| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
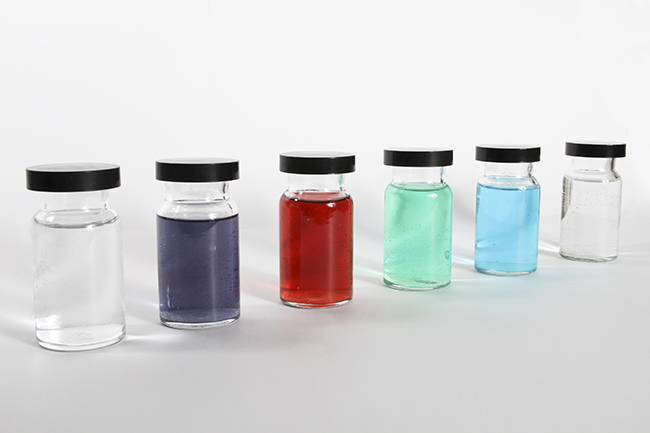
The hemoglobin in your blood, the chlorophyll in green plants, vitamin B-12, and the catalyst used in the manufacture of polyethylene all contain coordination compounds. Ions of the metals, especially the transition metals, are likely to form complexes. Many of these compounds are highly colored ( [link] ). In the remainder of this chapter, we will consider the structure and bonding of these remarkable compounds.

Remember that in most main group element compounds, the valence electrons of the isolated atoms combine to form chemical bonds that satisfy the octet rule. For instance, the four valence electrons of carbon overlap with electrons from four hydrogen atoms to form CH 4 . The one valence electron leaves sodium and adds to the seven valence electrons of chlorine to form the ionic formula unit NaCl ( [link] ). Transition metals do not normally bond in this fashion. They primarily form coordinate covalent bonds, a form of the Lewis acid-base interaction in which both of the electrons in the bond are contributed by a donor (Lewis base) to an electron acceptor (Lewis acid). The Lewis acid in coordination complexes, often called a central metal ion (or atom), is often a transition metal or inner transition metal, although main group elements can also form coordination compounds . The Lewis base donors, called ligands , can be a wide variety of chemicals—atoms, molecules, or ions. The only requirement is that they have one or more electron pairs, which can be donated to the central metal. Most often, this involves a donor atom with a lone pair of electrons that can form a coordinate bond to the metal.
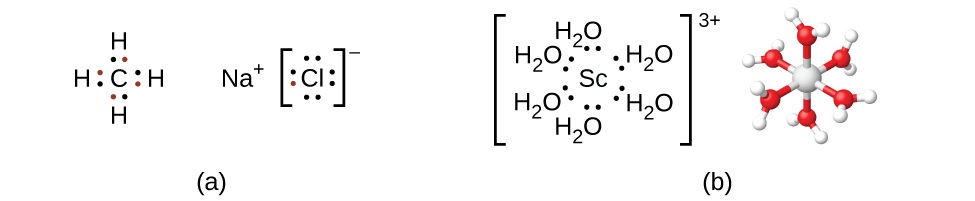
The coordination sphere consists of the central metal ion or atom plus its attached ligands. Brackets in a formula enclose the coordination sphere; species outside the brackets are not part of the coordination sphere. The coordination number of the central metal ion or atom is the number of donor atoms bonded to it. The coordination number for the silver ion in [Ag(NH 3 ) 2 ] + is two ( [link] ). For the copper(II) ion in [CuCl 4 ] 2− , the coordination number is four, whereas for the cobalt(II) ion in [Co(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+ the coordination number is six. Each of these ligands is monodentate , from the Greek for “one toothed,” meaning that they connect with the central metal through only one atom. In this case, the number of ligands and the coordination number are equal.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?