| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
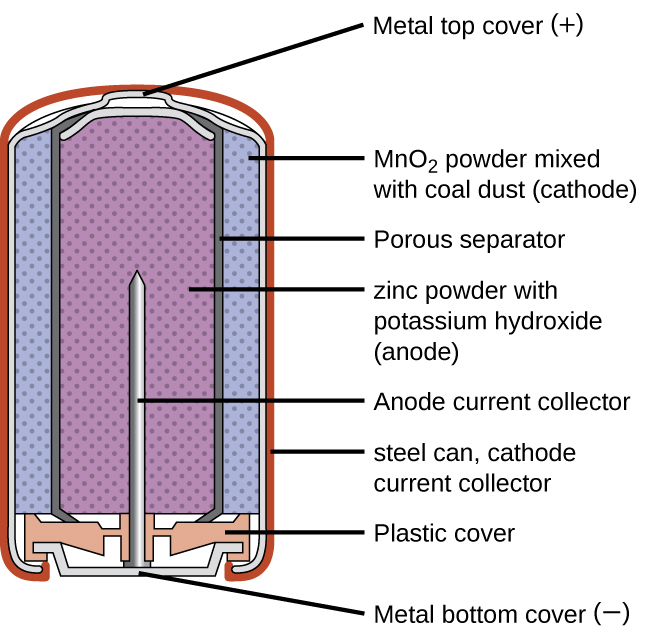
An alkaline battery can deliver about three to five times the energy of a zinc-carbon dry cell of similar size. Alkaline batteries are prone to leaking potassium hydroxide, so these should also be removed from devices for long-term storage. While some alkaline batteries are rechargeable, most are not. Attempts to recharge an alkaline battery that is not rechargeable often leads to rupture of the battery and leakage of the potassium hydroxide electrolyte.
Visit this site to learn more about alkaline batteries.
Secondary batteries are rechargeable. These are the types of batteries found in devices such as smartphones, electronic tablets, and automobiles.
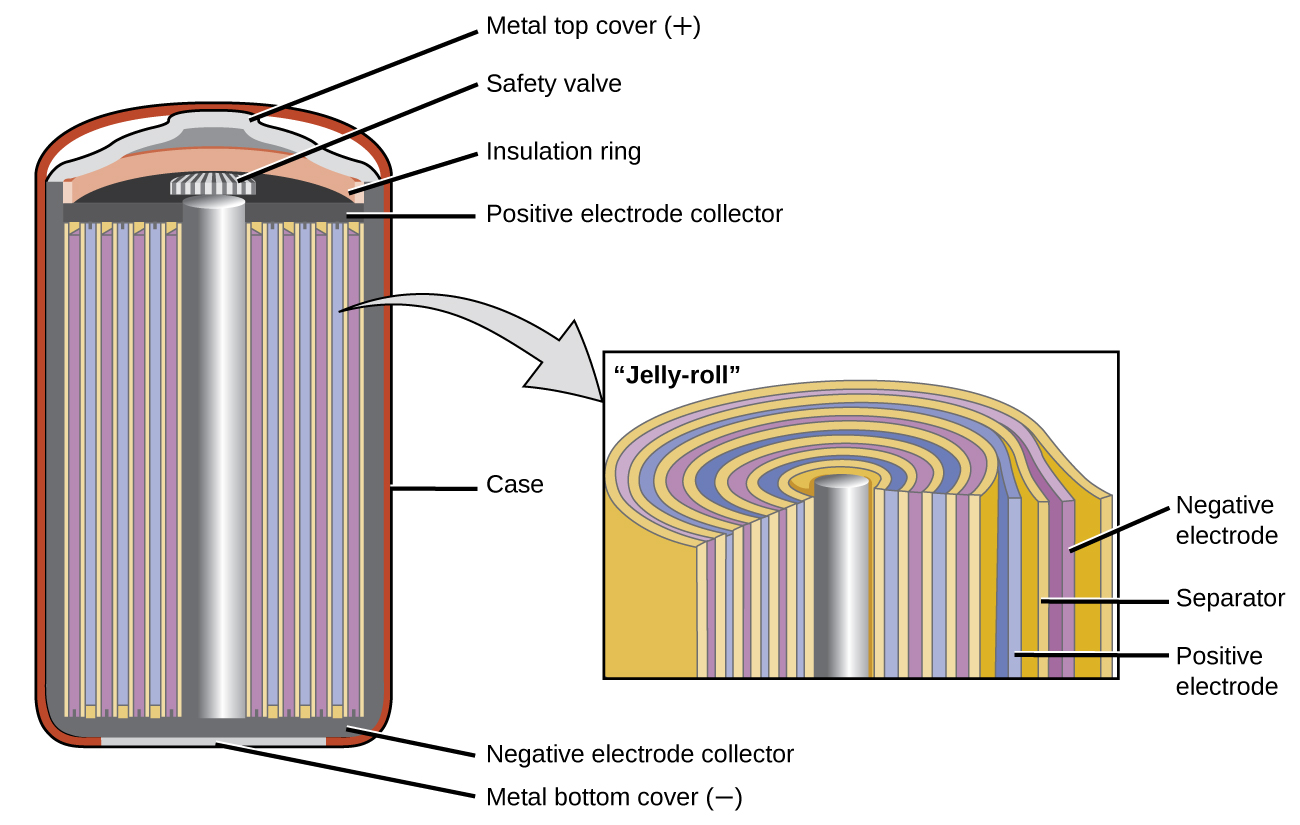
Nickel-cadmium , or NiCd, batteries ( [link] ) consist of a nickel-plated cathode, cadmium-plated anode, and a potassium hydroxide electrode. The positive and negative plates, which are prevented from shorting by the separator, are rolled together and put into the case. This is a “jelly-roll” design and allows the NiCd cell to deliver much more current than a similar-sized alkaline battery. The reactions are
