| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If a metal can exhibit two oxidation states, it may be necessary to control the stoichiometry in order to obtain the halide with the lower oxidation state. For example, preparation of tin(II) chloride requires a 1:1 ratio of Sn to Cl 2 , whereas preparation of tin(IV) chloride requires a 1:2 ratio:
The active representative metals—those that are easier to oxidize than hydrogen—react with gaseous hydrogen halides to produce metal halides and hydrogen. The reaction of zinc with hydrogen fluoride is:
The active representative metals also react with solutions of hydrogen halides to form hydrogen and solutions of the corresponding halides. Examples of such reactions include:
Hydroxides, carbonates, and some oxides react with solutions of the hydrogen halides to form solutions of halide salts. It is possible to prepare additional salts by the reaction of these hydroxides, carbonates, and oxides with aqueous solution of other acids:
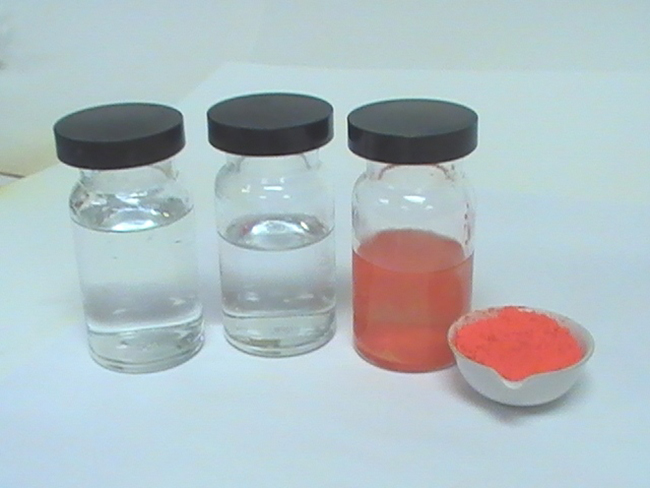
A few halides and many of the other salts of the representative metals are insoluble. It is possible to prepare these soluble salts by metathesis reactions that occur when solutions of soluble salts are mixed (see [link] ). Metathesis reactions are examined in the chapter on the stoichiometry of chemical reactions.

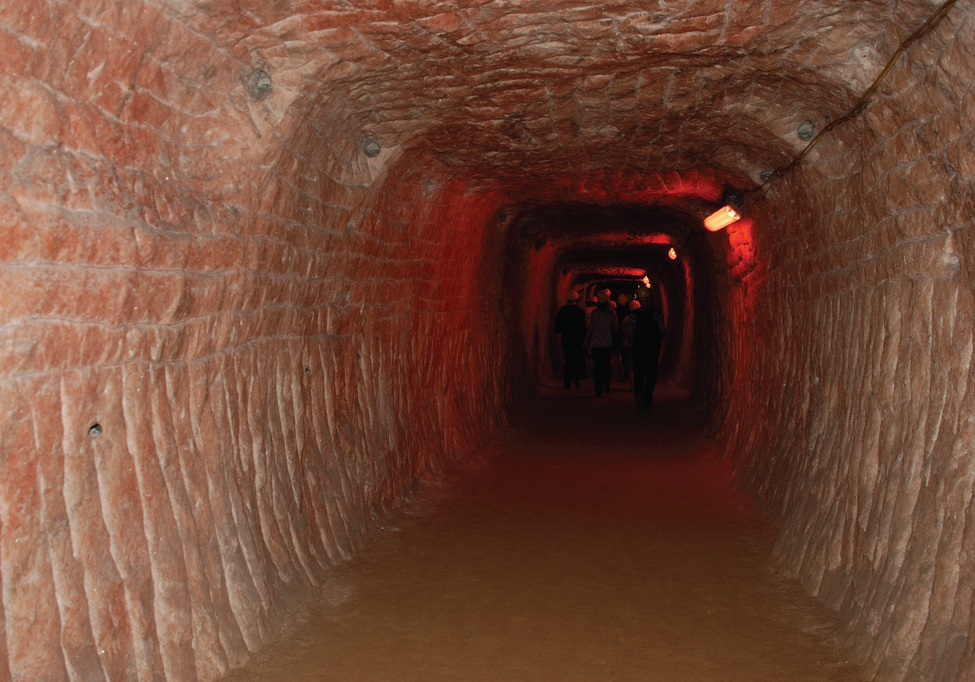
Several halides occur in large quantities in nature. The ocean and underground brines contain many halides. For example, magnesium chloride in the ocean is the source of magnesium ions used in the production of magnesium. Large underground deposits of sodium chloride, like the salt mine shown in [link] , occur in many parts of the world. These deposits serve as the source of sodium and chlorine in almost all other compounds containing these elements. The chlor-alkali process is one example.

Compounds formed from two or more different halogens are interhalogens . Interhalogen molecules consist of one atom of the heavier halogen bonded by single bonds to an odd number of atoms of the lighter halogen. The structures of IF 3 , IF 5 , and IF 7 are illustrated in [link] . Formulas for other interhalogens, each of which comes from the reaction of the respective halogens, are in [link] .
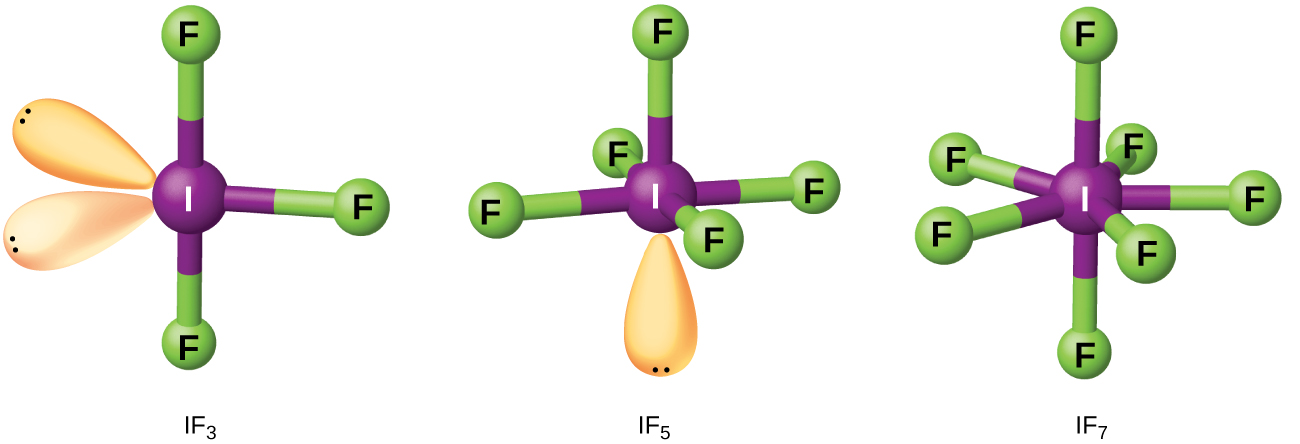
Note from [link] that fluorine is able to oxidize iodine to its maximum oxidation state, 7+, whereas bromine and chlorine, which are more difficult to oxidize, achieve only the 5+-oxidation state. A 7+-oxidation state is the limit for the halogens. Because smaller halogens are grouped about a larger one, the maximum number of smaller atoms possible increases as the radius of the larger atom increases. Many of these compounds are unstable, and most are extremely reactive. The interhalogens react like their component halides; halogen fluorides, for example, are stronger oxidizing agents than are halogen chlorides.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?