| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In 1923, G. N. Lewis proposed a generalized definition of acid-base behavior in which acids and bases are identified by their ability to accept or to donate a pair of electrons and form a coordinate covalent bond.
A coordinate covalent bond (or dative bond) occurs when one of the atoms in the bond provides both bonding electrons. For example, a coordinate covalent bond occurs when a water molecule combines with a hydrogen ion to form a hydronium ion. A coordinate covalent bond also results when an ammonia molecule combines with a hydrogen ion to form an ammonium ion. Both of these equations are shown here.
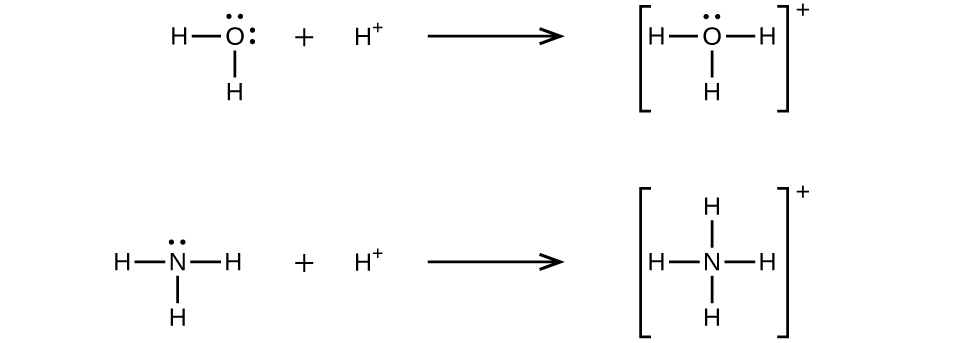
A Lewis acid is any species (molecule or ion) that can accept a pair of electrons, and a Lewis base is any species (molecule or ion) that can donate a pair of electrons.
A Lewis acid-base reaction occurs when a base donates a pair of electrons to an acid. A Lewis acid-base adduct , a compound that contains a coordinate covalent bond between the Lewis acid and the Lewis base, is formed. The following equations illustrate the general application of the Lewis concept.
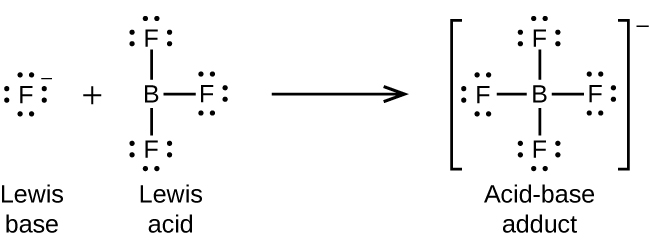
The boron atom in boron trifluoride, BF 3 , has only six electrons in its valence shell. Being short of the preferred octet, BF 3 is a very good Lewis acid and reacts with many Lewis bases; a fluoride ion is the Lewis base in this reaction, donating one of its lone pairs:
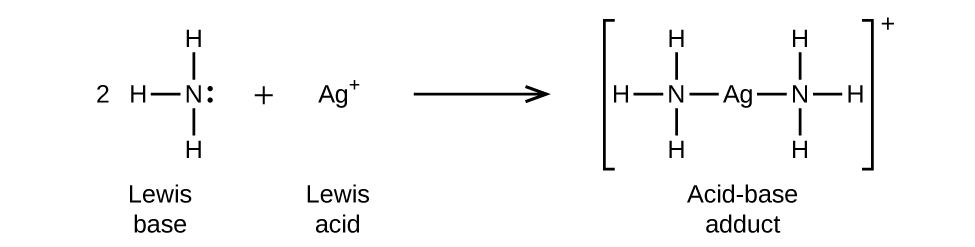
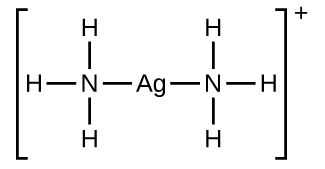
