| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As early chemists worked to purify ores and discovered more elements, they realized that various elements could be grouped together by their similar chemical behaviors. One such grouping includes lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K): These elements all are shiny, conduct heat and electricity well, and have similar chemical properties. A second grouping includes calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), and barium (Ba), which also are shiny, good conductors of heat and electricity, and have chemical properties in common. However, the specific properties of these two groupings are notably different from each other. For example: Li, Na, and K are much more reactive than are Ca, Sr, and Ba; Li, Na, and K form compounds with oxygen in a ratio of two of their atoms to one oxygen atom, whereas Ca, Sr, and Ba form compounds with one of their atoms to one oxygen atom. Fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and iodine (I) also exhibit similar properties to each other, but these properties are drastically different from those of any of the elements above.
Dimitri Mendeleev in Russia (1869) and Lothar Meyer in Germany (1870) independently recognized that there was a periodic relationship among the properties of the elements known at that time. Both published tables with the elements arranged according to increasing atomic mass. But Mendeleev went one step further than Meyer: He used his table to predict the existence of elements that would have the properties similar to aluminum and silicon, but were yet unknown. The discoveries of gallium (1875) and germanium (1886) provided great support for Mendeleev’s work. Although Mendeleev and Meyer had a long dispute over priority, Mendeleev’s contributions to the development of the periodic table are now more widely recognized ( [link] ).
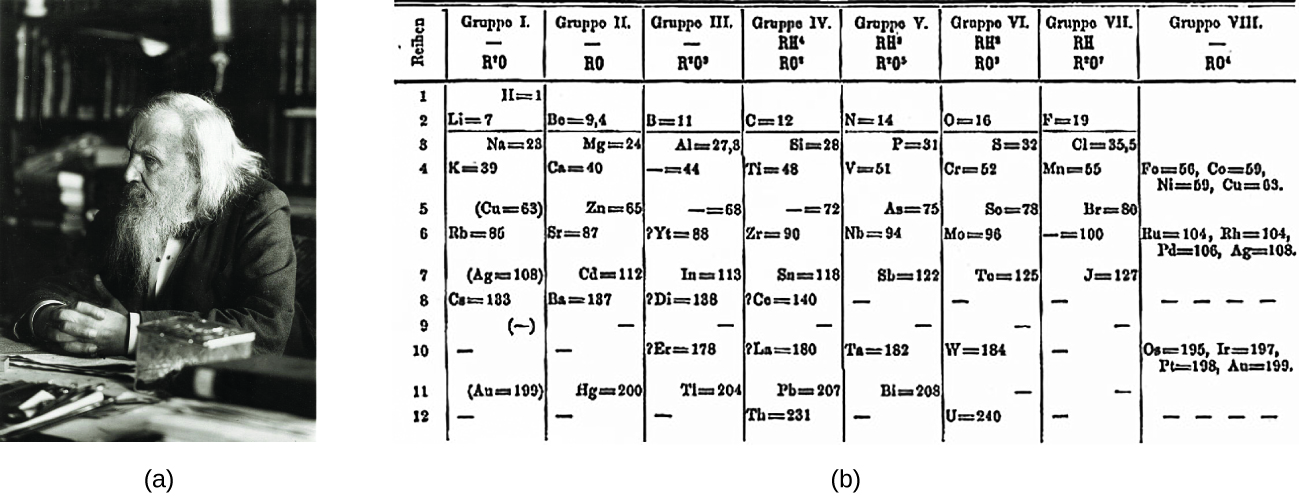
By the twentieth century, it became apparent that the periodic relationship involved atomic numbers rather than atomic masses. The modern statement of this relationship, the periodic law , is as follows: the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers . A modern periodic table arranges the elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers and groups atoms with similar properties in the same vertical column ( [link] ). Each box represents an element and contains its atomic number, symbol, average atomic mass, and (sometimes) name. The elements are arranged in seven horizontal rows, called periods or series , and 18 vertical columns, called groups . Groups are labeled at the top of each column. In the United States, the labels traditionally were numerals with capital letters. However, IUPAC recommends that the numbers 1 through 18 be used, and these labels are more common. For the table to fit on a single page, parts of two of the rows, a total of 14 columns, are usually written below the main body of the table.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?