The voltage is about 1.2 V to 1.25 V as the battery discharges. When properly treated, a NiCd battery can be recharged about 1000 times. Cadmium is a toxic heavy metal so NiCd batteries should never be opened or put into the regular trash.
Visit this site for more information about nickel cadmium rechargeable batteries.
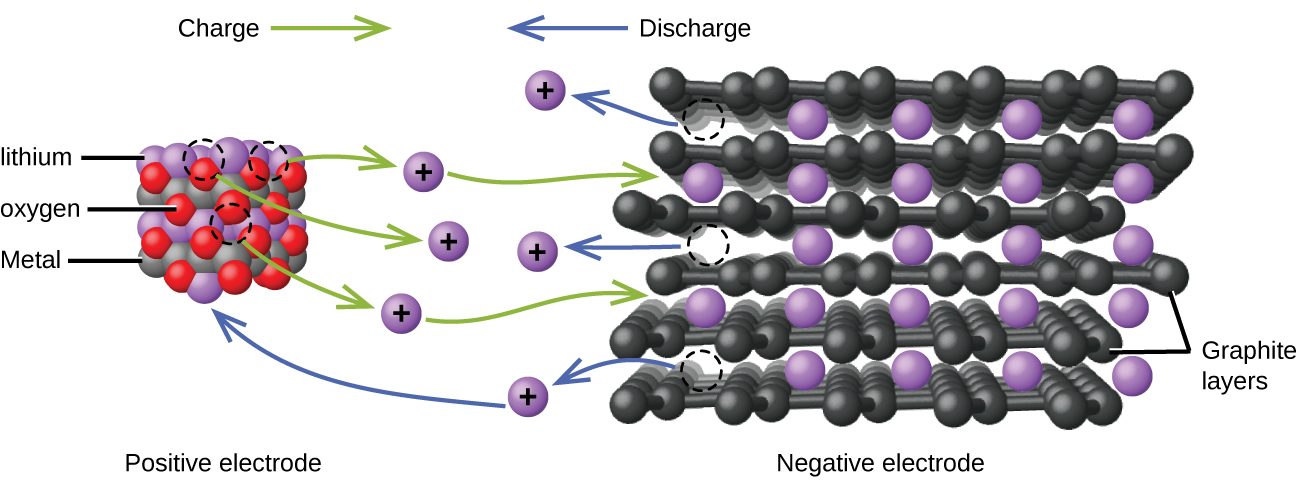
Lithium ion batteries ( [link] ) are among the most popular rechargeable batteries and are used in many portable electronic devices. The reactions are
With the coefficients representing moles, x is no more than about 0.5 moles. The battery voltage is about 3.7 V. Lithium batteries are popular because they can provide a large amount current, are lighter than comparable batteries of other types, produce a nearly constant voltage as they discharge, and only slowly lose their charge when stored.
Visit this site for more information about lithium ion batteries.
The lead acid battery ( [link] ) is the type of secondary battery used in your automobile. It is inexpensive and capable of producing the high current required by automobile starter motors. The reactions for a lead acid battery are

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?