In the following reaction, each of two ammonia molecules, Lewis bases, donates a pair of electrons to a silver ion, the Lewis acid:
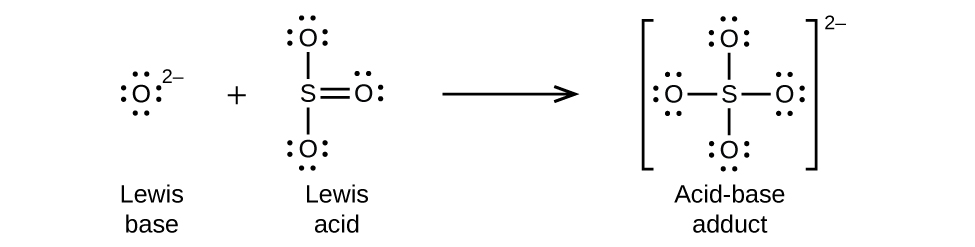
Nonmetal oxides act as Lewis acids and react with oxide ions, Lewis bases, to form oxyanions:
Many Lewis acid-base reactions are displacement reactions in which one Lewis base displaces another Lewis base from an acid-base adduct, or in which one Lewis acid displaces another Lewis acid:
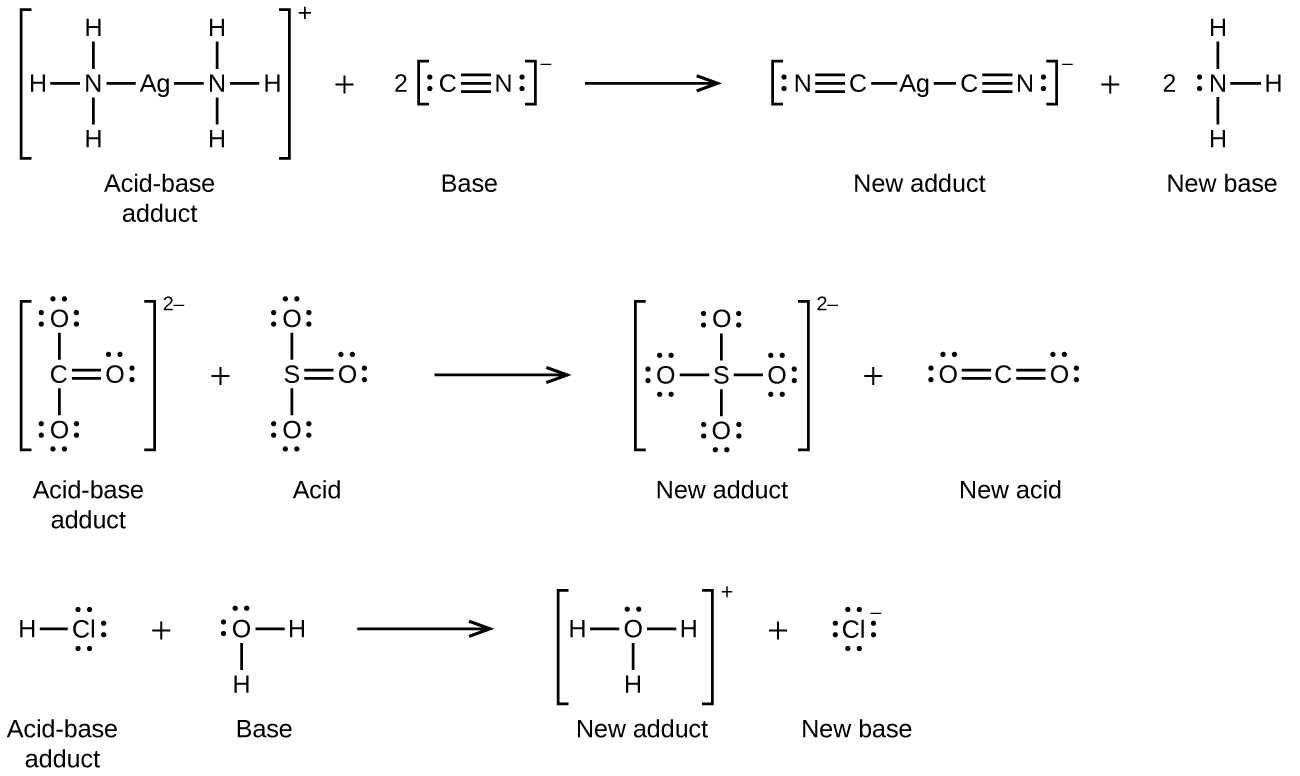
The last displacement reaction shows how the reaction of a Brønsted-Lowry acid with a base fits into the Lewis concept. A Brønsted-Lowry acid such as HCl is an acid-base adduct according to the Lewis concept, and proton transfer occurs because a more stable acid-base adduct is formed. Thus, although the definitions of acids and bases in the two theories are quite different, the theories overlap considerably.
Many slightly soluble ionic solids dissolve when the concentration of the metal ion in solution is decreased through the formation of complex (polyatomic) ions in a Lewis acid-base reaction. For example, silver chloride dissolves in a solution of ammonia because the silver ion reacts with ammonia to form the complex ion The Lewis structure of the ion is:
The equations for the dissolution of AgCl in a solution of NH 3 are:
Aluminum hydroxide dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide or another strong base because of the formation of the complex ion The Lewis structure of the ion is:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?