| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
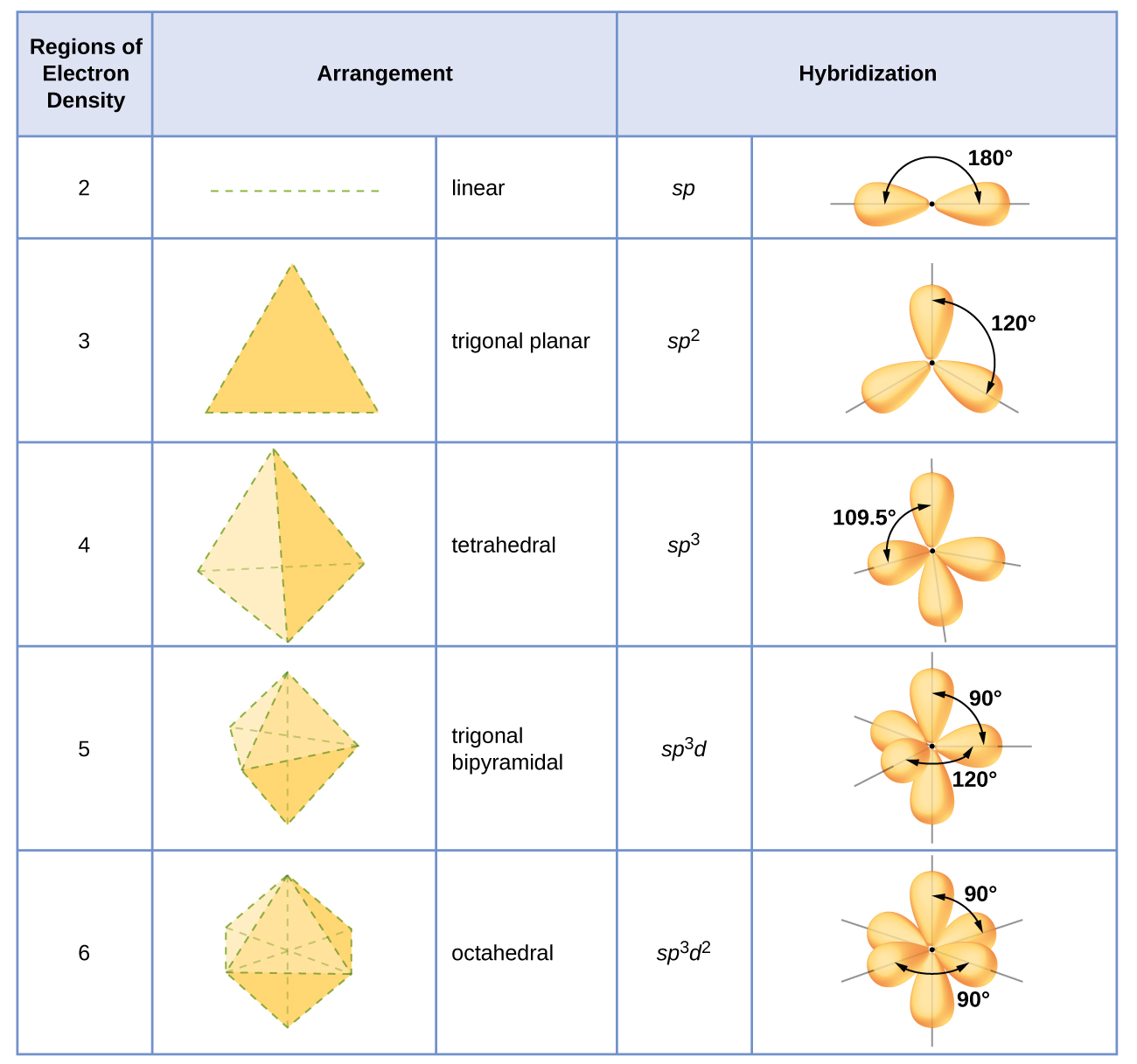
The hybridization of an atom is determined based on the number of regions of electron density that surround it. The geometrical arrangements characteristic of the various sets of hybrid orbitals are shown in [link] . These arrangements are identical to those of the electron-pair geometries predicted by VSEPR theory. VSEPR theory predicts the shapes of molecules, and hybrid orbital theory provides an explanation for how those shapes are formed. To find the hybridization of a central atom, we can use the following guidelines:
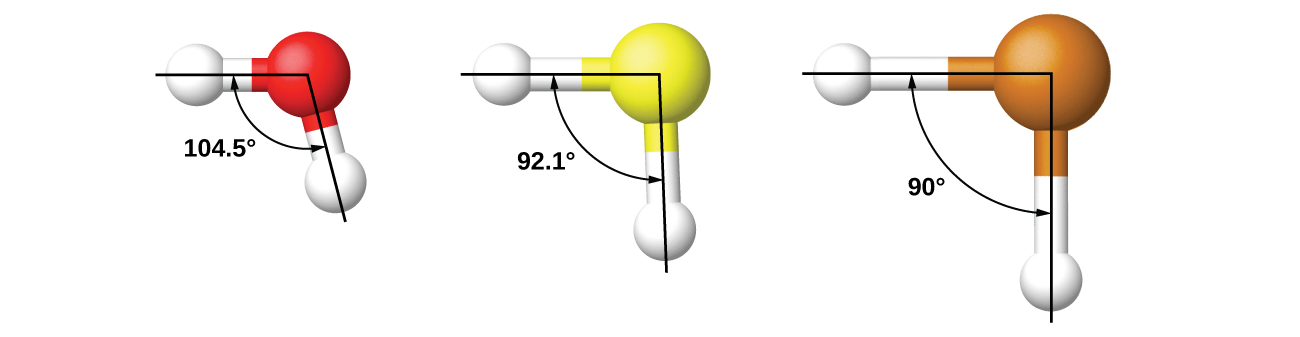
It is important to remember that hybridization was devised to rationalize experimentally observed molecular geometries. The model works well for molecules containing small central atoms, in which the valence electron pairs are close together in space. However, for larger central atoms, the valence-shell electron pairs are farther from the nucleus, and there are fewer repulsions. Their compounds exhibit structures that are often not consistent with VSEPR theory, and hybridized orbitals are not necessary to explain the observed data. For example, we have discussed the H–O–H bond angle in H 2 O, 104.5°, which is more consistent with sp 3 hybrid