| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
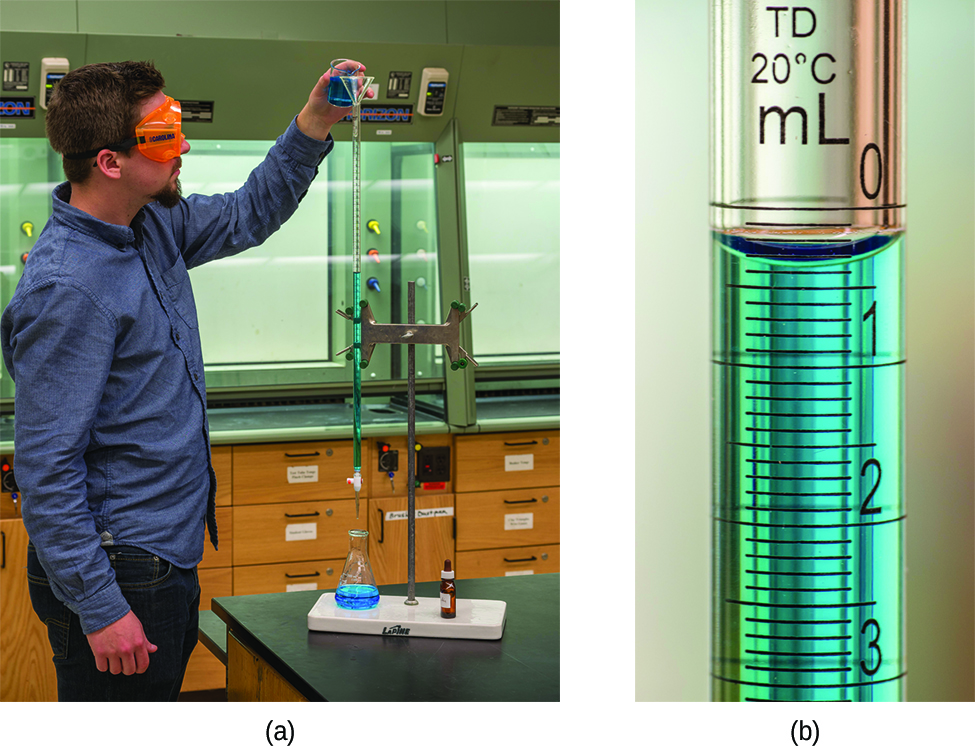
What is the molarity of the HCl?
For this exercise, the calculation will follow the following outlined steps:
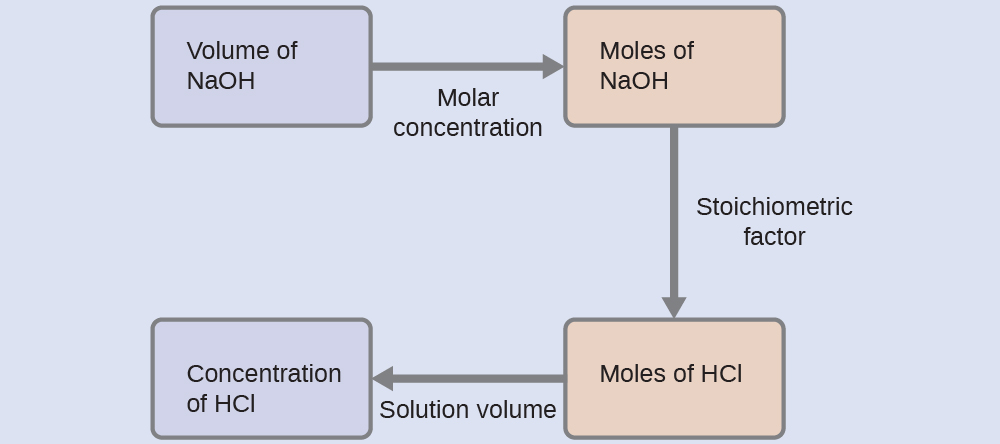
The molar amount of HCl is calculated to be:
Using the provided volume of HCl solution and the definition of molarity, the HCl concentration is:
Note: For these types of titration calculations, it is convenient to recognize that solution molarity is also equal to the number of milli moles of solute per milli liter of solution:
Using this version of the molarity unit will shorten the calculation by eliminating two conversion factors:
A volume of 23.24 mL was required to reach the end point. What is the oxalic acid molarity?
0.2648 M
A gravimetric analysis is one in which a sample is subjected to some treatment that causes a change in the physical state of the analyte that permits its separation from the other components of the sample. Mass measurements of the sample, the isolated analyte, or some other component of the analysis system, used along with the known stoichiometry of the compounds involved, permit calculation of the analyte concentration. Gravimetric methods were the first techniques used for quantitative chemical analysis, and they remain important tools in the modern chemistry laboratory.
The required change of state in a gravimetric analysis may be achieved by various physical and chemical processes. For example, the moisture (water) content of a sample is routinely determined by measuring the mass of a sample before and after it is subjected to a controlled heating process that evaporates the water. Also common are gravimetric techniques in which the analyte is subjected to a precipitation reaction of the sort described earlier in this chapter. The precipitate is typically isolated from the reaction mixture by filtration, carefully dried, and then weighed ( [link] ). The mass of the precipitate may then be used, along with relevant stoichiometric relationships, to calculate analyte concentration.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?