| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
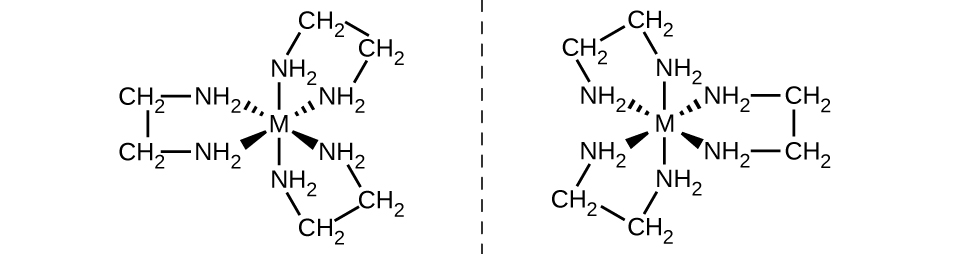
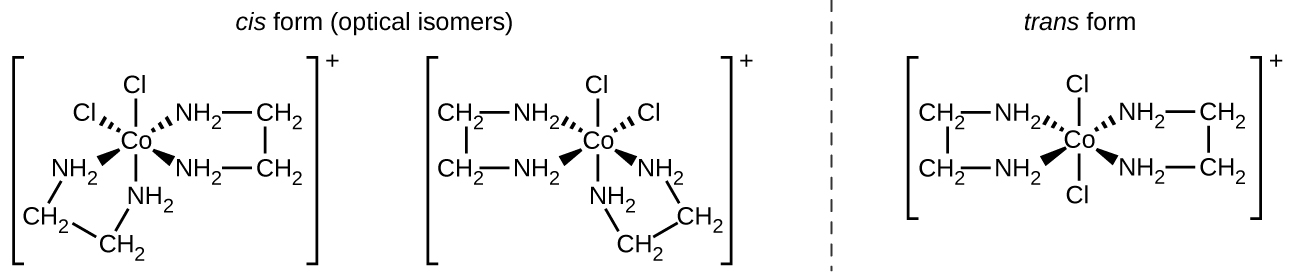
The [Co(en) 2 Cl 2 ] + ion exhibits geometric isomerism ( cis / trans ), and its cis isomer exists as a pair of optical isomers ( [link] ).
Linkage isomers occur when the coordination compound contains a ligand that can bind to the transition metal center through two different atoms. For example, the CN ligand can bind through the carbon atom (cyano) or through the nitrogen atom (isocyano). Similarly, SCN− can be bound through the sulfur or nitrogen atom, affording two distinct compounds ([Co(NH 3 ) 5 SCN] 2+ or [Co(NH 3 ) 5 NCS] 2+ ).
Ionization isomers (or coordination isomers ) occur when one anionic ligand in the inner coordination sphere is replaced with the counter ion from the outer coordination sphere. A simple example of two ionization isomers are [CoCl 6 ][Br]and [CoCl 5 Br][Cl].
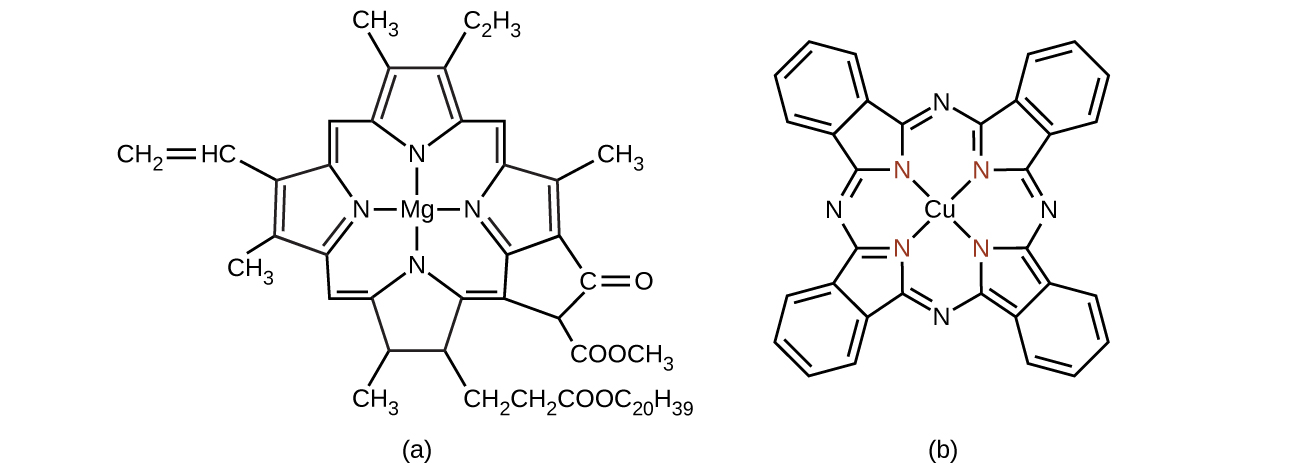
Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, is a complex that contains magnesium ( [link] ). This is an example of a main group element in a coordination complex. Plants appear green because chlorophyll absorbs red and purple light; the reflected light consequently appears green. The energy resulting from the absorption of light is used in photosynthesis.
One of the most important applications of transition metals is as industrial catalysts. As you recall from the chapter on kinetics, a catalyst increases the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy and is regenerated in the catalytic cycle. Over 90% of all manufactured products are made with the aid of one or more catalysts. The ability to bind ligands and change oxidation states makes transition metal catalysts well suited for catalytic applications. Vanadium oxide is used to produce 230,000,000 tons of sulfuric acid worldwide each year, which in turn is used to make everything from fertilizers to cans for food. Plastics are made with the aid of transition metal catalysts, along with detergents, fertilizers, paints, and more (see [link] ). Very complicated pharmaceuticals are manufactured with catalysts that are selective, reacting with one specific bond out of a large number of possibilities. Catalysts allow processes to be more economical and more environmentally friendly. Developing new catalysts and better understanding of existing systems are important areas of current research.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?