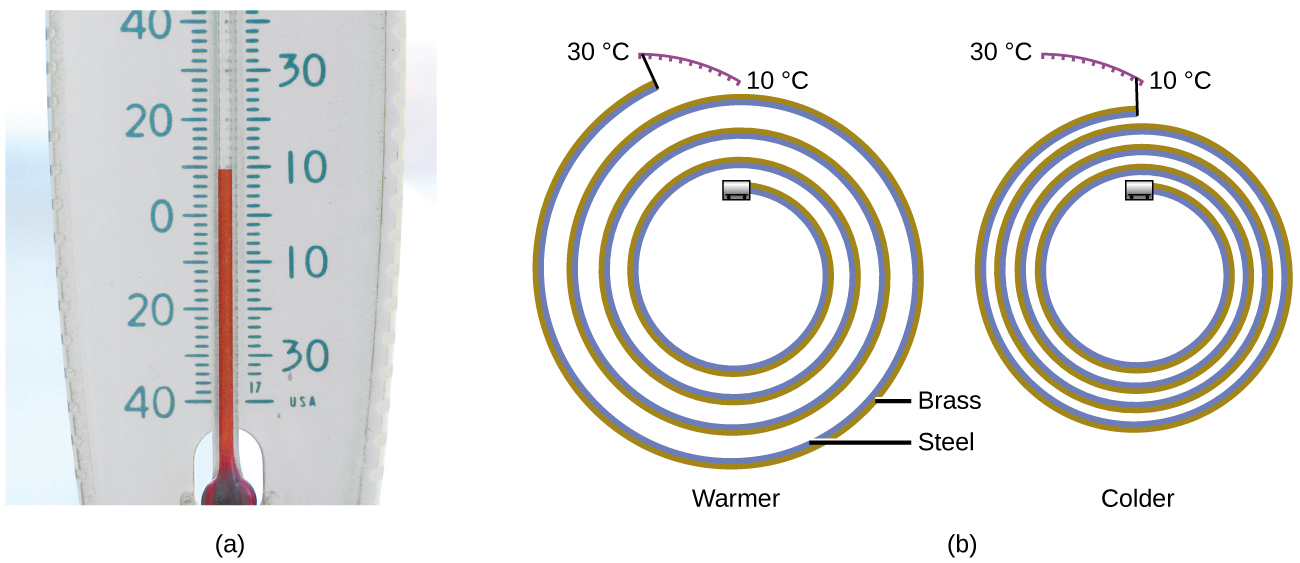

The following demonstration allows one to view the effects of heating and cooling a coiled bimetallic strip.
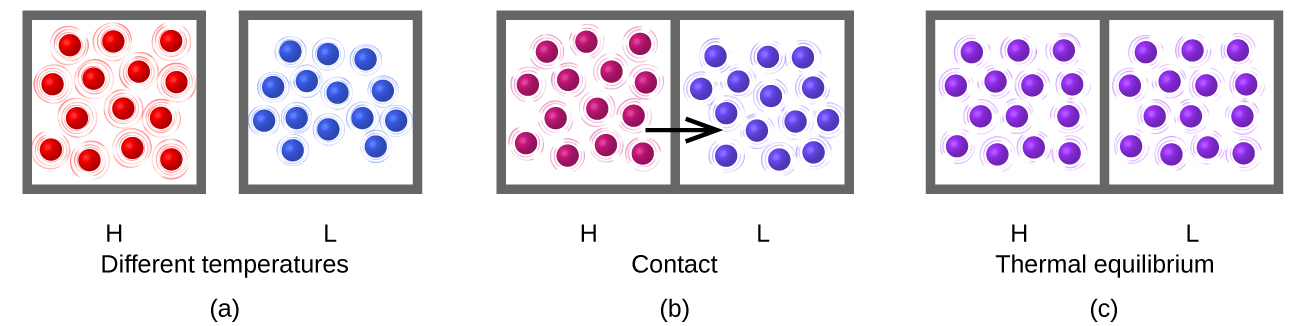
Heat ( q ) is the transfer of thermal energy between two bodies at different temperatures. Heat flow (a redundant term, but one commonly used) increases the thermal energy of one body and decreases the thermal energy of the other. Suppose we initially have a high temperature (and high thermal energy) substance (H) and a low temperature (and low thermal energy) substance (L). The atoms and molecules in H have a higher average KE than those in L. If we place substance H in contact with substance L, the thermal energy will flow spontaneously from substance H to substance L. The temperature of substance H will decrease, as will the average KE of its molecules; the temperature of substance L will increase, along with the average KE of its molecules. Heat flow will continue until the two substances are at the same temperature ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?