| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Dispersed colloidal particles are often electrically charged. A colloidal particle of iron(III) hydroxide, for example, does not contain enough hydroxide ions to compensate exactly for the positive charges on the iron(III) ions. Thus, each individual colloidal particle bears a positive charge, and the colloidal dispersion consists of charged colloidal particles and some free hydroxide ions, which keep the dispersion electrically neutral. Most metal hydroxide colloids have positive charges, whereas most metals and metal sulfides form negatively charged dispersions. All colloidal particles in any one system have charges of the same sign. This helps keep them dispersed because particles containing like charges repel each other.
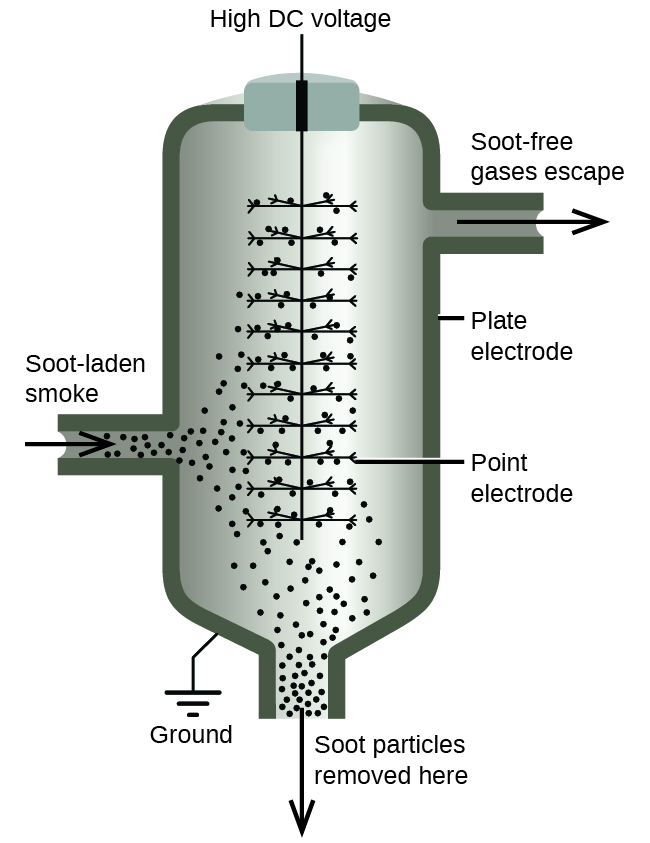
We can take advantage of the charge on colloidal particles to remove them from a variety of mixtures. If we place a colloidal dispersion in a container with charged electrodes, positively charged particles, such as iron(III) hydroxide particles, would move to the negative electrode. There, the colloidal particles lose their charge and coagulate as a precipitate.
The carbon and dust particles in smoke are often colloidally dispersed and electrically charged. Frederick Cottrell, an American chemist, developed a process to remove these particles.
Born in Oakland, CA in 1877, Frederick Cottrell devoured textbooks as if they were novels and graduated from high school at the age of 16. He then entered the University of California (UC), Berkeley, completing a Bachelor’s degree in three years. He saved money from his $1200 annual salary as a chemistry teacher at Oakland High School to fund his studies in chemistry in Berlin with Nobel prize winner Jacobus Henricus van’t Hoff, and in Leipzig with Wilhelm Ostwald, another Nobel awardee. After earning his PhD in physical chemistry, he returned to the United States to teach at UC Berkeley. He also consulted for the DuPont Company, where he developed the electrostatic precipitator, a device designed to curb air pollution by removing colloidal particles from air. Cottrell used the proceeds from his invention to fund a nonprofit research corporation to finance scientific research.
The charged particles are attracted to highly charged electrodes, where they are neutralized and deposited as dust ( [link] ). This is one of the important methods used to clean up the smoke from a variety of industrial processes. The process is also important in the recovery of valuable products from the smoke and flue dust of smelters, furnaces, and kilns. There are also ionic air filters designed for home use to improve indoor air quality.
