| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
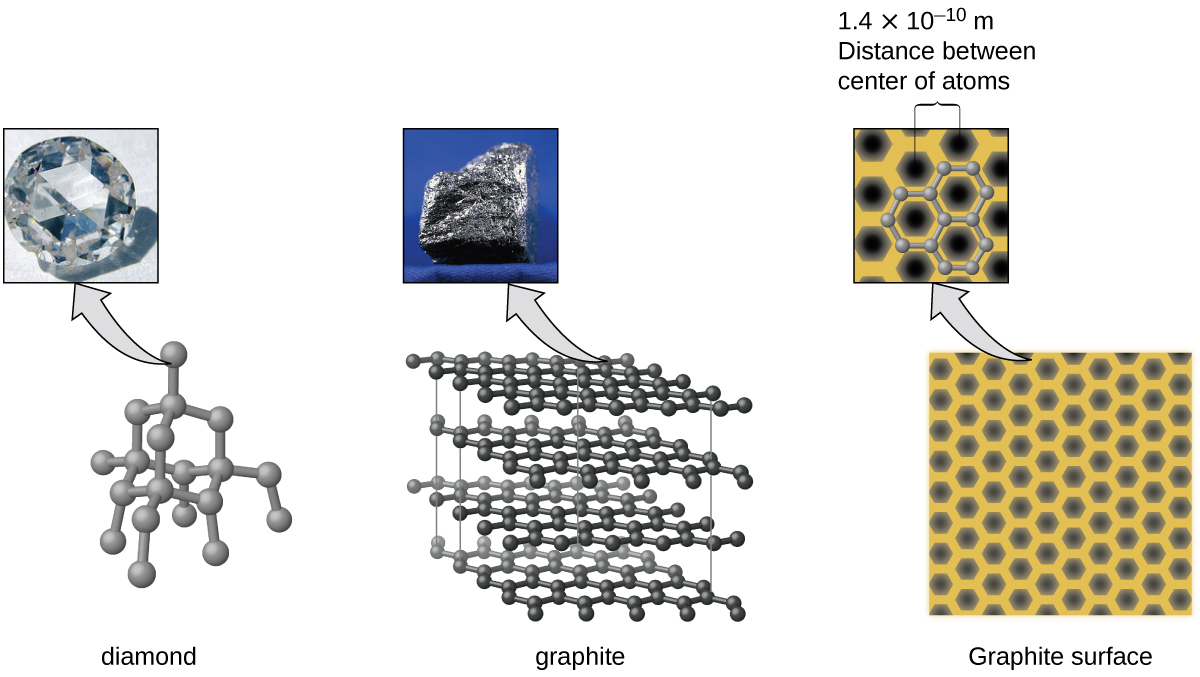
Carbon is an essential element in our world. The unique properties of carbon atoms allow the existence of carbon-based life forms such as ourselves. Carbon forms a huge variety of substances that we use on a daily basis, including those shown in [link] . You may be familiar with diamond and graphite, the two most common allotropes of carbon. (Allotropes are different structural forms of the same element.) Diamond is one of the hardest-known substances, whereas graphite is soft enough to be used as pencil lead. These very different properties stem from the different arrangements of the carbon atoms in the different allotropes.
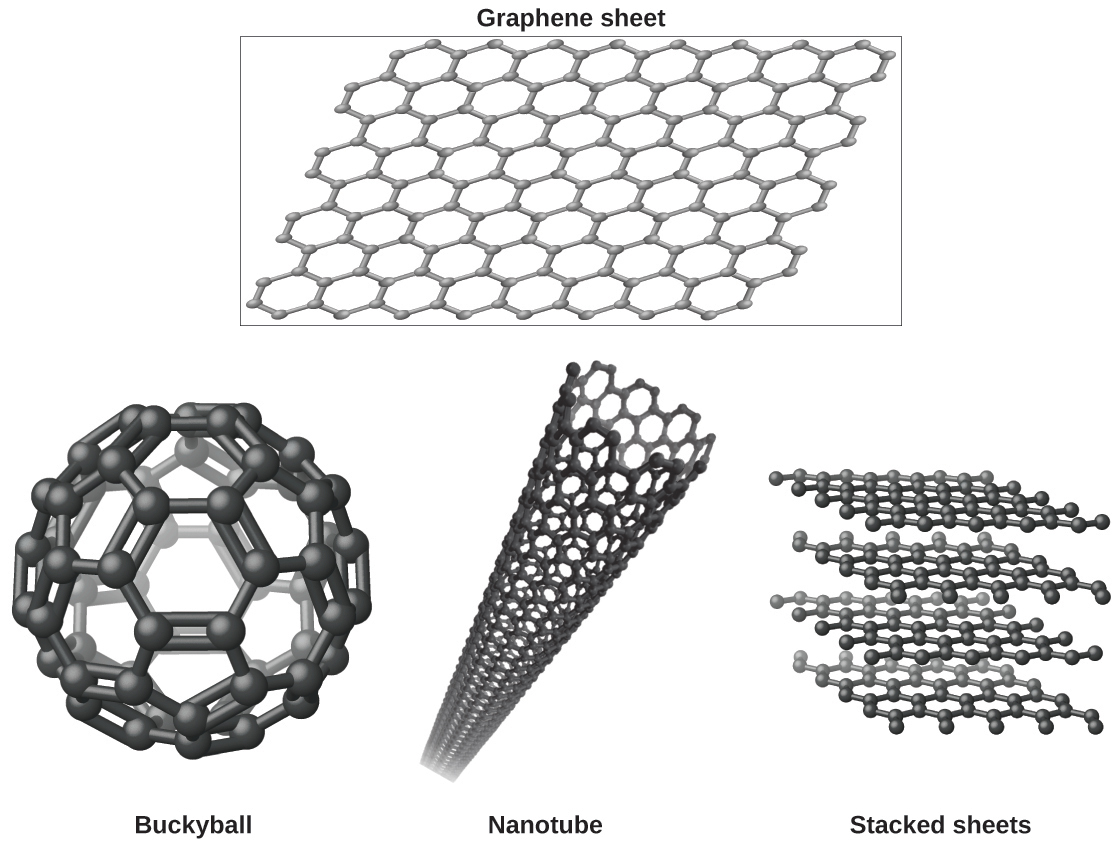
You may be less familiar with a recently discovered form of carbon: graphene. Graphene was first isolated in 2004 by using tape to peel off thinner and thinner layers from graphite. It is essentially a single sheet (one atom thick) of graphite. Graphene, illustrated in [link] , is not only strong and lightweight, but it is also an excellent conductor of electricity and heat. These properties may prove very useful in a wide range of applications, such as vastly improved computer chips and circuits, better batteries and solar cells, and stronger and lighter structural materials. The 2010 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov for their pioneering work with graphene.
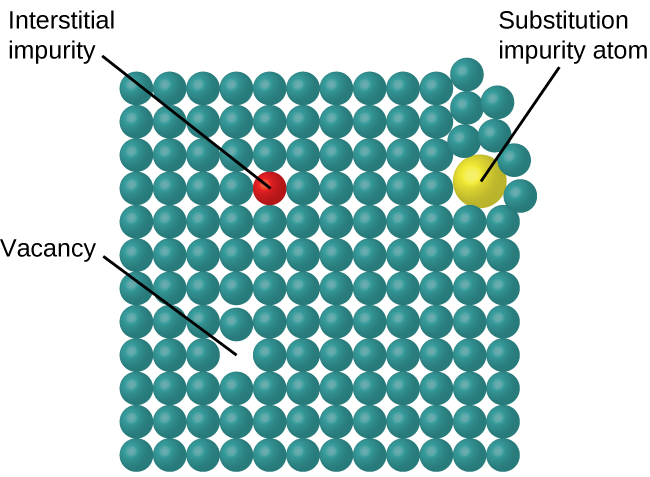
In a crystalline solid, the atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in a definite repeating pattern, but occasional defects may occur in the pattern. Several types of defects are known, as illustrated in [link] . Vacancies are defects that occur when positions that should contain atoms or ions are vacant. Less commonly, some atoms or ions in a crystal may occupy positions, called interstitial sites , located between the regular positions for atoms. Other distortions are found in impure crystals, as, for example, when the cations, anions, or molecules of the impurity are too large to fit into the regular positions without distorting the structure. Trace amounts of impurities are sometimes added to a crystal (a process known as doping) in order to create defects in the structure that yield desirable changes in its properties. For example, silicon crystals are doped with varying amounts of different elements to yield suitable electrical properties for their use in the manufacture of semiconductors and computer chips.
Some substances form crystalline solids consisting of particles in a very organized structure; others form amorphous (noncrystalline) solids with an internal structure that is not ordered. The main types of crystalline solids are ionic solids, metallic solids, covalent network solids, and molecular solids. The properties of the different kinds of crystalline solids are due to the types of particles of which they consist, the arrangements of the particles, and the strengths of the attractions between them. Because their particles experience identical attractions, crystalline solids have distinct melting temperatures; the particles in amorphous solids experience a range of interactions, so they soften gradually and melt over a range of temperatures. Some crystalline solids have defects in the definite repeating pattern of their particles. These defects (which include vacancies, atoms or ions not in the regular positions, and impurities) change physical properties such as electrical conductivity, which is exploited in the silicon crystals used to manufacture computer chips.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?