orbitals (109.5°) on the central atom than with 2 p orbitals (90°). Sulfur is in the same group as oxygen, and H 2 S has a similar Lewis structure. However, it has a much smaller bond angle (92.1°), which indicates much less hybridization on sulfur than oxygen. Continuing down the group, tellurium is even larger than sulfur, and for H 2 Te, the observed bond angle (90°) is consistent with overlap of the 5 p orbitals, without invoking hybridization. We invoke hybridization where it is necessary to explain the observed structures.
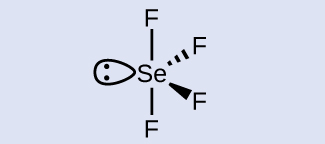
The selenium atom is sp 3 d hybridized.
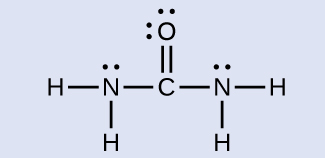
The nitrogen atoms are surrounded by four regions of electron density, which arrange themselves in a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry. The hybridization in a tetrahedral arrangement is sp 3 ( [link] ). This is the hybridization of the nitrogen atoms in urea.
The carbon atom is surrounded by three regions of electron density, positioned in a trigonal planar arrangement. The hybridization in a trigonal planar electron pair geometry is sp 2 ( [link] ), which is the hybridization of the carbon atom in urea.
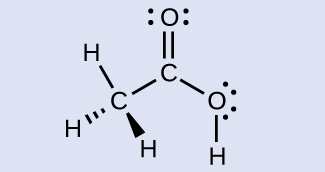
H 3 C , sp 3 ; C (O)OH, sp 2

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?