| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The hybrid orbital model appears to account well for the geometry of molecules involving single covalent bonds. Is it also capable of describing molecules containing double and triple bonds? We have already discussed that multiple bonds consist of σ and π bonds. Next we can consider how we visualize these components and how they relate to hybrid orbitals. The Lewis structure of ethene, C 2 H 4 , shows us that each carbon atom is surrounded by one other carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms.
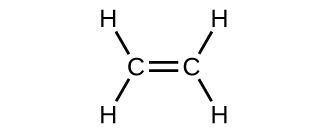
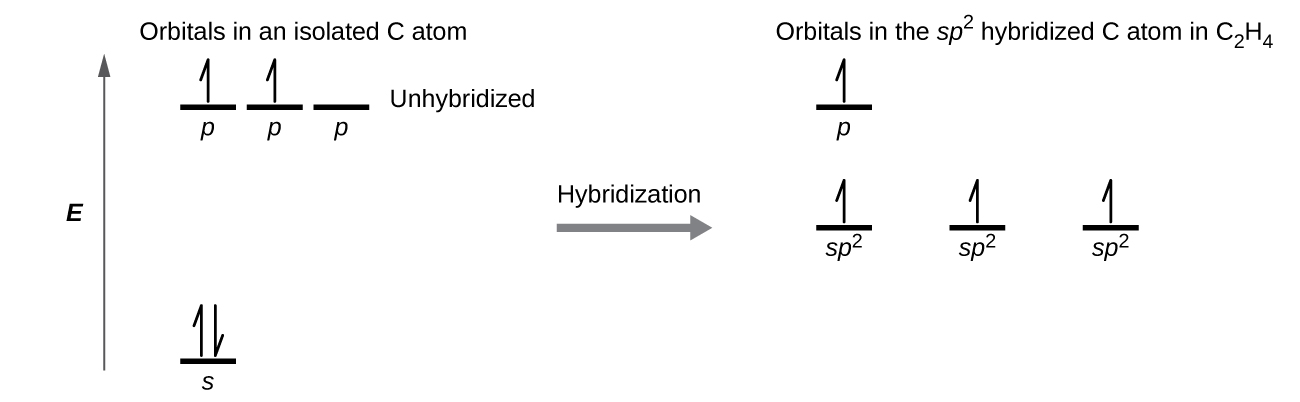
The three bonding regions form a trigonal planar electron-pair geometry. Thus we expect the σ bonds from each carbon atom are formed using a set of sp 2 hybrid orbitals that result from hybridization of two of the 2 p orbitals and the 2 s orbital ( [link] ). These orbitals form the C–H single bonds and the σ bond in the double bond ( [link] ) . The π bond in the double bond results from the overlap of the third (remaining) 2 p orbital on each carbon atom that is not involved in hybridization. This unhybridized p orbital (lobes shown in red and blue in [link] ) is perpendicular to the plane of the sp 2 hybrid orbitals. Thus the unhybridized 2 p orbitals overlap in a side-by-side fashion, above and below the internuclear axis ( [link] ) and form a π bond .
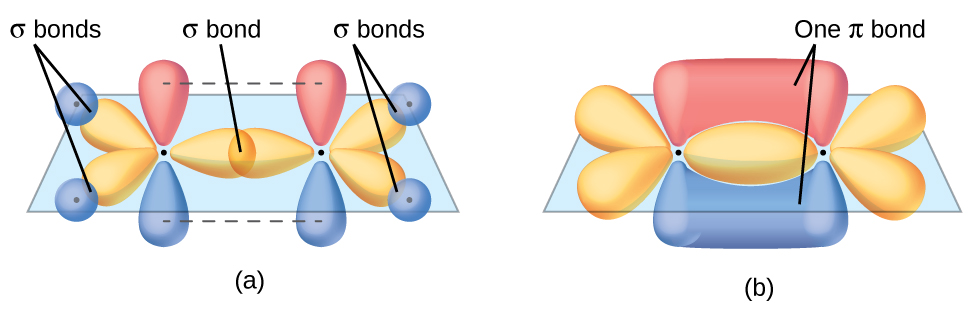
In an ethene molecule, the four hydrogen atoms and the two carbon atoms are all in the same plane. If the two planes of sp 2 hybrid orbitals tilted relative to each other, the p orbitals would not be oriented to overlap efficiently to create the π bond. The planar configuration for the ethene molecule occurs because it is the most stable bonding arrangement. This is a significant difference between σ and π bonds; rotation around single (σ) bonds occurs easily because the end-to-end orbital overlap does not depend on the relative orientation of the orbitals on each atom in the bond. In other words, rotation around the internuclear axis does not change the extent to which the σ bonding orbitals overlap because the bonding electron density is symmetric about the axis. Rotation about the internuclear axis is much more difficult for multiple bonds; however, this would drastically alter the off-axis overlap of the π bonding orbitals, essentially breaking the π bond.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?