| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
2 10 −24 J
Use this simulation program to experiment with the photoelectric effect to see how intensity, frequency, type of metal, and other factors influence the ejected photons.
(a) Increasing the brightness of incoming light increases the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons.
(b) Increasing the wavelength of incoming light increases the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons.
(c) Increasing the brightness of incoming light increases the number of ejected electrons.
(d) Increasing the frequency of incoming light can increase the number of ejected electrons.
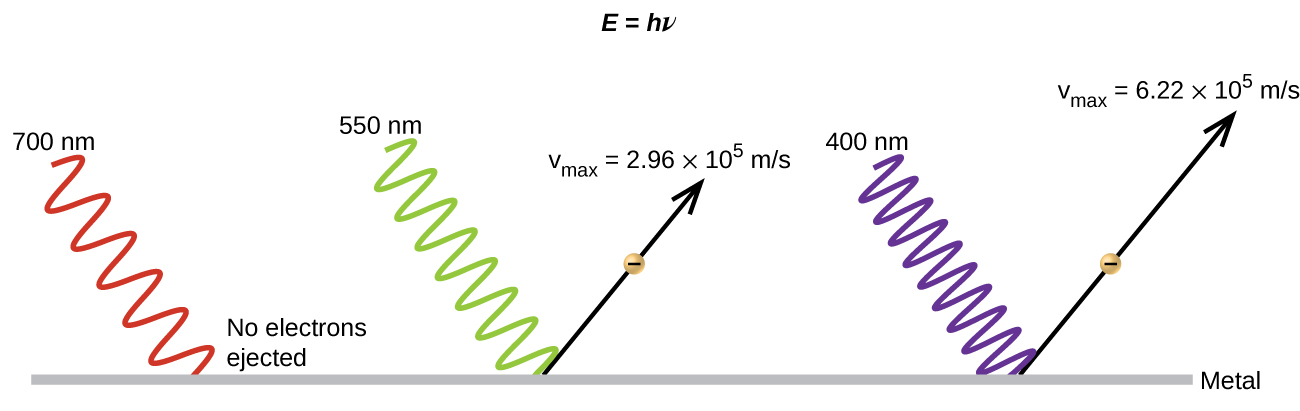
(b) False. Increasing the frequency of incoming light increases the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons. Frequency is proportional to energy and inversely proportional to wavelength. Frequencies above the threshold value transfer the excess energy into the kinetic energy of the electrons.
(c) True. Because the number of collisions with photons increases with brighter light, the number of ejected electrons increases.
(d) True with regard to the threshold energy binding the electrons to the metal. Below this threshold, electrons are not emitted and above it they are. Once over the threshold value, further increasing the frequency does not increase the number of ejected electrons
3.94 10 5 kJ/mol
Another paradox within the classical electromagnetic theory that scientists in the late nineteenth century struggled with concerned the light emitted from atoms and molecules. When solids, liquids, or condensed gases are heated sufficiently, they radiate some of the excess energy as light. Photons produced in this manner have a range of energies, and thereby produce a continuous spectrum in which an unbroken series of wavelengths is present. Most of the light generated from stars (including our sun) is produced in this fashion. You can see all the visible wavelengths of light present in sunlight by using a prism to separate them. As can be seen in [link] , sunlight also contains UV light (shorter wavelengths) and IR light (longer wavelengths) that can be detected using instruments but that are invisible to the human eye. Incandescent (glowing) solids such as tungsten filaments in incandescent lights also give off light that contains all wavelengths of visible light. These continuous spectra can often be approximated by blackbody radiation curves at some appropriate temperature, such as those shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?