| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
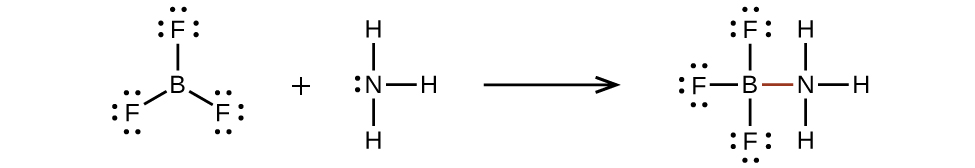
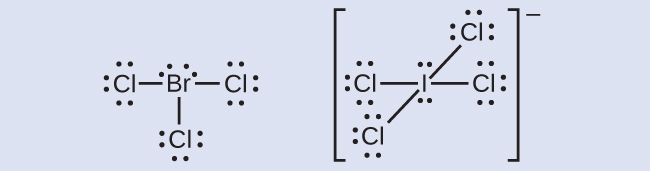
Elements in the second period of the periodic table ( n = 2) can accommodate only eight electrons in their valence shell orbitals because they have only four valence orbitals (one 2 s and three 2 p orbitals). Elements in the third and higher periods ( n ≥ 3) have more than four valence orbitals and can share more than four pairs of electrons with other atoms because they have empty d orbitals in the same shell. Molecules formed from these elements are sometimes called hypervalent molecules . [link] shows the Lewis structures for two hypervalent molecules, PCl 5 and SF 6.
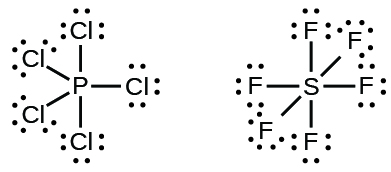
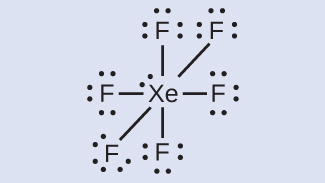
In some hypervalent molecules, such as IF 5 and XeF 4 , some of the electrons in the outer shell of the central atom are lone pairs:
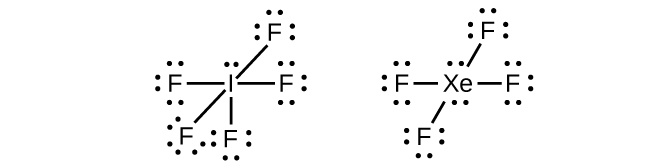
When we write the Lewis structures for these molecules, we find that we have electrons left over after filling the valence shells of the outer atoms with eight electrons. These additional electrons must be assigned to the central atom.
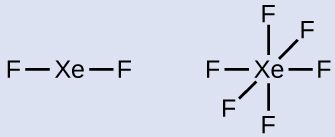
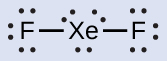
Valence electronic structures can be visualized by drawing Lewis symbols (for atoms and monatomic ions) and Lewis structures (for molecules and polyatomic ions). Lone pairs, unpaired electrons, and single, double, or triple bonds are used to indicate where the valence electrons are located around each atom in a Lewis structure. Most structures—especially those containing second row elements—obey the octet rule, in which every atom (except H) is surrounded by eight electrons. Exceptions to the octet rule occur for odd-electron molecules (free radicals), electron-deficient molecules, and hypervalent molecules.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?