| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The molecular structure of water is consistent with a tetrahedral arrangement of two lone pairs and two bonding pairs of electrons. Thus we say that the oxygen atom is sp 3 hybridized, with two of the hybrid orbitals occupied by lone pairs and two by bonding pairs. Since lone pairs occupy more space than bonding pairs, structures that contain lone pairs have bond angles slightly distorted from the ideal. Perfect tetrahedra have angles of 109.5°, but the observed angles in ammonia (107.3°) and water (104.5°) are slightly smaller. Other examples of sp 3 hybridization include CCl 4 , PCl 3 , and NCl 3 .
To describe the five bonding orbitals in a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement, we must use five of the valence shell atomic orbitals (the s orbital, the three p orbitals, and one of the d orbitals), which gives five sp 3 d hybrid orbitals . With an octahedral arrangement of six hybrid orbitals, we must use six valence shell atomic orbitals (the s orbital, the three p orbitals, and two of the d orbitals in its valence shell), which gives six sp 3 d 2 hybrid orbitals . These hybridizations are only possible for atoms that have d orbitals in their valence subshells (that is, not those in the first or second period).
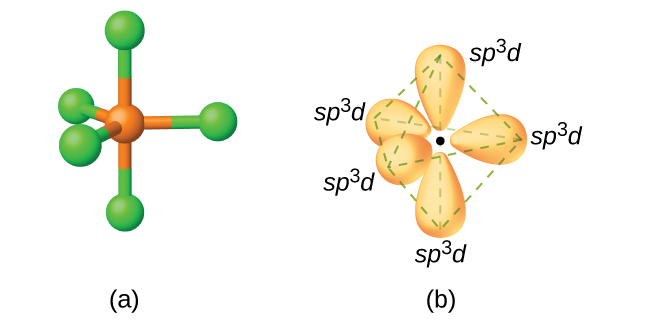
In a molecule of phosphorus pentachloride, PCl 5 , there are five P–Cl bonds (thus five pairs of valence electrons around the phosphorus atom) directed toward the corners of a trigonal bipyramid. We use the 3 s orbital, the three 3 p orbitals, and one of the 3 d orbitals to form the set of five sp 3 d hybrid orbitals ( [link] ) that are involved in the P–Cl bonds. Other atoms that exhibit sp 3 d hybridization include the sulfur atom in SF 4 and the chlorine atoms in ClF 3 and in (The electrons on fluorine atoms are omitted for clarity.)
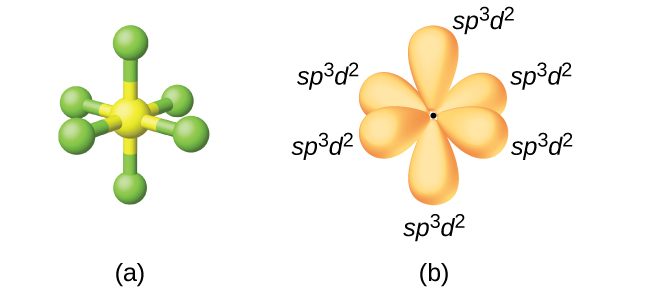
The sulfur atom in sulfur hexafluoride, SF 6 , exhibits sp 3 d 2 hybridization. A molecule of sulfur hexafluoride has six bonding pairs of electrons connecting six fluorine atoms to a single sulfur atom. There are no lone pairs of electrons on the central atom. To bond six fluorine atoms, the 3 s orbital, the three 3 p orbitals, and two of the 3 d orbitals form six equivalent sp 3 d 2 hybrid orbitals, each directed toward a different corner of an octahedron. Other atoms that exhibit sp 3 d 2 hybridization include the phosphorus atom in the iodine atom in the interhalogens IF 5 , and the xenon atom in XeF 4 .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?