| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Galvanic cells , also known as voltaic cells , are electrochemical cells in which spontaneous oxidation-reduction reactions produce electrical energy. In writing the equations, it is often convenient to separate the oxidation-reduction reactions into half-reactions to facilitate balancing the overall equation and to emphasize the actual chemical transformations.
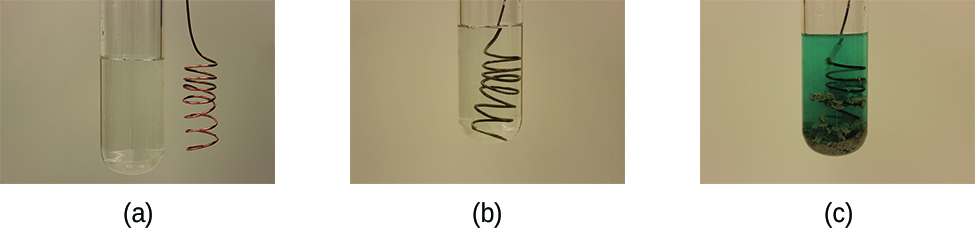
Consider what happens when a clean piece of copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate ( [link] ). As soon as the copper metal is added, silver metal begins to form and copper ions pass into the solution. The blue color of the solution on the far right indicates the presence of copper ions. The reaction may be split into its two half-reactions. Half-reactions separate the oxidation from the reduction, so each can be considered individually.
The equation for the reduction half-reaction had to be doubled so the number electrons “gained” in the reduction half-reaction equaled the number of electrons “lost” in the oxidation half-reaction.
Galvanic or voltaic cells involve spontaneous electrochemical reactions in which the half-reactions are separated ( [link] ) so that current can flow through an external wire. The beaker on the left side of the figure is called a half-cell, and contains a 1 M solution of copper(II) nitrate [Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ] with a piece of copper metal partially submerged in the solution. The copper metal is an electrode. The copper is undergoing oxidation; therefore, the copper electrode is the anode . The anode is connected to a voltmeter with a wire and the other terminal of the voltmeter is connected to a silver electrode by a wire. The silver is undergoing reduction; therefore, the silver electrode is the cathode . The half-cell on the right side of the figure consists of the silver electrode in a 1 M solution of silver nitrate (AgNO 3 ). At this point, no current flows—that is, no significant movement of electrons through the wire occurs because the circuit is open. The circuit is closed using a salt bridge, which transmits the current with moving ions. The salt bridge consists of a concentrated, nonreactive, electrolyte solution such as the sodium nitrate (NaNO 3 ) solution used in this example. As electrons flow from left to right through the electrode and wire, nitrate ions (anions) pass through the porous plug on the left into the copper(II) nitrate solution. This keeps the beaker on the left electrically neutral by neutralizing the charge on the copper(II) ions that are produced in the solution as the copper metal is oxidized. At the same time, the nitrate ions are moving to the left, sodium ions (cations) move to the right, through the porous plug, and into the silver nitrate solution on the right. These added cations “replace” the silver ions that are removed from the solution as they were reduced to silver metal, keeping the beaker on the right electrically neutral. Without the salt bridge, the compartments would not remain electrically neutral and no significant current would flow. However, if the two compartments are in direct contact, a salt bridge is not necessary. The instant the circuit is completed, the voltmeter reads +0.46 V, this is called the cell potential . The cell potential is created when the two dissimilar metals are connected, and is a measure of the energy per unit charge available from the oxidation-reduction reaction. The volt is the derived SI unit for electrical potential

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?