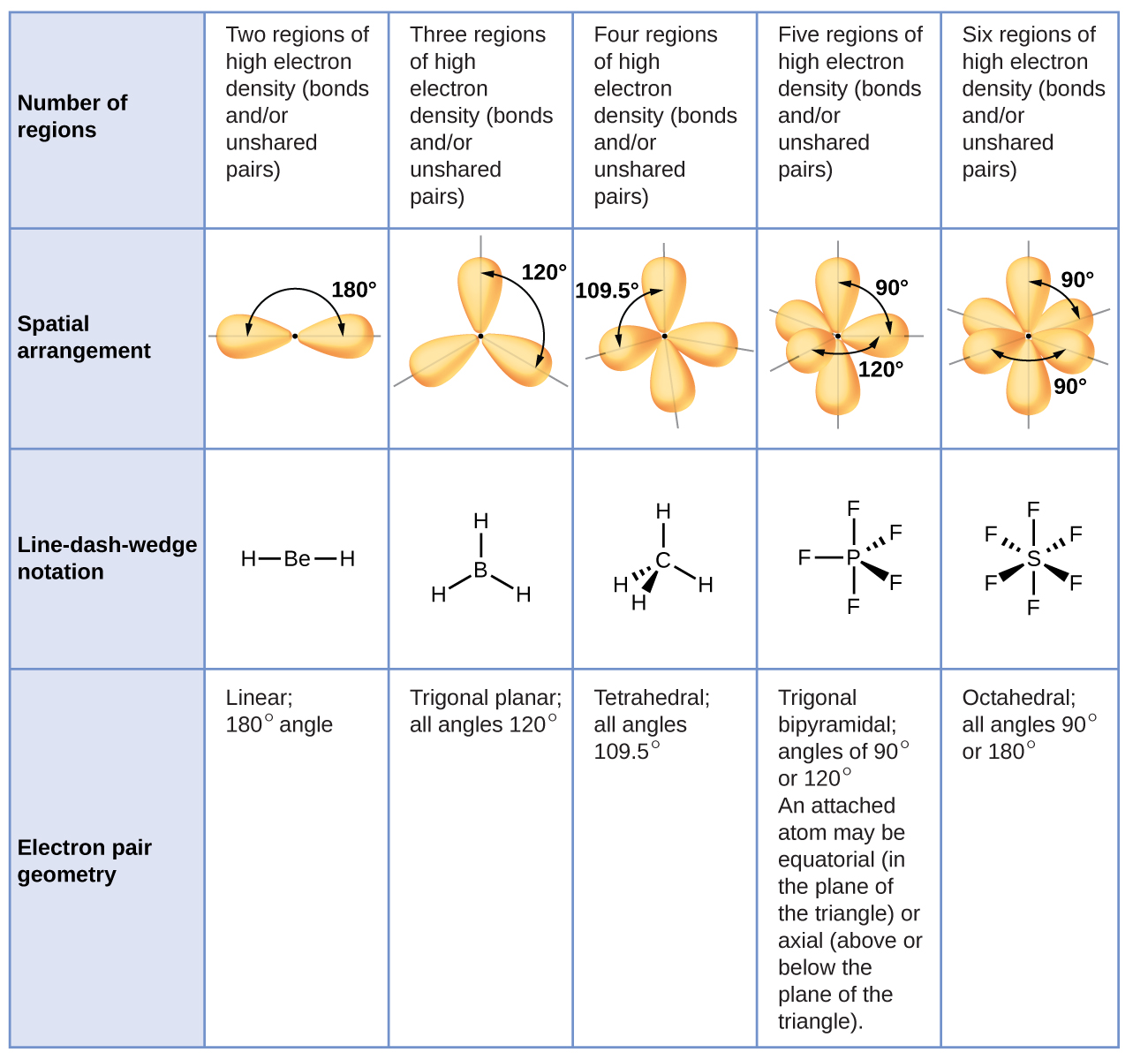
| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is important to note that electron-pair geometry around a central atom is not the same thing as its molecular structure. The electron-pair geometries shown in [link] describe all regions where electrons are located, bonds as well as lone pairs. Molecular structure describes the location of the atoms , not the electrons.
We differentiate between these two situations by naming the geometry that includes all electron pairs the electron-pair geometry . The structure that includes only the placement of the atoms in the molecule is called the molecular structure . The electron-pair geometries will be the same as the molecular structures when there are no lone electron pairs around the central atom, but they will be different when there are lone pairs present on the central atom.
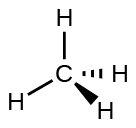
For example, the methane molecule, CH 4 , which is the major component of natural gas, has four bonding pairs of electrons around the central carbon atom; the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral, as is the molecular structure ( [link] ). On the other hand, the ammonia molecule, NH 3 , also has four electron pairs associated with the nitrogen atom, and thus has a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry. One of these regions, however, is a lone pair, which is not included in the molecular structure, and this lone pair influences the shape of the molecule ( [link] ).
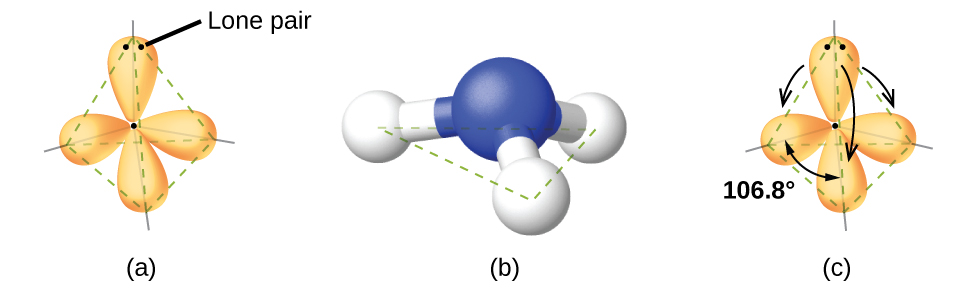
As seen in [link] , small distortions from the ideal angles in [link] can result from differences in repulsion between various regions of electron density. VSEPR theory predicts these distortions by establishing an order of repulsions and an order of the amount of space occupied by different kinds of electron pairs. The order of electron-pair repulsions from greatest to least repulsion is:
This order of repulsions determines the amount of space occupied by different regions of electrons. A lone pair of electrons occupies a larger region of space than the electrons in a triple bond; in turn, electrons in a triple bond occupy more space than those in a double bond, and so on. The order of sizes from largest to smallest is:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?