| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A larger reduction potential means that it is easier to reduce the reactant. Permanganate, with the largest reduction potential, is the strongest oxidizer under these conditions. Dichromate is next, followed by titanium dioxide as the weakest oxidizing agent (the hardest to reduce) of this set.
no reaction because Pt( s ) will not be oxidized by H +
Ancient civilizations knew about iron, copper, silver, and gold. The time periods in human history known as the Bronze Age and Iron Age mark the advancements in which societies learned to isolate certain metals and use them to make tools and goods. Naturally occurring ores of copper, silver, and gold can contain high concentrations of these metals in elemental form ( [link] ). Iron, on the other hand, occurs on earth almost exclusively in oxidized forms, such as rust (Fe 2 O 3 ). The earliest known iron implements were made from iron meteorites. Surviving iron artifacts dating from approximately 4000 to 2500 BC are rare, but all known examples contain specific alloys of iron and nickel that occur only in extraterrestrial objects, not on earth. It took thousands of years of technological advances before civilizations developed iron smelting , the ability to extract a pure element from its naturally occurring ores and for iron tools to become common.
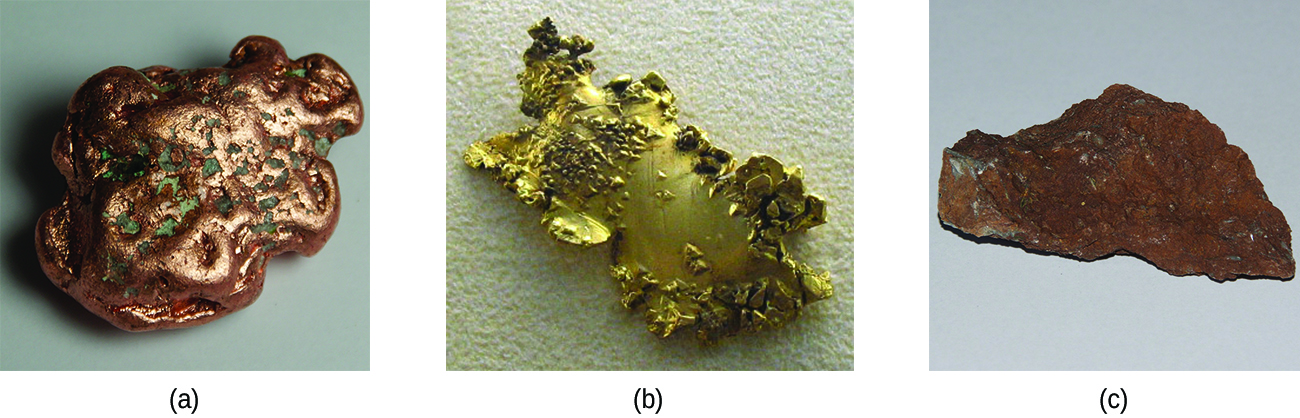
Generally, the transition elements are extracted from minerals found in a variety of ores. However, the ease of their recovery varies widely, depending on the concentration of the element in the ore, the identity of the other elements present, and the difficulty of reducing the element to the free metal.
In general, it is not difficult to reduce ions of the d -block elements to the free element. Carbon is a sufficiently strong reducing agent in most cases. However, like the ions of the more active main group metals, ions of the f -block elements must be isolated by electrolysis or by reduction with an active metal such as calcium.
We shall discuss the processes used for the isolation of iron, copper, and silver because these three processes illustrate the principal means of isolating most of the d -block metals. In general, each of these processes involves three principal steps: preliminary treatment, smelting, and refining.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?