| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. This allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom.
The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f. [link] depicts how these two trends in increasing energy relate. The 1 s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. However, this pattern does not hold for larger atoms. The 3 d orbital is higher in energy than the 4 s orbital. Such overlaps continue to occur frequently as we move up the chart.
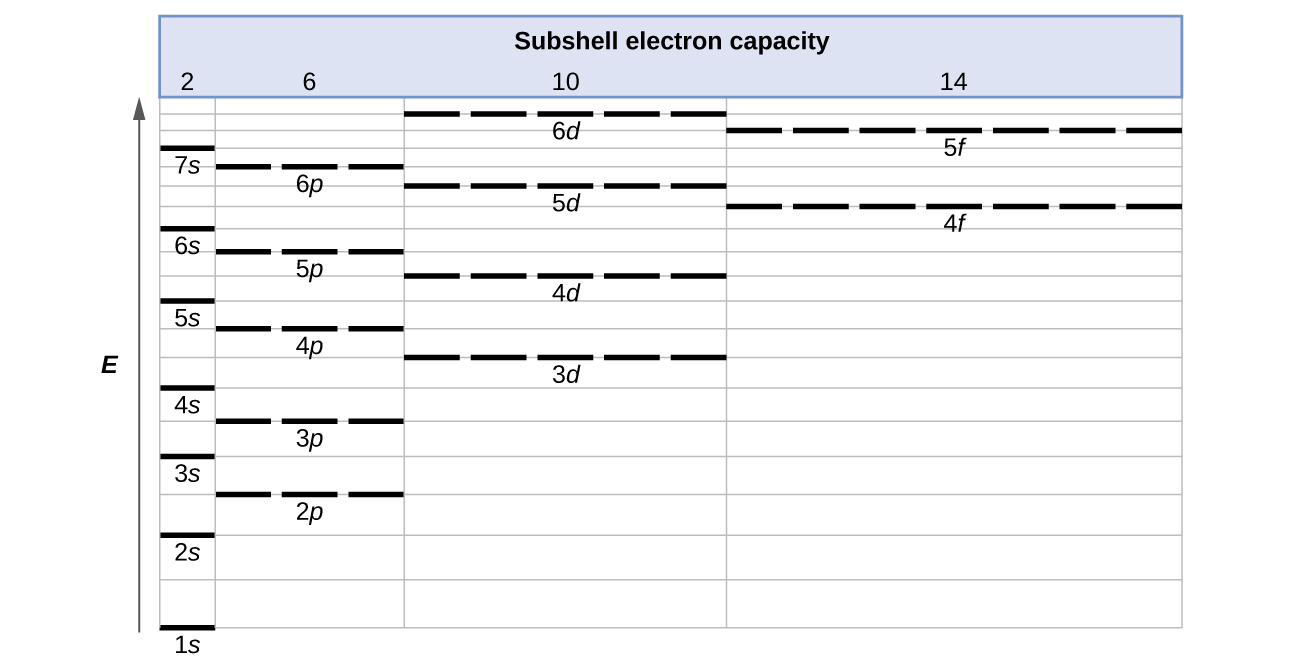
Electrons in successive atoms on the periodic table tend to fill low-energy orbitals first. Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5 p orbitals fill immediately after the 4 d , and immediately before the 6 s . The filling order is based on observed experimental results, and has been confirmed by theoretical calculations. As the principal quantum number, n , increases, the size of the orbital increases and the electrons spend more time farther from the nucleus. Thus, the attraction to the nucleus is weaker and the energy associated with the orbital is higher (less stabilized). But this is not the only effect we have to take into account. Within each shell, as the value of l increases, the electrons are less penetrating (meaning there is less electron density found close to the nucleus), in the order s > p > d > f . Electrons that are closer to the nucleus slightly repel electrons that are farther out, offsetting the more dominant electron–nucleus attractions slightly (recall that all electrons have −1 charges, but nuclei have + Z charges). This phenomenon is called shielding and will be discussed in more detail in the next section. Electrons in orbitals that experience more shielding are less stabilized and thus higher in energy. For small orbitals (1 s through 3 p ), the increase in energy due to n is more significant than the increase due to l ; however, for larger orbitals the two trends are comparable and cannot be simply predicted. We will discuss methods for remembering the observed order.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?