| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The nonmetals are elements located in the upper right portion of the periodic table. Their properties and behavior are quite different from those of metals on the left side. Under normal conditions, more than half of the nonmetals are gases, one is a liquid, and the rest include some of the softest and hardest of solids. The nonmetals exhibit a rich variety of chemical behaviors. They include the most reactive and least reactive of elements, and they form many different ionic and covalent compounds. This section presents an overview of the properties and chemical behaviors of the nonmetals, as well as the chemistry of specific elements. Many of these nonmetals are important in biological systems.
In many cases, trends in electronegativity enable us to predict the type of bonding and the physical states in compounds involving the nonmetals. We know that electronegativity decreases as we move down a given group and increases as we move from left to right across a period. The nonmetals have higher electronegativities than do metals, and compounds formed between metals and nonmetals are generally ionic in nature because of the large differences in electronegativity between them. The metals form cations, the nonmetals form anions, and the resulting compounds are solids under normal conditions. On the other hand, compounds formed between two or more nonmetals have small differences in electronegativity between the atoms, and covalent bonding—sharing of electrons—results. These substances tend to be molecular in nature and are gases, liquids, or volatile solids at room temperature and pressure.
In normal chemical processes, nonmetals do not form monatomic positive ions (cations) because their ionization energies are too high. All monatomic nonmetal ions are anions; examples include the chloride ion, Cl − , the nitride ion, N 3− , and the selenide ion, Se 2− .
The common oxidation states that the nonmetals exhibit in their ionic and covalent compounds are shown in [link] . Remember that an element exhibits a positive oxidation state when combined with a more electronegative element and that it exhibits a negative oxidation state when combined with a less electronegative element.
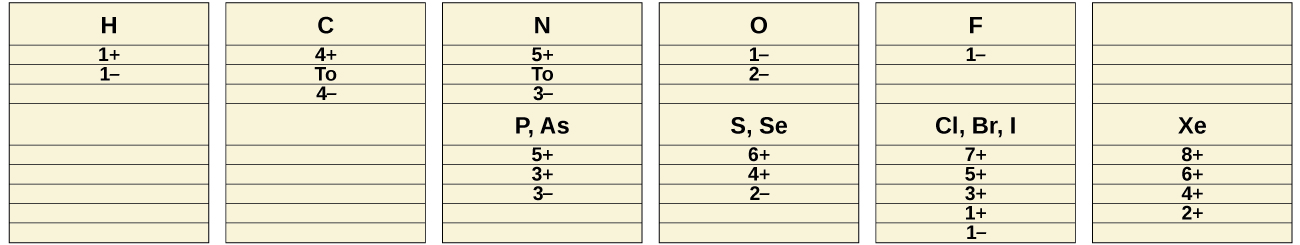
The first member of each nonmetal group exhibits different behaviors, in many respects, from the other group members. The reasons for this include smaller size, greater ionization energy, and (most important) the fact that the first member of each group has only four valence orbitals (one 2 s and three 2 p ) available for bonding, whereas other group members have empty d orbitals in their valence shells, making possible five, six, or even more bonds around the central atom. For example, nitrogen forms only NF 3, whereas phosphorus forms both PF 3 and PF 5 .
Another difference between the first group member and subsequent members is the greater ability of the first member to form π bonds. This is primarily a function of the smaller size of the first member of each group, which allows better overlap of atomic orbitals. Nonmetals, other than the first member of each group, rarely form π bonds to nonmetals that are the first member of a group. For example, sulfur-oxygen π bonds are well known, whereas sulfur does not normally form stable π bonds to itself.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?