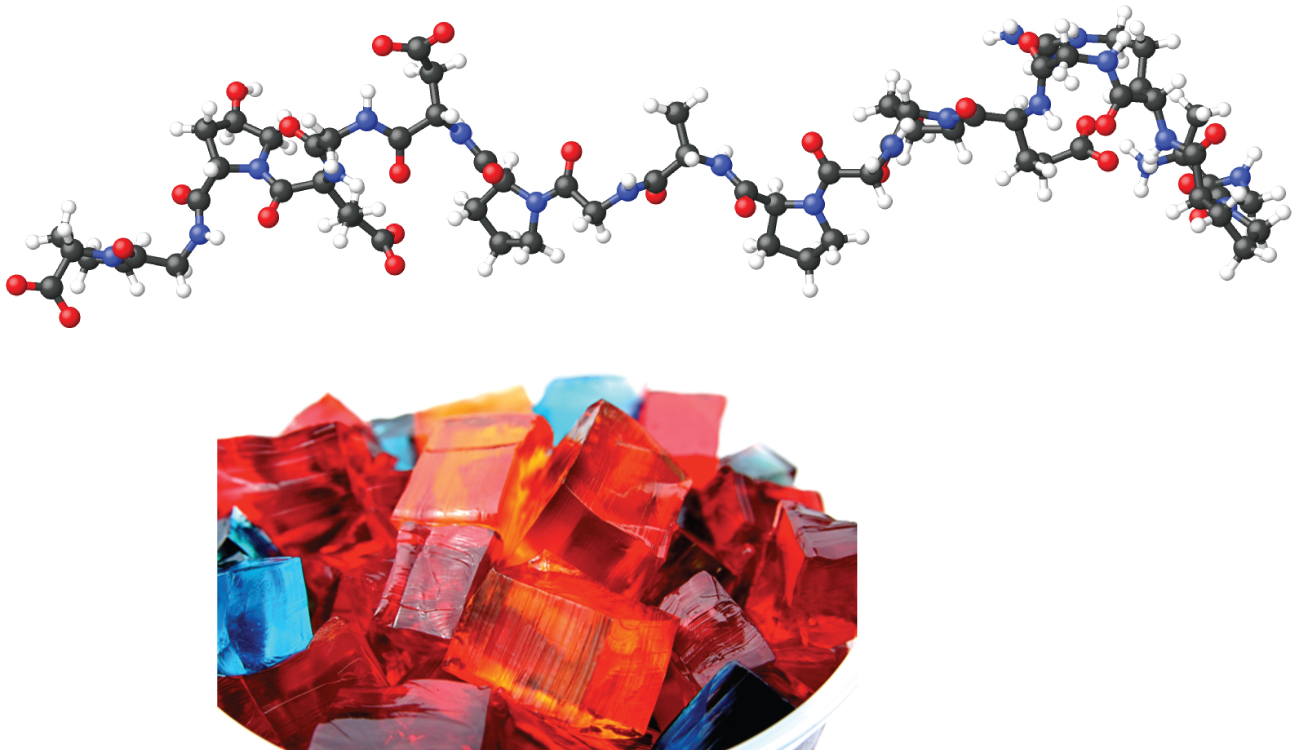
When we make gelatin, such as Jell-O, we are making a type of colloid ( [link] ). Gelatin sets on cooling because the hot aqueous mixture of gelatin coagulates as it cools and the whole mass, including the liquid, sets to an extremely viscous body known as a gel , a colloid in which the dispersing medium is a solid and the dispersed phase is a liquid. It appears that the fibers of the dispersing medium form a complex three-dimensional network, the interstices being filled with the liquid medium or a dilute solution of the dispersing medium. Because the formation of a gel is accompanied by the taking up of water or some other solvent, the gel is said to be hydrated or solvated.
Pectin, a carbohydrate from fruit juices, is a gel-forming substance important in jelly making. Silica gel, a colloidal dispersion of hydrated silicon dioxide, is formed when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a dilute solution of sodium silicate. Canned Heat is a gel made by mixing alcohol and a saturated aqueous solution of calcium acetate.
Colloids are mixtures in which one or more substances are dispersed as relatively large solid particles or liquid droplets throughout a solid, liquid, or gaseous medium. The particles of a colloid remain dispersed and do not settle due to gravity, and they are often electrically charged. Colloids are widespread in nature and are involved in many technological applications.
Identify the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium in each of the following colloidal systems: starch dispersion, smoke, fog, pearl, whipped cream, floating soap, jelly, milk, and ruby.
| Colloidal System | Dispersed Phase | Dispersion Medium |
|---|---|---|
| starch dispersion | starch | water |
| smoke | solid particles | air |
| fog | water | air |
| pearl | water | calcium carbonate (CaCO 3 ) |
| whipped cream | air | cream |
| floating soap | air | soap |
| jelly | fruit juice | pectin gel |
| milk | butterfat | water |
| ruby | chromium(III) oxide (Cr 2 O 3 ) | aluminum oxide (Al 2 O 3 ) |
Distinguish between dispersion methods and condensation methods for preparing colloidal systems.
How do colloids differ from solutions with regard to dispersed particle size and homogeneity?
Colloidal dispersions consist of particles that are much bigger than the solutes of typical solutions. Colloidal particles are either very large molecules or aggregates of smaller species that usually are big enough to scatter light. Colloids are homogeneous on a macroscopic (visual) scale, while solutions are homogeneous on a microscopic (molecular) scale.
Explain the cleansing action of soap.
How can it be demonstrated that colloidal particles are electrically charged?
If they are placed in an electrolytic cell, dispersed particles will move toward the electrode that carries a charge opposite to their own charge. At this electrode, the charged particles will be neutralized and will coagulate as a precipitate.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?