| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
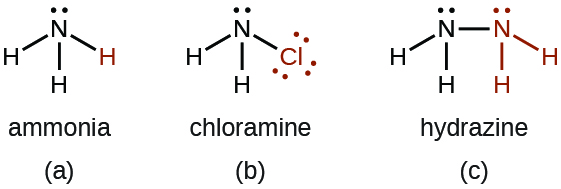
Chloramine, NH 2 Cl, results from the reaction of sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl, with ammonia in basic solution. In the presence of a large excess of ammonia at low temperature, the chloramine reacts further to produce hydrazine, N 2 H 4 :
Anhydrous hydrazine is relatively stable in spite of its positive free energy of formation:
Hydrazine is a fuming, colorless liquid that has some physical properties remarkably similar to those of H 2 O (it melts at 2 °C, boils at 113.5 °C, and has a density at 25 °C of 1.00 g/mL). It burns rapidly and completely in air with substantial evolution of heat:
Like ammonia, hydrazine is both a Brønsted base and a Lewis base, although it is weaker than ammonia. It reacts with strong acids and forms two series of salts that contain the and ions, respectively. Some rockets use hydrazine as a fuel.
The most important hydride of phosphorus is phosphine, PH 3 , a gaseous analog of ammonia in terms of both formula and structure. Unlike ammonia, it is not possible to form phosphine by direct union of the elements. There are two methods for the preparation of phosphine. One method is by the action of an acid on an ionic phosphide. The other method is the disproportionation of white phosphorus with hot concentrated base to produce phosphine and the hydrogen phosphite ion:
Phosphine is a colorless, very poisonous gas, which has an odor like that of decaying fish. Heat easily decomposes phosphine and the compound burns in air. The major uses of phosphine are as a fumigant for grains and in semiconductor processing. Like ammonia, gaseous phosphine unites with gaseous hydrogen halides, forming phosphonium compounds like PH 4 Cl and PH 4 I. Phosphine is a much weaker base than ammonia; therefore, these compounds decompose in water, and the insoluble PH 3 escapes from solution.
Hydrogen sulfide, H 2 S, is a colorless gas that is responsible for the offensive odor of rotten eggs and of many hot springs. Hydrogen sulfide is as toxic as hydrogen cyanide; therefore, it is necessary to exercise great care in handling it. Hydrogen sulfide is particularly deceptive because it paralyzes the olfactory nerves; after a short exposure, one does not smell it.
The production of hydrogen sulfide by the direct reaction of the elements (H 2 + S) is unsatisfactory because the yield is low. A more effective preparation method is the reaction of a metal sulfide with a dilute acid. For example:
It is easy to oxidize the sulfur in metal sulfides and in hydrogen sulfide, making metal sulfides and H 2 S good reducing agents. In acidic solutions, hydrogen sulfide reduces Fe 3+ to Fe 2+ , to Mn 2+ , to Cr 3+ , and HNO 3 to NO 2 . The sulfur in H 2 S usually oxidizes to elemental sulfur, unless a large excess of the oxidizing agent is present. In which case, the sulfide may oxidize to or (or to SO 2 or SO 3 in the absence of water):

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?